The nurse working in the eye doctor's office is completing an assessment on an elderly client. Which of the following would a nurse expect to assess in a client with esotropia?
Eye malalignment
Eye turning outward
Eye oscillating
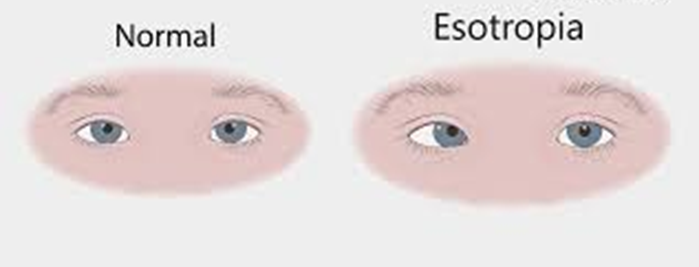
Eye turning inward
The Correct Answer is D
Choice a reason:
Eye malalignment is a general term that refers to any form of misalignment of the eyes, which can include esotropia but is not specific to it. Esotropia is a type of strabismus where there is a specific pattern of eye malalignment.
Choice b reason:
Eye turning outward is known as exotropia, which is the opposite of esotropia. In exotropia, one or both eyes turn outward away from the nose, which is not characteristic of esotropia.
Choice c reason:
Eye oscillating refers to nystagmus, a condition where the eyes make repetitive, uncontrolled movements, often resulting in reduced vision and depth perception. While nystagmus can occur in conjunction with esotropia, it is not a defining characteristic of esotropia itself.
Choice d reason:
Eye turning inward is the hallmark of esotropia. In this condition, one or both eyes turn inward towards the nose. It can be constant or intermittent and may affect one eye or alternate between both eyes. Esotropia can be comitant, meaning the degree of deviation is the same in every direction of gaze, or incomitant, where the deviation varies with gaze direction.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice a reason:
A client recently diagnosed with a chronic illness would require a comprehensive health history that includes past medical history, medications, and lifestyle factors. While important, it is not typically categorized as an emergency health history unless the chronic condition has acutely worsened.
Choice b reason:
A client presenting with hypotension (low blood pressure), tachycardia (rapid heart rate), an oxygen saturation of 85% (indicating potential hypoxemia), and a recent gunshot wound is experiencing a life-threatening situation that requires immediate medical attention. An Emergency health history is crucial in this scenario to quickly gather information that will guide urgent treatment decisions.
Choice c reason:
A client who has just confirmed pregnancy would need a detailed health history, including obstetric and gynecological history, but this is not considered an emergency unless there are complications or concerns that require immediate attention.
Choice d reason:
A client who frequently visits the hospital reporting the same symptom may indicate a chronic issue that needs ongoing management rather than an emergency. However, if the symptom suggests an acute exacerbation or a new, serious condition, it could escalate to an emergency.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Rhinitis medicamentosa, also known as rebound congestion, is a condition of nasal congestion without other cold or allergy symptoms, typically caused by the overuse of nasal decongestant sprays. It does not usually present with chronic headaches or tenderness over the sinuses, which are more indicative of sinusitis.
Choice B Reason:
Acute bacterial sinusitis is likely the correct diagnosis in this scenario. It often follows a viral upper respiratory infection and presents with symptoms such as thick, discolored nasal mucus, decreased sense of smell, and facial pain or tenderness over the affected sinuses. The chronic headache and noted tenderness upon palpation over the sinuses in the client are consistent with this condition.
Choice C Reason:
Epistaxis, or nosebleed, is bleeding from the nose that can be caused by various factors, including trauma, medication, or environmental conditions. While it can be a symptom of other nasal conditions, it is not typically associated with chronic headaches or sinus tenderness following an upper respiratory infection.
Choice D Reason:
Allergic rhinitis is an allergic reaction to allergens such as pollen, dust, or pet dander, causing symptoms like sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, and sometimes headaches. However, the chronic headache and sinus tenderness described by the client after an infection are more suggestive of sinusitis rather than allergic rhinitis.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
