A young adult patient is admitted to the hospital for evaluation of right lower quadrant abdominal pain with nausea and vomiting. Which action should the nurse take?
Palpate the abdomen for rebound tenderness.
Suggest the patient lie on the side, flexing the right leg.
Assist the patient to cough and deep breathe.
Encourage the patient to sip clear, non-carbonated liquids.
The Correct Answer is B
The nurse should suggest the patient lie on the side, flexing the right leg². This position may help relieve pain and reduce tension in the abdominal muscles¹. Palpating the abdomen for rebound tenderness (a) may cause pain and should be avoided¹. Assisting the patient to cough and deep breathe (c) may be helpful for respiratory issues but not for abdominal pain¹. Encouraging the patient to sip clear, non-carbonated liquids (d) may be helpful for hydration but does not address the abdominal pain¹.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
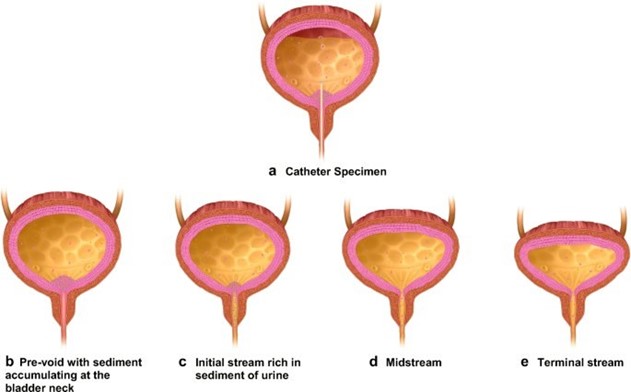
This is because the persistent dysuria suggests that the initial treatment was not effective, and there may be a possibility of a resistant organism. Obtaining a midstream urine specimen for culture and sensitivity testing will help identify the specific microorganism causing the infection and determine the most effective antibiotic to use. The nurse should also instruct the patient to continue to drink plenty of fluids, as this will help flush out the bacteria and relieve symptoms. The nurse may suggest the use of acetaminophen (Tylenol) to relieve discomfort, but this should not be the only action taken, as treating the underlying infection is crucial. The nurse should not tell the patient to take trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole for an additional three days, as the initial treatment was not effective, and a different course of treatment may be required based on the results of the urine culture and sensitivity testing.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
The correct action for the nurse to take first when preparing to teach a newly diagnosed 43-year-old man with type 2 diabetes home management of the disease is to assess the patient's perception of what it means to have diabetes. This will help the nurse to identify any misconceptions or fears the patient may have about the condition, and tailor the education to meet the patient's specific needs. Options A, C, and D are important components of diabetes education but can be addressed after the nurse has assessed the patient's perception of the disease.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
