A 46-year-old female patient returns to the clinic with continued dysuria after being treated with trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole for 3 days. Which action will the nurse plan to take?
Remind the patient about the need to drink 1000 mL of fluids daily.
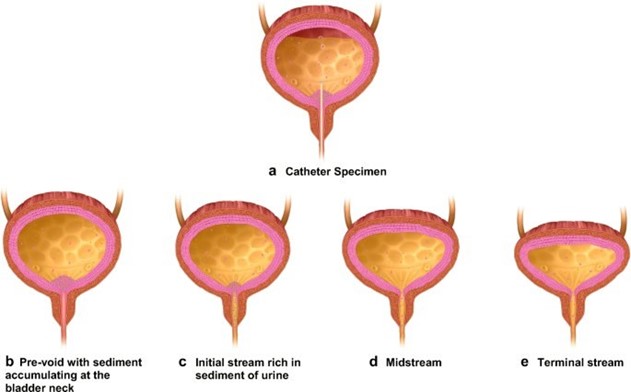
Obtain a midstream urine specimen for culture and sensitivity testing.
Suggest that the patient use acetaminophen (Tylenol) to relieve symptoms.
Tell the patient to take trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole for 3 days.
The Correct Answer is B
This is because the persistent dysuria suggests that the initial treatment was not effective, and there may be a possibility of a resistant organism. Obtaining a midstream urine specimen for culture and sensitivity testing will help identify the specific microorganism causing the infection and determine the most effective antibiotic to use. The nurse should also instruct the patient to continue to drink plenty of fluids, as this will help flush out the bacteria and relieve symptoms. The nurse may suggest the use of acetaminophen (Tylenol) to relieve discomfort, but this should not be the only action taken, as treating the underlying infection is crucial. The nurse should not tell the patient to take trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole for an additional three days, as the initial treatment was not effective, and a different course of treatment may be required based on the results of the urine culture and sensitivity testing.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Diabetes insipidus is a condition in which the body is unable to properly regulate fluid balance, leading to excessive urination (polyuria) and thirst. Therefore, the nurse should anticipate the clinical manifestation of polyuria in a patient admitted to the hospital with diabetes insipidus. The patient may excrete large amounts of dilute urine, which can lead to dehydration if adequate fluid replacement is not provided. The other options listed (fluid volume overload, decreased gas exchange, and generalized edema) are not typically associated with diabetes insipidus, as this condition is characterized by a deficiency of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) rather than an excess of fluid.

Correct Answer is D
Explanation
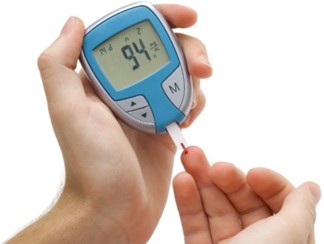
When performing a self-monitoring blood glucose test, it is essential to choose the puncture site on the side of the fingertip, slightly off-center, and to rotate the puncture sites to prevent lipoatrophy and injury to the nerves and blood vessels in the finger. Puncturing the center of the fingertip can lead to pain, injury to the nerves, and tissue damage.
Options a, b, and c are correct and indicate appropriate actions during self-monitoring of blood glucose. Washing the puncture site using warm water and soap helps to reduce the risk of infection. Waiting for a minute with the arm down before puncturing the site helps to increase blood flow and make it easier to obtain a blood sample. A blood glucose result of 120 mg/dL indicates good blood sugar control within the target range for many patients with diabetes.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
