A 25 year-old female patient will begin taking phenytoin for epilepsy. The patient tells the nurse she is taking oral contraceptives (OCPs). Which response will the nurse give?
"Continue taking OCPS because phenytoin is not safe during pregnancy."
"You should use a backup method of contraception along with OCPs."
"You should stop taking OCPs because of drug-drug interactions with phenytoin."
"You should take low-dose aspirin while taking these medications to reduce your risk of stroke."
The Correct Answer is B
A. "Continue taking OCPS because phenytoin is not safe during pregnancy."
This statement is not accurate. While it's essential to address pregnancy risk, phenytoin can reduce the effectiveness of oral contraceptives. Women on phenytoin are often advised to use additional contraceptive measures.
B. "You should use a backup method of contraception along with OCPs."
This is the correct response. Phenytoin can accelerate the metabolism of oral contraceptives, potentially reducing their effectiveness. Using a backup method, such as condoms, is recommended to ensure adequate contraception.
C. "You should stop taking OCPs because of drug-drug interactions with phenytoin."
This advice is generally not recommended without consulting the healthcare provider. Abruptly stopping OCPs without an alternative form of contraception can increase the risk of unintended pregnancy.
D. "You should take low-dose aspirin while taking these medications to reduce your risk of stroke."
This statement is not relevant to the situation described. Low-dose aspirin is not typically recommended for contraception, and its use in this context does not address the potential interaction between phenytoin and oral contraceptives.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
A. Carbidopa-levodopa
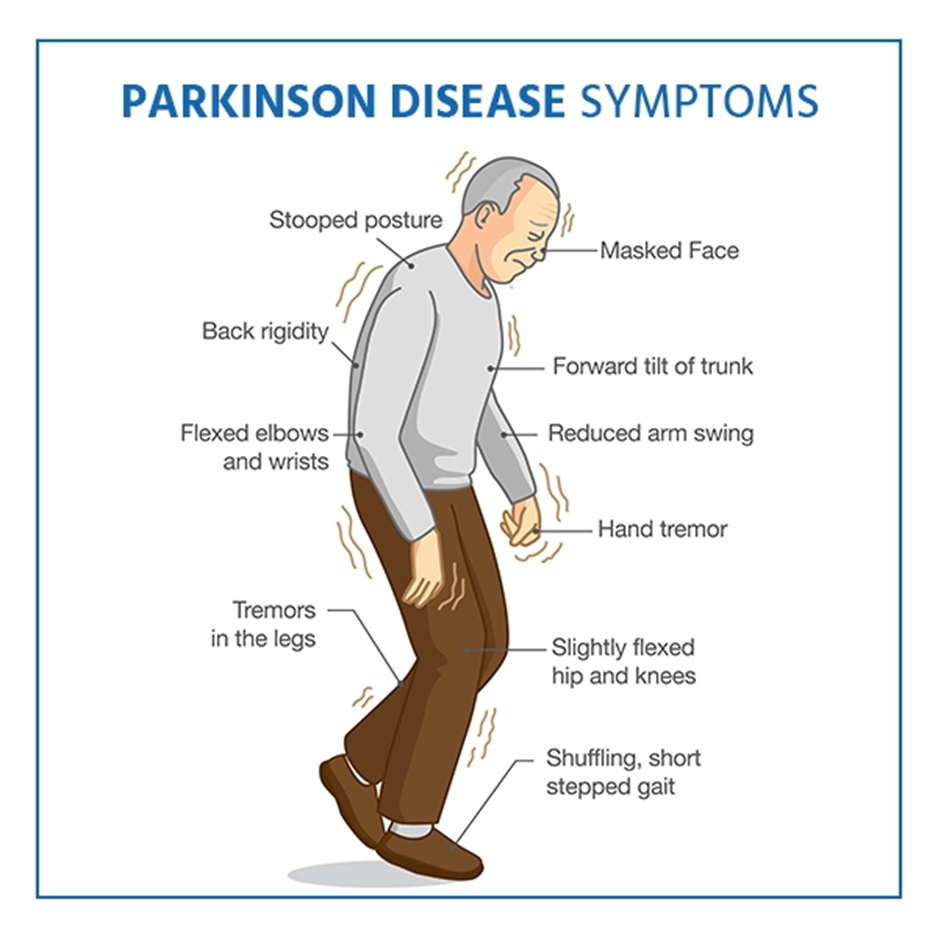
The symptoms described, including a shuffling gait, lack of facial expression, and tremors at rest, are characteristic of Parkinson's disease. Carbidopa-levodopa is a common medication used in the management of Parkinson's disease.
B. Donepezil
Donepezil is used in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, a condition characterized by cognitive decline and memory impairment. It is not indicated for Parkinson's disease.
C. Rivastigmine
Rivastigmine is another medication used in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, and it is also used in Parkinson's disease dementia. However, it is not the primary medication for the motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease.
D. Tacrine
Tacrine was once used in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, but it is no longer commonly prescribed due to safety concerns and the availability of newer, safer medications. It is not indicated for Parkinson's disease.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A. Calm the patient to reduce acid production.
This description is not accurate for sucralfate. Calming the patient to reduce acid production is typically associated with medications like proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) or H2 receptor blockers.
B. Block the H2 receptors.
Blocking H2 receptors is the mechanism of action for H2 receptor blockers, such as ranitidine. It is not the mechanism of action for sucralfate.
C. Neutralize the gastric acids.
Neutralizing gastric acids is the mechanism of action for antacids, such as aluminum hydroxide or calcium carbonate. Sucralfate works differently; it forms a protective coating on the gastric lining rather than directly neutralizing acids.
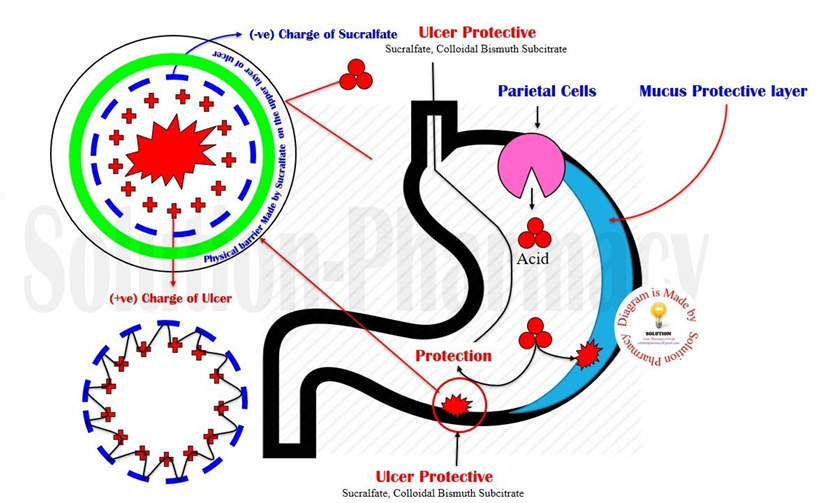
D. Coat the gastric lining.
This is the correct mechanism of action for sucralfate. It forms a protective coating on the gastric lining, adhering to the ulcer site and providing a barrier against gastric acid.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
