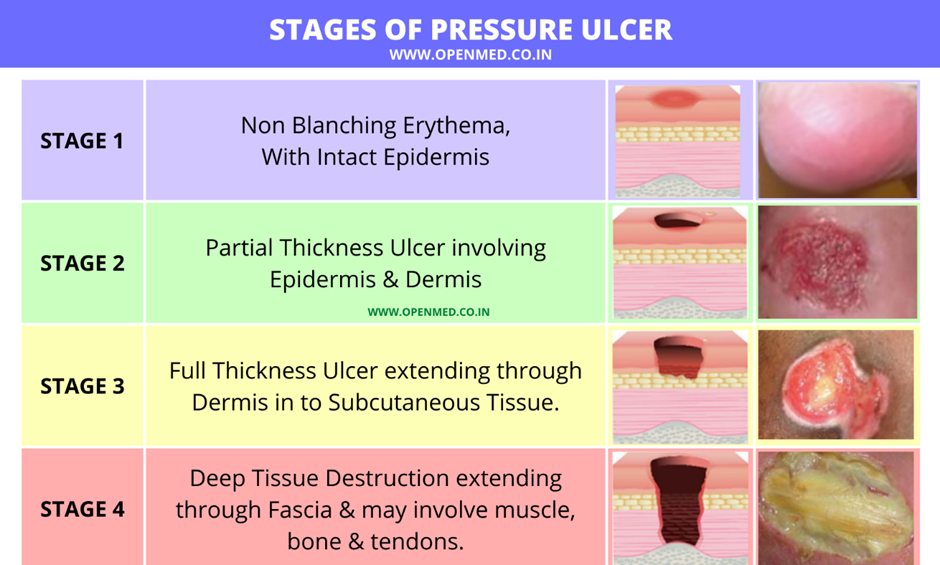
A nurse is collecting data on a client who has a stage 2 pressure injury. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect?
Intact skin with localized erythema.
Full thickness skin loss with visible bone
Full thickness skin loss with visible adipose tissue.
Partial-thickness skin loss with red tissue in wound bed.
The Correct Answer is D
A. Intact skin with localized erythema:
Explanation: This description is more consistent with a stage 1 pressure injury, where there is non-blanchable erythema.
B. Full thickness skin loss with visible bone:
Explanation: This description is more consistent with a stage 4 pressure injury, which involves extensive tissue loss, including exposure of bone.
C. Full thickness skin loss with visible adipose tissue:
Explanation: This finding is characteristic of a stage 3 pressure injury, where the loss of tissue extends down to the subcutaneous layer.
D. Partial-thickness skin loss with red tissue in the wound bed:
Explanation: This description is consistent with a stage 2 pressure injury, where there is partial-thickness skin loss involving the epidermis and possibly the dermis, forming a shallow open ulcer with a red-pink wound bed.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A. Diminished reflexes:
Explanation: Diminished reflexes are not typically associated with hypoglycemia. Instead, hypoglycemia may cause hyperactive reflexes or tremors.
B. Rapid respirations:
Explanation: Rapid respirations are not a common manifestation of hypoglycemia. In hypoglycemia, the body might respond with shallow, rapid breathing or hyperventilation.
C. Acetone breath:
Explanation: Acetone breath, often described as fruity or sweet, is associated with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), which is a complication of hyperglycemia rather than hypoglycemia.
D. Headache:
Explanation: Headache is a common manifestation of hypoglycemia. It can occur as a result of decreased glucose levels affecting the brain.

Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A. Abrasion:
This type of wound occurs when the skin rubs or scrapes against a rough surface. It's often referred to as a "scrape" and typically involves superficial damage to the skin without penetration or tearing.
B. Contusion:
Commonly known as a bruise, a contusion results from blunt trauma to the body, causing blood vessels to break and leak blood into the surrounding tissues. The skin remains intact, but there's discoloration due to the blood.
C. Laceration:
This type of wound involves a tear or irregular cut in the skin, often with jagged or rough edges. Lacerations typically result from sharp or blunt trauma that causes the skin to tear.
D. Puncture:
Puncture wounds occur when a sharp object pierces the skin and underlying tissues, creating a small, deep hole. These wounds might not bleed much externally but can cause damage to internal structures and carry a risk of infection due to the depth and possible trapping of debris.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
