Which of the following is the priority nursing action for a client at 33 weeks of gestation with a diagnosis of placenta previa?
Insert an IV catheter.
Monitor vaginal bleeding.
Apply an external fetal monitor.
Administer glucocorticoids.
The Correct Answer is B
Choice A reason:
Inserting an IV catheter is a standard procedure in many hospital admissions and can be necessary for administering medications and fluids. However, it is not the immediate priority in the case of placenta previa. Placenta previa is a condition where the placenta covers the cervix, and the main risk associated with it is bleeding.
Choice B reason:
Monitoring vaginal bleeding is the priority nursing action for a client with placenta previa. This condition can lead to significant bleeding, which can be life-threatening for both the mother and the fetus. The nurse must assess the amount, color, and duration of any bleeding to make timely decisions regarding the need for further medical intervention or potential delivery if the bleeding is severe.
Choice C reason:
Applying an external fetal monitor is important to assess the fetus's well-being, especially if there is vaginal bleeding or other complications. However, it is not the first action to take. The immediate concern with placenta previa is the risk of hemorrhage, which can compromise the oxygen supply to the fetus, making monitoring maternal bleeding a higher priority.
Choice D reason:
Administering glucocorticoids may be indicated to accelerate fetal lung maturity if preterm delivery is anticipated. While this is an important consideration in the management of placenta previa, especially if there is a risk of preterm birth, it is not the first line of action. The initial focus should be on assessing and controlling any bleeding to stabilize the mother's condition.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
It is not necessary to avoid food and fluids the day of the procedure unless specifically instructed by the healthcare provider. Amniocentesis does not typically require fasting; however, some facilities may have different protocols.
Choice B Reason:
A bowel prep protocol is not required for an amniocentesis. This procedure is unrelated to the gastrointestinal tract, and bowel preparation is more commonly associated with procedures like colonoscopy.
Choice C Reason:
Emptying the bladder immediately prior to the procedure is important. A full bladder can obstruct the view of the uterus during ultrasound, which is used to guide the amniocentesis needle. Additionally, an empty bladder reduces the risk of accidental puncture during the procedure.
Choice D Reason:
Washing the abdomen with soap and water the morning of the procedure is a good hygiene practice but is not specifically required for amniocentesis. The area will be cleaned with antiseptic by the healthcare provider before the procedure.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A reason:
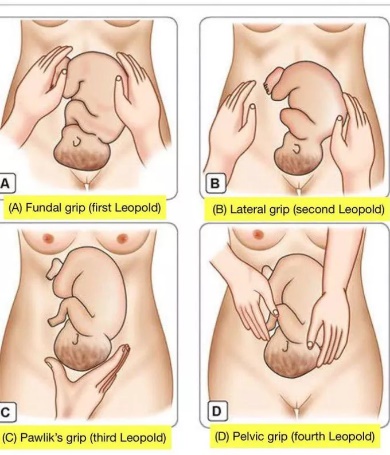
The left lower quadrant is not typically where fetal heart tones are auscultated when the round, firm part of the fetus (usually the head) is palpated in the fundus and the long smooth surface (indicative of the back) is on the right side. Fetal heart tones are best heard through the back of the fetus, and in this position, the back is not located in the left lower quadrant.
Choice B reason:
The right upper quadrant is the correct location to auscultate fetal heart tones in this scenario. The Leopold's maneuvers suggest that the fetus is in a cephalic presentation with its back facing the right side of the mother's abdomen. Therefore, the fetal heart tones are most likely to be heard in the right upper quadrant, just below the level of the fundus.
Choice C reason:
The right lower quadrant is generally not the area to auscultate fetal heart tones if the fetus's back is on the right side and the head is in the fundus. The heart tones are typically higher up and closer to where the back is palpated.
Choice D reason:
The left upper quadrant would not be the correct place to find fetal heart tones given the described position of the fetus. With the back on the right side, auscultation on the left would not yield the clear heart tones expected.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
