A nurse is preparing to administer clindamycin to a client who states she forgot to report to the provider that she is allergic to penicillin. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
Give the client the prescribed dose of the clindamycin.
Obtain a prescription for an alternative antibiotic.
Premeditate the client with epinephrine before administering the antibiotic.
Administer the clindamycin using a desensitization schedule.
The Correct Answer is B
Choice A Reason:
Giving the prescribed dose of clindamycin is not appropriate due to the reported penicillin allergy, which increases the risk of an allergic reaction.
Choice B Reason:
Obtain a prescription for an alternative antibiotic is correct. Given the client's reported allergy to penicillin, which is in the same antibiotic class as clindamycin (both are antibiotics that belong to the beta-lactam group), there is a higher risk of cross-reactivity and potential allergic reaction. Therefore, it's important to avoid administering clindamycin in such cases and seek an alternative antibiotic that does not have a similar chemical structure to penicillin to prevent an allergic reaction.
Choice C Reason:
Premeditating the client with epinephrine before administering the antibiotic is not a standard practice in this context. Epinephrine is used to treat severe allergic reactions but is not used as a preventive measure before administering antibiotics.
Choice D Reason:
Administering the clindamycin using a desensitization schedule might be an option in certain situations under the guidance of an allergist or immunologist, but it's not typically performed by nurses and requires a specific protocol and expertise in managing drug allergies. Obtaining an alternative antibiotic is a more appropriate and immediate action to avoid the risk of an allergic reaction in this scenario.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
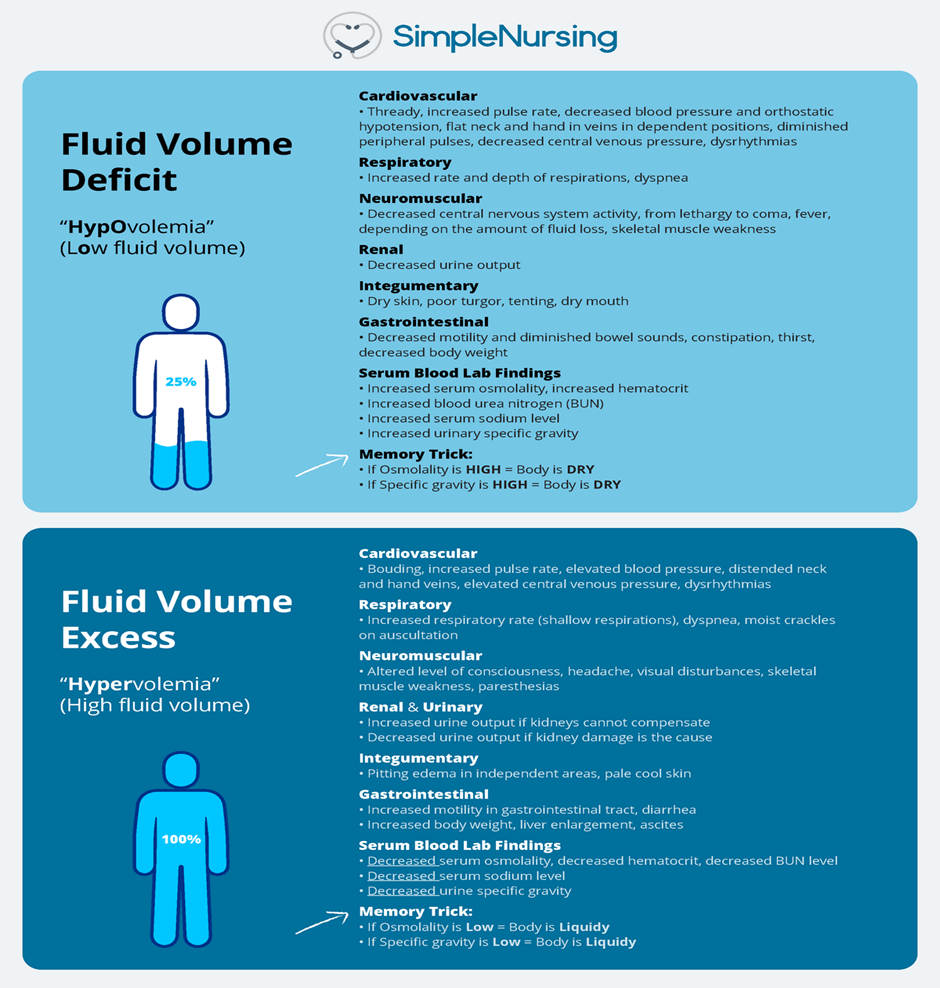
Bilateral muscle weakness is not typically associated specifically with fluid volume excess. Muscle weakness can result from various causes, such as electrolyte imbalances or certain medical conditions, but it's not a primary manifestation of fluid volume excess.
Choice B Reason:
Thready pulse is not correct. A thready pulse refers to a weak and barely palpable pulse. This is more commonly associated with conditions like shock or reduced cardiac output rather than fluid volume excess.
Choice C Reason:
Decreased bowel sounds is not correct. Reduced or absent bowel sounds may indicate gastrointestinal issues, but they are not a direct manifestation of fluid volume excess. Increased bowel sounds might be more associated with certain types of gastrointestinal disturbances or fluid imbalances, but decreased sounds are not a typical sign of fluid volume excess.
Choice D Reason:
Distended neck veins is correct. In a client experiencing fluid volume excess, distended neck veins can often be observed due to increased venous pressure. This occurs as a result of the body retaining more fluid than it can handle, leading to an increase in blood volume and pressure within the vascular system. This can cause the jugular veins in the neck to appear distended or prominent.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
"You should monitor for hearing difficulties." is correct. Loop diuretics like bumetanide can occasionally cause ototoxicity, resulting in hearing difficulties or ringing in the ears (tinnitus) as a potential adverse effect. It's important for clients taking these medications to be aware of such symptoms and report them promptly to their healthcare provider.
Choice B Reason:
"You should take the medication at bedtime." Is incorrect. Bumetanide is commonly prescribed to be taken in the morning to avoid nighttime diuresis and potential sleep disruption due to increased urination.
Choice C Reason:
"You should decrease your intake of foods high in potassium." Is incorrect. Loop diuretics often lead to potassium loss, so clients may actually need to increase their intake of potassium-rich foods or take potassium supplements under healthcare provider guidance to maintain normal potassium levels.
Choice D Reason:
"You should take this medication on an empty stomach." Is incorrect. Bumetanide can be taken with or without food, so it's not necessary to take it on an empty stomach.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
