A nurse caring for a client with acute peritonitis reviews the physician's orders. The orders include an NPO diet, insertion of a nasogastric tube set to low intermittent suction, and IV fluids at 50 mL per hour. When asked why he will need the NG tube, what is the nurse's best reply?
To administer medications and electrolytes
To dilate the stomach as a presurgical preparation
You will not be able to eat for several days
To remove secretions and decompress your stomach
The Correct Answer is D
Choice A Reason: This is incorrect because administering medications and electrolytes is not the primary purpose of inserting a nasogastric tube for a client with acute peritonitis. Medications and electrolytes can be given through other routes, such as IV or oral.
Choice B Reason: This is incorrect because dilating the stomach as a presurgical preparation is not a relevant Reason for inserting a nasogastric tube for a client with acute peritonitis. Dilating the stomach may be done before some types of gastric surgery, but it does not apply to peritonitis.
Choice C Reason: This is incorrect because stating that you will not be able to eat for several days is not an adequate explanation for inserting a nasogastric tube for a client with acute peritonitis. This statement does not address the rationale or the benefits of the procedure. It may also cause anxiety and resentment in the client.
Choice D Reason: This is the correct choice because removing secretions and decompressing the stomach is the main Reason for inserting a nasogastric tube for a client with acute peritonitis. Peritonitis is an inflammation of the peritoneum, the membrane that lines the abdominal cavity. It can cause abdominal distension, pain, nausea, and vomiting. A nasogastric tube can suction out the gastric contents and reduce the pressure and irritation in the abdomen.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["A","B","D"]
Explanation
Choice A Reason: This is a correct choice. Standing next to the client when speaking is an action that the nurse should plan to take, as it helps the client hear better and see the nurse's facial expressions and lip movements. The nurse should also speak clearly and slowly, use simple words and sentences, and avoid covering their mouth.
Choice B Reason: This is a correct choice. Guiding the client away from background noise is an action that the nurse should plan to take, as it reduces distractions and interference with hearing. The nurse should also choose a well-lit and quiet place for communication and turn off any unnecessary devices or appliances.
Choice C Reason: This is an incorrect choice. Providing a copy of the instructions printed in Braille is not an action that the nurse should plan to take, as it is not helpful for clients with hearing loss. Braille is a system of raised dots that represents letters and numbers for people who are blind or visually impaired. The nurse should provide a copy of the instructions printed in large font or use pictures or diagrams to supplement verbal information.
Choice D Reason: This is a correct choice. Repeating any phrases that the client misunderstands is an action that the nurse should plan to take, as it ensures comprehension and clarification of important information. The nurse should also ask open-ended questions, encourage feedback, and summarize key points at the end of the conversation.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
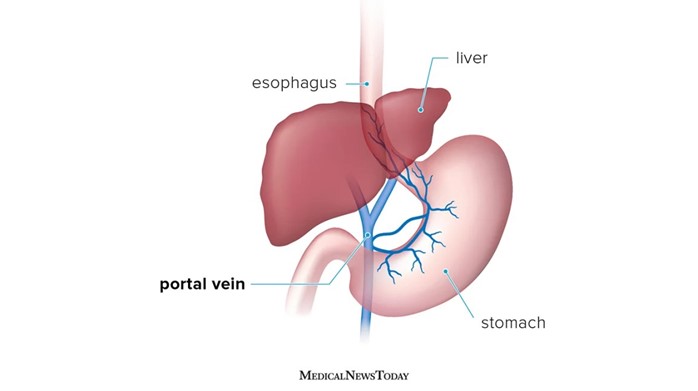
Choice A reason: This is the correct answer because portal hypertension means that there is high blood pressure in the portal vein, which carries blood from the digestive organs to the liver. When the liver is damaged by hepatitis, it becomes scarred and obstructs the blood flow, causing increased pressure in the portal vein. This leads to fluid accumulation in the abdomen, called ascites, which causes abdominal swelling.
Choice B reason: This is incorrect because portal hypertension is not caused by the heart overworking but by liver damage. The heart does not pump blood into the portal vein, but into the hepatic artery, which supplies oxygenated blood to the liver.
Choice C reason: This is incorrect because portal hypertension does not develop when cirrhosis begins to resolve, but when it progresses. Cirrhosis is a chronic condition that causes irreversible scarring of the liver tissue, which worsens over time and increases portal hypertension.
Choice D reason: This is incorrect because eating high-sodium foods and a stressful lifestyle do not cause portal hypertension, but they can aggravate it. High-sodium foods can increase fluid retention and worsen ascites, while stress can increase blood pressure and worsen bleeding complications. The nurse should advise the client to limit sodium intake and manage stress levels.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
