The registered nurse is discussing care of an infant diagnosed with a patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) with a nursing student. The registered nurse determines that the nursing student needs further teaching regarding a PDA when the student states that which circulatory change is a characteristic of this disorder?
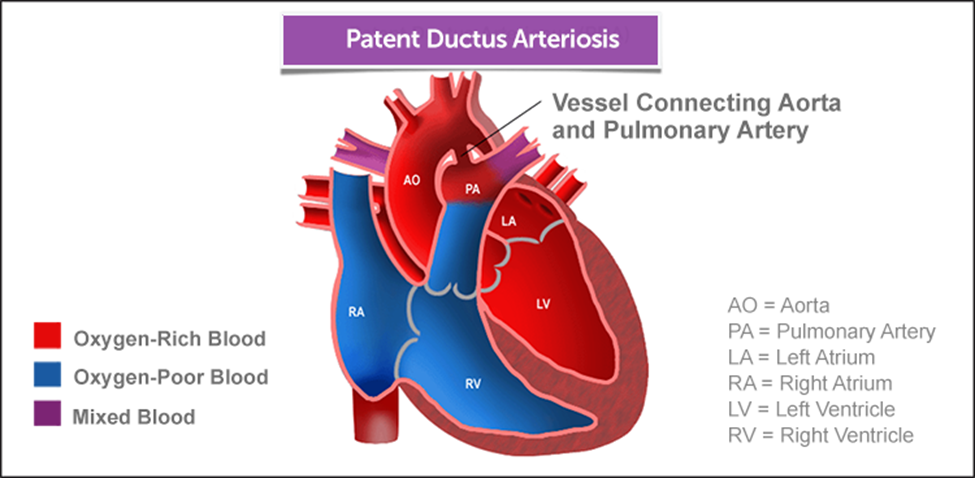
This shunting allows oxygenated and unoxygenated blood to mix.
Blood is shunted to the right side of the heart.
This shunting results in increased pulmonary blood flow.
Blood is shunted to the left side of the heart.
The Correct Answer is D
A. "This shunting allows oxygenated and unoxygenated blood to mix."
Explanation: This statement is correct. In PDA, the shunting of blood between the aorta and pulmonary artery allows oxygenated and unoxygenated blood to mix, leading to decreased oxygen saturation in the systemic circulation.
B. "Blood is shunted to the right side of the heart."
Explanation: This statement is correct. In PDA, blood is shunted from the left side of the heart (aorta) to the right side of the heart (pulmonary artery).
C. "This shunting results in increased pulmonary blood flow."
Explanation: This statement is correct. PDA leads to increased pulmonary blood flow as a result of the shunting of blood from the aorta to the pulmonary artery.
D. "Blood is shunted to the left side of the heart."
Explanation:
A patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is a congenital heart defect where the ductus arteriosus, a fetal blood vessel that normally closes shortly after birth, remains open. In PDA, blood is shunted from the aorta (left side of the heart) to the pulmonary artery (right side of the heart), resulting in increased pulmonary blood flow. Therefore, the correct statement is that "Blood is shunted to the right side of the heart."
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A. "I'll check my child's temperature."
Explanation: Monitoring the child's temperature is a general indicator of well-being and can help identify signs of infection or other postoperative concerns.
B. "I'll give medication so that my child will be comfortable."
Explanation: Administering prescribed medication for comfort is a suitable practice to manage postoperative pain or discomfort.
C. "I'll check my child's voiding to be sure there's no problem."
Explanation:
After an orchiopexy procedure, checking voiding may not be directly related to the surgical intervention. Orchiopexy is a procedure to correct cryptorchidism, which involves repositioning an undescended testicle into the scrotum. While monitoring for general signs of well-being is important, specifically checking voiding might not be directly relevant to the surgical recovery process.
D. "I'll let my child decide when to return to play activities."
Explanation: Allowing the child to gradually resume play activities based on their comfort and recovery is a reasonable approach, considering individual variations in recovery times.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A. Crayons and a coloring book:
Incorrect: Crayons and coloring books may not be appropriate for a 12-month-old, as they may pose a choking hazard. Additionally, they might require more direct contact, which may not be ideal under contact precautions.
B. Modeling clay:
Incorrect: Modeling clay may also pose a choking hazard for a toddler. Moreover, it can be messy and may not be suitable for use in a hospital room with contact precautions.
C. Hanging crib toys.
Correct Answer: Hanging crib toys can provide visual and tactile stimulation for the toddler without the need for direct contact. These toys can be attached to the crib, allowing the child to engage with them safely.
D. Large building blocks:
Incorrect: While large building blocks can be suitable for a toddler's developmental needs, they may not be the best option in a confined hospital room under contact precautions. The child's access to and handling of the blocks may be limited in this setting.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
