The progression of chronic bronchitis is best halted by?
Regular of bronchodilators
Postural chest drainage techniques
Identification of early signs of infection
Smoking cessation
The Correct Answer is D
Chronic bronchitis is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) that is characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the bronchial tubes, which can lead to symptoms such as cough, shortness of breath, and wheezing. The primary cause of chronic bronchitis is smoking, and the most effective way to halt its progression is by quitting smoking.

Smoking cessation is the cornerstone of treatment for chronic bronchitis, as continued smoking can worsen inflammation in the airways and accelerate the progression of the disease. In addition to smoking cessation, other treatments may include bronchodilators (such as albuterol) to help open the airways and improve breathing, postural chest drainage techniques to help clear mucus from the lungs, and antibiotics to treat bacterial infections.
While these treatments can help manage symptoms and prevent complications, they are not as effective as smoking cessation in halting the progression of chronic bronchitis. Therefore, it is important for individuals with chronic bronchitis to quit smoking as soon as possible to slow the disease process and improve their overall health.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
When the left ventricle is unable to pump blood effectively, blood backs up into the lungs, leading to pulmonary congestion and edema. This can cause symptoms such as shortness of breath, coughing, and wheezing. Decreased venous pressure and hyperoxygenation are not typically associated with left ventricular failure. Bradycardia may occur in some cases, but it is not a defining feature of left ventricular failure.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
The mitral and tricuspid valves are located between the atria and ventricles in the heart, and they open and close to allow blood to flow in one direction through the heart. During diastole, when the heart is relaxed and filling with blood, the mitral and tricuspid valves are open to allow blood to flow from the atria into the ventricles.
Once the ventricles are filled with blood, they begin to contract during systole to pump the blood out to the lungs (right ventricle) and the rest of the body (left ventricle). As the ventricles contract, the pressure within them increases, which causes the mitral and tricuspid valves to be pushed closed by the blood within the ventricles. This closure prevents the backflow of blood into the atria during ventricular contraction (systole).
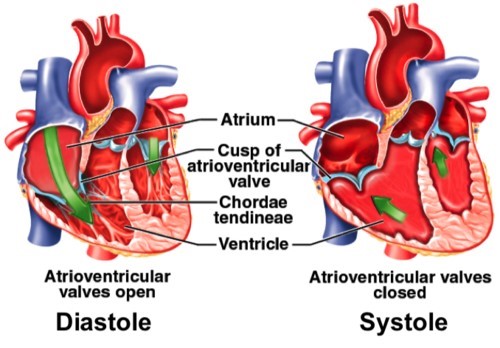
The chordae tendineae are thin, fibrous cords that connect the mitral and tricuspid valves to the papillary muscles within the ventricles. These structures help to anchor the valves in place during ventricular contraction, and prevent them from prolapsing (bulging back into the atria) and causing regurgitation (backflow of blood).
The trabeculae carneae are muscular ridges within the ventricles that help to increase the force of ventricular contraction, but they do not play a direct role in closing the mitral and tricuspid valves. Similarly, the reduced pressure in the atria during ventricular contraction is due to the fact that blood is being pumped out of the atria and into the ventricles, rather than the atria "pulling" the valves closed.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
