A male client reports to the on-call clinic nurse that he took two tablets of 10 mg lisinopril by mouth two hours ago and his skin now feels flushed. He reports a history of stable angina, but denies experiencing any chest pain at the moment or recently. Which action should the nurse take?
Instruct the client to increase his intake of oral fluids until the skin flushing is relieved.
Advise the client to place one nitroglycerin tablet under his tongue as a precaution.
Tell the client to have someone bring him to an emergency department immediately.
Reassure the client that facial flushing is a common side effect of the medication.
The Correct Answer is D
Choice A: Increasing oral fluids may help with hydration, but it will not reduce skin flushing caused by lisinopril. Lisinopril is an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE. inhibitor that dilates blood vessels and lowers blood pressure. Flushing occurs due to increased blood flow to the skin.
Choice B: Nitroglycerin is a vasodilator that relaxes smooth muscle in blood vessels and reduces chest pain caused by angina. It is not indicated for skin flushing caused by lisinopril. Moreover, nitroglycerin can lower blood pressure further and cause hypotension, headache, dizziness, and fainting.
Choice C: Going to an emergency department is not necessary for skin flushing caused by lisinopril. Flushing is not a sign of an allergic reaction or anaphylaxis, which would require immediate medical attention. Flushing is also not a symptom of a heart attack or stroke, which would present with other signs such as chest pain, shortness of breath, arm numbness, or slurred speech.
Choice D: Reassuring the client that facial flushing is a common side effect of lisinopril is the best action for the nurse to take. Flushing is not harmful or dangerous, and it usually subsides within a few hours. The nurse should explain the mechanism of action of lisinopril and its benefits for lowering blood pressure and preventing angina. The nurse should also advise the client to monitor his blood pressure regularly and report any signs of hypotension, such as dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A: Creatinine is not a relevant laboratory test for the nurse to monitor, as this reflects renal function and is not affected by naproxen or arthritis. This is a distractor choice.
Choice B: Serum calcium is not a pertinent laboratory test for the nurse to monitor, as this indicates bone metabolism and is not related to naproxen or arthritis. This is another distractor choice.
Choice C: Erythrocyte sedimentation rate is not an important laboratory test for the nurse to monitor, as this measures inflammation and is not influenced by naproxen or stomach pain. This is another distractor choice.
Choice D: Hemoglobin is an essential laboratory test for the nurse to monitor, as this shows blood oxygen-carrying capacity and can be reduced by naproxen-induced gastrointestinal bleeding, which can cause stomach pain, weakness, and fatigue. Therefore, this is the correct choice.
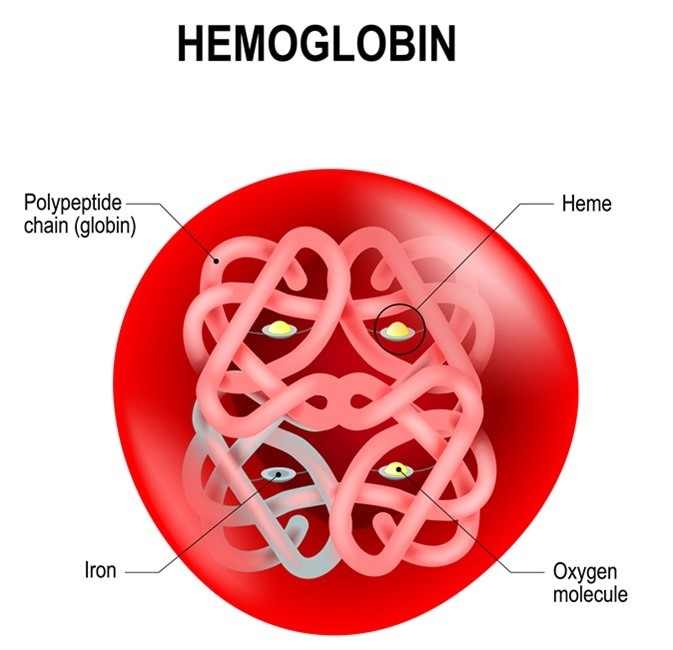
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A reason: When the client has ankle edema, it is important for the nurse to assess for other signs of fluid retention, such as weight gain, jugular venous distension, and crackles in the lungs. However, ankle edema alone is not a specific indicator of preeclampsia or eclampsia, which are conditions that can cause hyperreflexia or increased DTRs.
Choice C reason: During admission to labor and delivery, it is important for the nurse to assess various aspects of the client's health status, such as vital signs, fetal heart rate, contractions, cervical dilation, and pain level. However, assessing DTRs is not a routine part of labor and delivery assessment unless there are signs of preeclampsia or eclampsia.
Choice D reason: Within the first trimester of pregnancy, it is important for the nurse to assess for signs of pregnancy-related nausea and vomiting, bleeding, infection, and ectopic pregnancy. However, assessing DTRs is not a routine part of first trimester assessment unless there are signs of neurological disorders or spinal cord injury.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
