The systemic circuit:
Brings oxygen-poor blood from the lungs.
Brings oxygen-rich blood from the tissues.
Sends oxygen-poor blood to the heart.
Sends oxygen-rich blood to the tissues.
The Correct Answer is D
The systemic circuit sends oxygen-rich blood to the tissues.
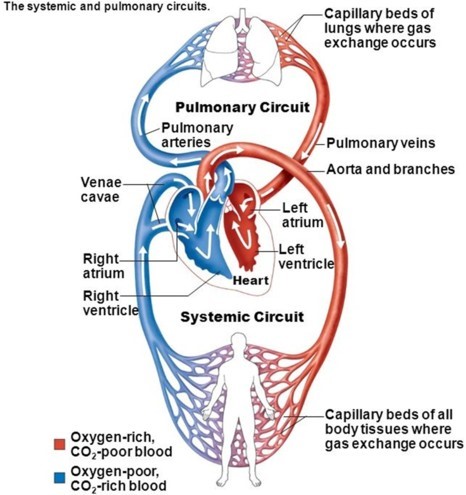
It is part of the circulatory system that carries blood away from the heart, delivers it to most of the organs and tissues, and returns it to the heart again.
Choice A is wrong because it describes the pulmonary circuit, which brings oxygen-poor blood from the heart to the lungs.
Choice B is wrong because it is the opposite of what the systemic circuit does.
The systemic circuit brings oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the tissues, not from the tissues.
Choice C is wrong because it is also the opposite of what the systemic circuit does. The systemic circuit sends oxygen-poor blood to the heart, not from the heart.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
It is measured as part of a blood test and depends on the number and size of red blood cells. It is normally 40.7–50.3% for males and 36.1–44.3% for females.
Red blood cells contain hemoglobin, which transports oxygen and nutrients to the cells and tissues of the body.
Choice A is wrong because the color of plasma is not hematocrit.
Plasma is the liquid part of blood that carries blood cells and other substances.
Choice B is wrong because hematocrit is not a disease.
It is a test that can indicate conditions such as anemia or polycythemia.
Choice C is wrong because hematocrit is not a clotting factor.
Clotting factors are proteins that help the blood to clot and prevent bleeding.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
The pulmonary circuit sends oxygen-poor blood to the lungs, where it is oxygenated and returned to the heart.
This is distinguished from the systemic circuit, which sends oxygen-rich blood to the tissues and returns oxygen-poor blood to the heart.
Choice A is wrong because it confuses the pulmonary circuit with the systemic circuit. The pulmonary circuit does not send blood to the tissues but to the lungs.
Choice B is wrong because it only describes part of the pulmonary circuit.
The pulmonary circuit sends oxygen-poor blood to the heart, but only after it has been oxygenated in the lungs.
Choice C is wrong because it confuses the pulmonary circuit with the systemic circuit. The pulmonary circuit does not bring blood from the tissues but from the heart.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
