A 75-year-old female patient presented to the office for an annual wellness visit. During the nurse's assessment, the patient explains she has been experiencing bilateral knee pain for the past eleven months. Based on the duration of the patient's symptoms, how would the nurse categorize the patient's pain?
Acute Pain
Intermittent Pain
Chronic Pain
Idiopathic Pain
The Correct Answer is C
Choice A reason:
Acute pain is typically sudden in onset and is usually the result of a specific injury or illness. It is characterized by its sharp quality and tends to last for a short duration, generally not longer than six months. Since the patient's knee pain has persisted for eleven months, it does not fall under the category of acute pain.
Choice B reason:
Intermittent pain is pain that comes and goes at intervals. Although the patient's pain could be intermittent, the classification based on duration would not be described as intermittent. This term refers more to the pattern of the pain rather than its chronicity or cause.
Choice C reason:
Chronic pain is defined as pain that persists for longer than six months, often continuing even after the injury or illness that caused it has healed. The patient's bilateral knee pain has been present for eleven months, which exceeds the six-month threshold, thus categorizing it as chronic pain.
Choice D reason:
Idiopathic pain refers to pain that arises without a clear cause. It is not categorized based on the duration of the pain but rather on the absence of an identifiable underlying reason. Since the patient's pain has a specific duration, it is not appropriate to classify it as idiopathic without further information regarding its cause.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A reason:
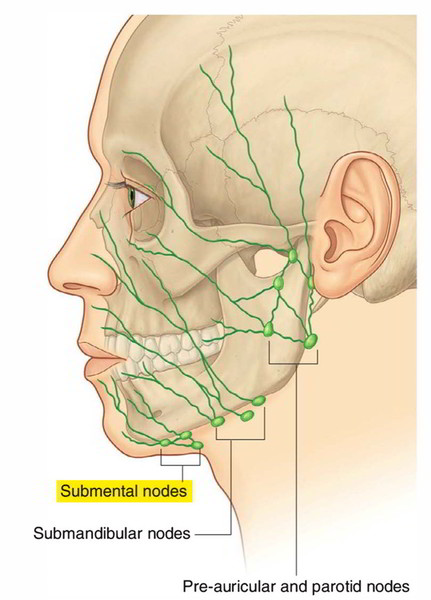
Palpating in front of the ear would assess the preauricular lymph nodes, not the submental lymph nodes. The preauricular nodes are located just in front of the ears and are typically examined when there is an infection or inflammation in the eyes, ears, or scalp.
Choice B reason:
The submental lymph nodes are located in the midline, just under the chin, behind the bony prominence of the mandible. This is the correct area for palpation when assessing the submental lymph nodes. These nodes drain the lower lip, the floor of the mouth, the tip of the tongue, and the incisors, and they can become enlarged due to infections or malignancies in these areas.
Choice C reason:
Palpating superficial to the sternomastoid would assess the cervical lymph nodes, specifically the anterior cervical nodes, which are not the submental lymph nodes. The sternomastoid muscle is a landmark for several lymph node groups in the neck, but not for the submental group.
Choice D reason:
Palpating at the angle of the mandible would assess the submandibular lymph nodes, not the submental lymph nodes. The submandibular nodes are located beneath the jawline and can become enlarged due to infections or malignancies in the mouth, throat, and salivary glands.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A reason:
A formal hearing test, or audiometry, is the most comprehensive method for assessing hearing loss, which can be a side effect of ototoxic medications. These tests can detect both conductive and sensorineural hearing loss, providing a detailed profile of hearing function across different frequencies. For clients receiving ototoxic antibiotics, regular monitoring through formal hearing tests is recommended to detect any early signs of hearing impairment and to implement timely interventions.
Choice B reason:
The rubbing fingers test is a rudimentary hearing screening method where the examiner rubs their fingers together near the patient's ear, asking them to indicate when they hear the sound. While this test can be used as a quick check for hearing loss, it is not as sensitive or specific as formal audiometry and may not detect early or mild hearing loss caused by ototoxic drugs.
Choice C reason:
Tuning fork tests, such as the Weber and Rinne tests, are used to differentiate between conductive and sensorineural hearing loss. These tests can be useful in a clinical setting to provide immediate information about the type of hearing loss; however, they are not as comprehensive as formal hearing tests and may not be sufficient for monitoring ototoxicity.
Choice D reason:
The whisper hearing test involves the examiner whispering words or numbers and asking the patient to repeat them. This test can be useful for detecting significant hearing loss but may not be sensitive enough to detect the early stages of ototoxicity. Moreover, the test's accuracy can be affected by the examiner's voice level and the testing environment.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
