Which assessment should the home health nurse include during a routine home visit for a client who was discharged home with a suprapubic catheter?
Observe insertion site.
Palpate flank area.
Measure abdominal girth.
Assess perineal area.
The Correct Answer is A
Choice A: Observing insertion site is an essential assessment for a client who has a suprapubic catheter. The insertion site is located in the lower abdomen, where urine drains from an opening in the bladder through a catheter into a drainage bag. The nurse should inspect the site for signs of infection, inflammation, bleeding, or leakage. The nurse should also clean the site with soap and water and apply a sterile dressing as needed.
Choice B: Palpating flank area is not a relevant assessment for a client who has a suprapubic catheter. The flank area is located on the sides of the back, where the kidneys are located. Palpating the flank area can detect tenderness or pain that may indicate kidney infection or stones, but it does not provide information about the suprapubic catheter or its function.
Choice C: Measuring abdominal girth is not a relevant assessment for a client who has a suprapubic catheter. The abdominal girth is the circumference of the abdomen at the level of the umbilicus. Measuring abdominal girth can detect changes in fluid balance, ascites, or bowel obstruction, but it does not provide information about the suprapubic catheter or its function.
Choice D: Assessing perineal area is not a relevant assessment for a client who has a suprapubic catheter. The perineal area is located between the anus and the genitals. Assessing perineal area can detect signs of infection, irritation, or injury in the genital or anal regions, but it does not provide information about the suprapubic catheter or its function.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A: 18%. This is not the correct percentage, as it only accounts for one lower extremity. According to the rule of nines, each lower extremity accounts for 9% of body surface area on both anterior and posterior sides, so both lower extremities would account for 18% x 2 = 36%.
Choice B: 27%. This is not the correct percentage, as it only accounts for one and a half lower extremities. According to the rule of nines, each lower extremity accounts for 9% of body surface area on both anterior and posterior sides, so one and a half lower extremities would account for 9% x 3 = 27%.
Choice C: 36%. This is the correct percentage, as it accounts for both lower extremities. According to the rule of nines, each lower extremity accounts for 9% of body surface area on both anterior and posterior sides, so both lower extremities would account for 9% x 4 = 36%.
Choice D: 45%. This is not the correct percentage, as it accounts for more than both lower extremities. According to the rule of nines, each lower extremity accounts for 9% of body surface area on both anterior and posterior sides, so more than both lower extremities would account for more than 9% x 4 = 36%.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
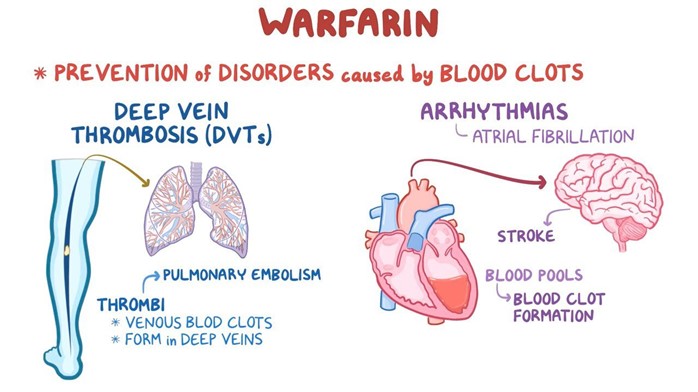
Choice A reason: Increasing the intake of dark green leafy vegetables while taking warfarin is not a good instruction because it can decrease the effectiveness of warfarin. Dark green leafy vegetables are rich in vitamin K, which is a coagulation factor that counteracts the anticoagulant effect of warfarin.
Choice B reason: Eating two servings of dark green leafy vegetables daily and continuing for 30 days after warfarin therapy is completed is not a good instruction because it can cause bleeding complications. Dark green leafy vegetables are rich in vitamin K, which is a coagulation factor that counteracts the anticoagulant effect of warfarin. Stopping warfarin while continuing to eat high amounts of vitamin K can increase the risk of clot formation and thromboembolism.
Choice D reason: Avoiding eating any foods that contain any vitamin K because it is an antagonist of warfarin is not a good instruction because it can cause bleeding complications. Dark green leafy vegetables are rich in vitamin K, which is a coagulation factor that counteracts the anticoagulant effect of warfarin. Eliminating vitamin K from the diet can increase the sensitivity to warfarin and cause excessive bleeding and bruising.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
