A nurse is caring for a male infant who has a palpable mass in the upper right quadrant and stools mixed with blood and mucus. The nurse should recognize that which of the following diagnoses is associated with these findings?
Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis
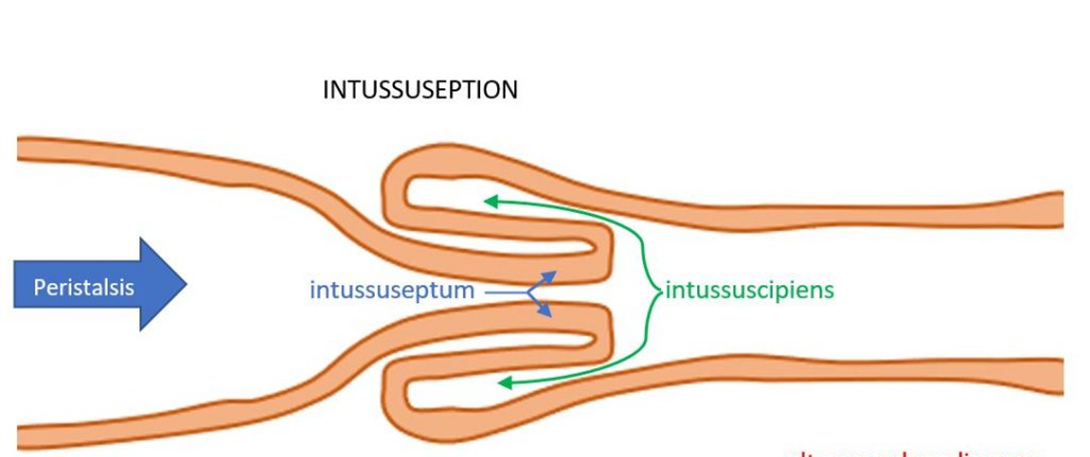
Intussusception
Inguinal hernia
Tracheoesophageal fistula
The Correct Answer is B
Choice A reason: Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis is a condition in which the pyloric sphincter becomes thickened and obstructs the passage of food from the stomach to the duodenum. It causes projectile vomiting, dehydration, and weight loss, but not a palpable mass or bloody stools.
Choice B reason: Intussusception is a condition in which a segment of the intestine telescopes into another segment, causing obstruction, inflammation, and ischemia. It causes a palpable mass in the upper right quadrant, abdominal pain, and stools mixed with blood and mucus, also known as "currant jelly" stools.
Choice C reason: Inguinal hernia is a condition in which a part of the intestine protrudes through a weak spot in the abdominal wall near the inguinal canal. It causes a bulge in the groin area, especially when the infant cries or strains. It does not cause a mass in the upper right quadrant or bloody stools.
Choice D reason: Tracheoesophageal fistula is a congenital anomaly in which there is an abnormal connection between the trachea and the esophagus. It causes excessive drooling, choking, coughing, and cyanosis during feeding, but not a palpable mass or bloody stools.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A reason: Barley contains gluten, a protein that triggers an immune reaction in people with celiac disease. This reaction damages the lining of the small intestine and prevents it from absorbing nutrients. Therefore, barley should be avoided by people with celiac disease.
Choice B reason: Wheat also contains gluten and should be avoided by people with celiac disease for the same reason as barley.
Choice C reason: Rice is a gluten-free grain and can be safely consumed by people with celiac disease. Rice is a good source of carbohydrates, fiber, and vitamins.
Choice D reason: Potatoes are also gluten-free and can be safely consumed by people with celiac disease. Potatoes are a good source of potassium, vitamin C, and starch.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A reason: This statement is incorrect, as giving an oral rehydration solution to an infant who is projectile vomiting may worsen the dehydration and electrolyte imbalance. The nurse should advise the parent to stop feeding the infant and seek medical attention.
Choice B reason: This statement is incorrect, as burping the baby more frequently during feedings may not prevent the projectile vomiting, which is caused by a mechanical obstruction of the stomach, not by air swallowing. The nurse should assess the parent for signs of pyloric stenosis, such as a palpable olive-shaped mass in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen.
Choice C reason: This statement is correct, as bringing the baby in to the clinic today is the best course of action for an infant who is projectile vomiting, which is a sign of a serious condition such as pyloric stenosis, a narrowing of the opening between the stomach and the small intestine. The nurse should inform the parent that the infant needs immediate evaluation and treatment to prevent complications such as dehydration, malnutrition, and metabolic alkalosis.
Choice D reason: This statement is incorrect, as trying switching to a different formula may not help the infant who is projectile vomiting, which is not related to the type of formula, but to a structural problem in the gastrointestinal tract. The nurse should not suggest changing the formula without consulting the provider.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
