A nurse is caring for a client who has a urinary tract infection.
Drag words from the choices below to fill in each blank in the following sentence.
The client is at an increased risk for developing
Choice A rationale: Target conditions are not mentioned in the sentence, and there is no context to suggest their relevance to the client's situation. Choice B rationale: Hyperactive reflexes are not commonly associated with a urinary tract infection or the prescribed medications. Choice C rationale: The client with a urinary tract infection and the medications mentioned (Furosemide and Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole) are at an increased risk of hypokalemia (low potassium levels) due to Furosemide's diuretic effect, fluid volume deficit (dehydration) from the infection, and hypertension (high blood pressure) as a potential side effect of Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole. Choice D rationale: Urinary retention is not expected in a client with a urinary tract infection; it is more commonly associated with urinary obstruction or other urinary conditions unrelated to an infection.
The Correct Answer is {"dropdown-group-1":"C"}
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["A","D","E"]
Explanation
A, D, and E.
Choice A rationale:
Furosemide is a loop diuretic that promotes diuresis, causing an increase in urine output. It is essential for the patient to expect this effect and understand that it helps in reducing fluid overload.
Choice B rationale:
Feeling weak and dizzy is not an expected effect of furosemide. It is more commonly associated with dehydration or excessive fluid loss, which can occur if the medication causes too much diuresis.
Choice C rationale:
Taking furosemide before going to sleep is not recommended because it can lead to nighttime diuresis, disrupting sleep and potentially causing electrolyte imbalances.
Choice D rationale:
Swelling of the face or hands may indicate an adverse reaction to furosemide or an underlying medical issue. The nurse should instruct the patient to report any such symptoms promptly.
Choice E rationale:
Monitoring body weight daily is crucial for patients on diuretic therapy to assess fluid status and response to treatment. Rapid weight gain may indicate worsening fluid overload, while significant weight loss may indicate excessive diuresis.
Correct Answer is ["A","B","C"]
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
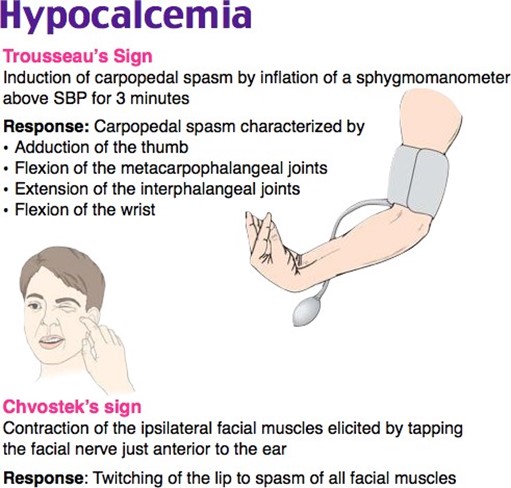
The nurse considered contraction of facial muscles as a finding of hypocalcemia because it is associated with Chvostek's sign, which indicates neuromuscular irritability due to low calcium levels.
Choice B rationale:
Complaints of fingers tingling are indicative of hypocalcemia since tingling sensations (paresthesias) in the extremities can result from decreased calcium levels affecting nerve function.
Choice C rationale:
Carpal spasm with blood pressure measurement is known as Trousseau's sign and is associated with hypocalcemia. When the blood pressure cuff is inflated above systolic pressure, it can cause tetany in the hand if the calcium levels are low.
Choice D rationale:
Asking when foot numbness would go away does not directly relate to hypocalcemia or its symptoms. It is not a finding used to come to the conclusion of hypocalcemia in this scenario.
Choice E rationale:
The heart rate being 88 and regular does not directly indicate hypocalcemia. While hypocalcemia can lead to cardiac arrhythmias, a heart rate of 88 and regular is within the normal range and not a specific finding for hypocalcemia.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
