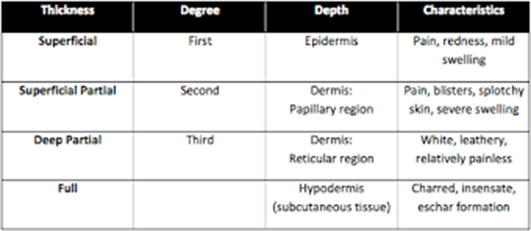
A nurse is caring for a preschooler who has a partial-thickness burn on her right forearm. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect? (Select all that apply.)
Blisters
Wound blanches with pressure
Dry face
Intact epidermis
Sensitive to touch
Correct Answer : A,B,E
Choice A rationale: partial-thickness burns are usually characterized by the formation of blisters as a result of increased capillary permeability resulting in edema formation separating the epidermis from the dermis.
Choice B rationale: wound blanching with pressure is expected in partial-thickness burns due to compromised blood circulation.
Choice C rationale: This is not a typical finding in a partial-thickness burn.
Choice D rationale: this is incorrect since partial-thickness burns involve damage to the epidermis.
Choice E rationale: nerve endings are damaged in partial-thickness burns thus making the area sensitive to touch.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A rationale: When removing personal protective equipment (PPE) after a procedure involving contact precautions, the nurse should remove the items in a specific order to minimize the risk of contamination. Gloves should be removed first because they are the most likely to be contaminated and can transfer microorganisms to other surfaces or PPE during removal.
Choice B rationale: The mask should be removed after gloves and gown. Removing the mask first could potentially contaminate the hands, leading to the risk of transferring microorganisms to the face during mask removal.
Choice C rationale: The gown should be removed after gloves and before the mask. Removing the gown too early could lead to potential contamination of the hands.
Choice D rationale: The face shield should be removed after gloves, mask, and gown. It provides additional protection for the face and should be retained until the end of the removal process to minimize the risk of contamination.
Correct Answer is ["A","B","D","E"]
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Hyperlipidemia, particularly elevated cholesterol levels, can be associated with impaired wound healing. High cholesterol levels can contribute to atherosclerosis, leading to reduced blood flow to the wound site. Adequate blood supply is crucial for delivering oxygen and nutrients essential for the healing process.
Choice B rationale: Diabetes mellitus is a well-known risk factor for delayed wound healing. High blood sugar levels can impair the function of white blood cells, reduce collagen formation, and impair the overall healing process. Furthermore, individuals with diabetes are more prone to infections and may experience slower wound closure.
Choice C rationale: Medication history alone does not provide specific information about factors that directly affect wound healing. However, certain medications, such as corticosteroids or immunosuppressive drugs, may impact the healing process.
Choice D rationale: High cholesterol levels can contribute to atherosclerosis, leading to reduced blood flow to the wound site. Adequate blood supply is crucial for delivering oxygen and nutrients essential for the healing process.
Choice E rationale: Prealbumin is a marker of protein status and nutritional adequacy. Low prealbumin levels can indicate malnutrition, which is a risk factor for delayed wound healing. Adequate protein intake is crucial for collagen synthesis and overall tissue repair.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
