A nurse is caring for a client who is at 32 weeks of gestation and is in labor. Which of the following medications is contraindicated for this client?
Misoprostol
Folic acid
Nifedipine
Terbutaline sulfate
The Correct Answer is A
Choice A rationale: Misoprostol is a prostaglandin analog and is contraindicated for use during labor at 32 weeks of gestation as it can lead to uterine hyperstimulation, which may pose a risk to the preterm fetus.
Choice B rationale: Folic acid is a vitamin supplement and is not contraindicated during labor. However, it is typically taken earlier in pregnancy to prevent neural tube defects.
Choice C rationale: Nifedipine is a calcium channel blocker that may be used to suppress preterm labor, and it is not contraindicated at 32 weeks of gestation.
Choice D rationale: Terbutaline is a beta-adrenergic agonist that may be used to relax the uterine smooth muscles and inhibit preterm labor. It is not contraindicated at 32 weeks of gestation.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Ventricular septal defect (VSD) is a congenital heart defect and is not directly related to respiratory distress syndrome or respiratory acidosis.
Choice B rationale: Cesarean birth, while it can have other implications, is not a direct risk factor for respiratory distress syndrome or respiratory acidosis. The mode of delivery does not directly impact the newborn's respiratory function.
Choice C rationale: While being small for gestational age can be associated with certain health challenges, it is not a direct risk factor for respiratory distress syndrome or respiratory acidosis. The baby's size does not determine its respiratory status.
Choice D rationale: Maternal history of asthma is a risk factor that can predispose the newborn to respiratory difficulties, including respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) and respiratory acidosis. Infants born to mothers with asthma may have a higher likelihood of developing respiratory problems due to potential genetic factors and exposure to environmental triggers during pregnancy.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
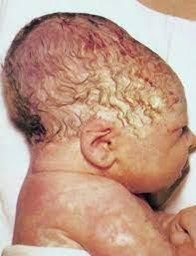
Choice A rationale: The Mongolian spot is a bluish-gray birthmark that is often seen on the lower back or buttocks of newborns with darker skin tones. It is not related to the swelling described in the scenario.
Choice B rationale: Caput succedaneum is a common condition in newborns delivered by vacuum extraction. It is characterized by swelling of the soft tissues of the scalp that crosses the suture lines. The swelling occurs due to pressure from the vacuum extractor during delivery and is caused by fluid accumulation between the scalp and the skull. Caput succedaneum is typically a benign and self-resolving condition that does not require treatment.
Choice C rationale: Cephalhematoma is a collection of blood between the periosteum and the skull bone. Unlike caput succedaneum, it does not cross the suture lines and can take weeks to months to resolve.
Choice D rationale: Erythema toxicum is a common skin rash in newborns characterized by red or pink spots with a yellow or white bump in the center. It is not related to the swelling described in the scenario.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
