A nurse is assisting in identifying clients on the medical surgical floor with skin problems. Which of the following are most likely to become chronic wounds?
Cluster of oral herpes sores
Abdominal surgical incision
Diabetic foot ulcer
Posterior scalp wound
The Correct Answer is C
A. Cluster of oral herpes sores: Oral herpes sores typically heal within a few weeks and do not generally become chronic wounds unless there are complications or underlying immune system issues. They are more acute in nature and tend to resolve without becoming chronic.
B. Abdominal surgical incision: Surgical incisions are designed to heal within a specific timeframe, usually a few weeks to a couple of months, depending on the type of surgery and individual healing factors. While surgical wounds can sometimes have delayed healing or complications, they are not typically categorized as chronic wounds unless they fail to heal or become recurrent over an extended period.
C. Diabetic foot ulcer: Diabetic foot ulcers are highly prone to becoming chronic wounds due to the underlying pathology associated with diabetes, such as neuropathy (nerve damage), peripheral vascular disease (poor circulation), and impaired immune function. These factors can impair the normal healing process, leading to delayed healing, infection, and the potential for the wound to become chronic if not managed appropriately.
D. Posterior scalp wound: Scalp wounds can heal relatively quickly, especially with proper wound care and management. However, certain factors such as the size of the wound, depth, presence of infection, and underlying conditions can influence the likelihood of a scalp wound becoming chronic. In general, scalp wounds are less likely to become chronic compared to wounds in areas with higher risk factors, such as diabetic foot ulcers.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A. Superficial infections are caused by fungus.
While fungal infections can indeed cause superficial skin infections like tinea (ringworm) or candidiasis, they are not the common factor for the etiology and pathophysiology of folliculitis, furuncles, and carbuncles. These conditions primarily involve bacterial infections of the hair follicles, typically caused by Staphylococcus aureus bacteria.
B. Parasites get underneath the skin.
Parasitic infections can cause various skin conditions, but they are not the common factor for folliculitis, furuncles, and carbuncles. These conditions are specifically related to bacterial infections of the hair follicles rather than parasitic infestations.
C. Hair follicles are infected or inflamed.
This is the correct choice and the common factor for folliculitis, furuncles, and carbuncles. All three conditions involve the infection or inflammation of hair follicles, primarily due to Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. Folliculitis is the inflammation of one or more hair follicles, furuncles are deeper infections involving the hair follicle and surrounding tissue, and carbuncles are clusters of interconnected furuncles with deeper tissue involvement.
D. There is an allergic response to an allergen.
An allergic response to an allergen does not play a role in the etiology and pathophysiology of folliculitis, furuncles, and carbuncles. These conditions are primarily infectious in nature, involving bacterial colonization and subsequent inflammation of the hair follicles rather than an allergic response.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
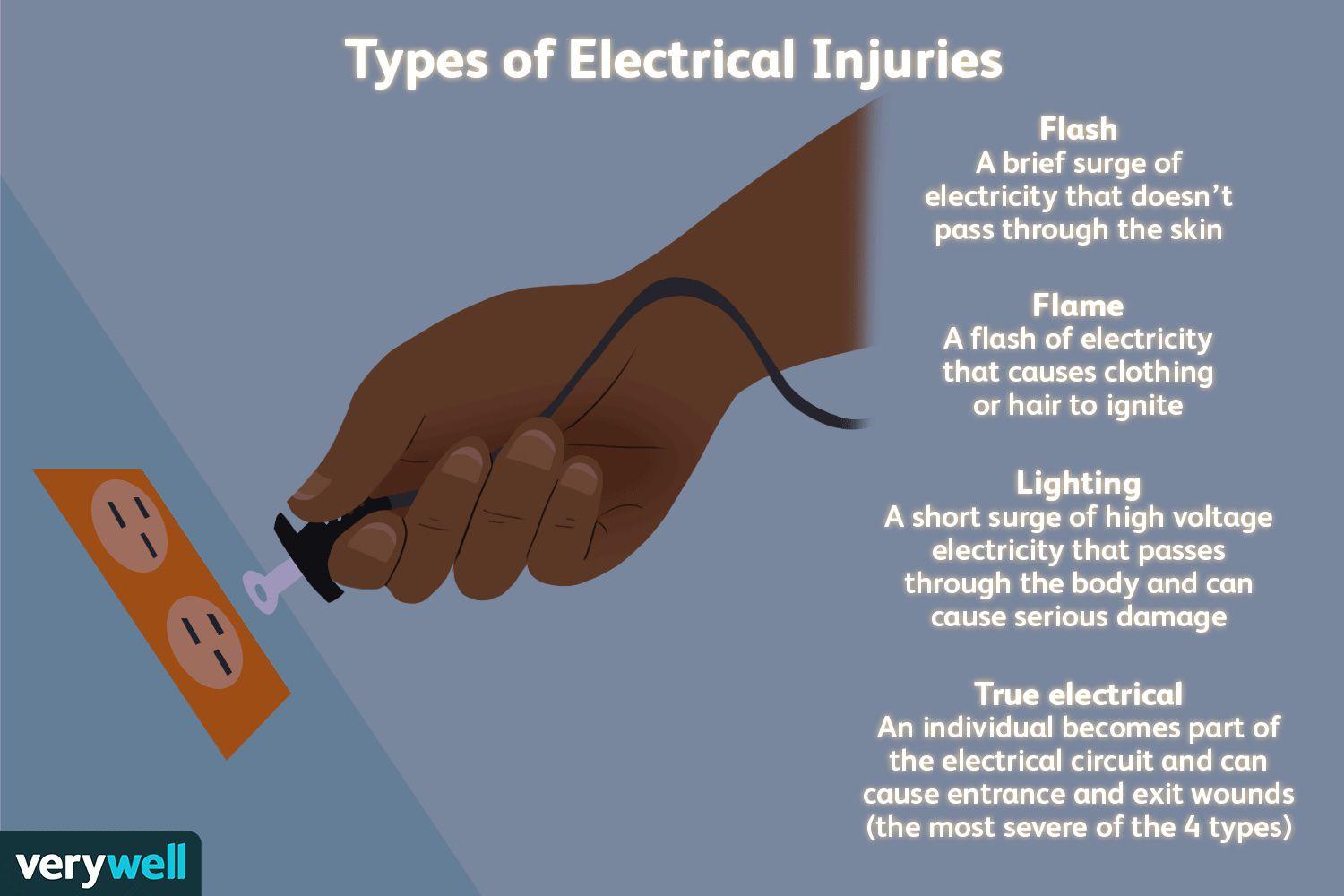
A. Electrical burns can have small amounts of skin damage, but more extensive damage beneath the skin.
This response is the best choice because it educates the client about the potential for deeper tissue damage associated with electrical burns. It acknowledges that while the burn on the skin may appear small, the damage underneath could be more extensive, affecting muscles, nerves, and blood vessels.
B. Electrical burns commonly cause reddened/purplish skin without blistering.
This statement is not the best response because it focuses solely on the appearance of the skin without addressing the potential for deeper tissue damage. While it is true that electrical burns can present with reddened or purplish skin without blistering, this response does not provide comprehensive information about the nature and severity of electrical burns.
C. Electrical burns typically are minor.
This response is incorrect because it downplays the seriousness of electrical burns. While some electrical burns may indeed be minor, others can cause significant tissue damage and complications. It's important for the nurse to educate the client about the range of severity that electrical burns can present.
D. Electrical burns usually cause much more skin damage than what can be seen on your skin.
This statement is partially accurate but does not provide as much information as choice A. While it acknowledges that electrical burns can cause more damage than what is visible on the skin's surface, it doesn't emphasize the potential for deeper tissue damage as effectively as choice A does.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
