The nurse is caring for a client after a thoracentesis that drained 50 mL of clear fluid from the left lung. Which assessment finding should the nurse report to the healthcare provider immediately?
Dullness bilaterally on percussion.
Serosanguinous drainage from the chest tube.
Diminished breath sounds in the left lower lobe.
Mediastinal shift to the right.
The Correct Answer is D
A) Incorrect- Dullness bilaterally on percussion is not a normal finding, but it is not an immediate concern after thoracentesis. It may indicate fluid accumulation or consolidation in both lungs, which could be related to other conditions such as pneumonia or heart failure.
B) Incorrect- Serosanguinous drainage from the chest tube is expected after thoracentesis, as long as it is not excessive or continuous. The nurse should monitor the amount and color of the drainage and document it accordingly.
C) Incorrect- Diminished breath sounds in the left lower lobe are also expected after thoracentesis, as the procedure removes fluid and air from the pleural space and reduces lung expansion. The nurse should auscultate the lungs before and after the procedure and compare the findings. The breath sounds should improve gradually as the lung re-expands.
D) Correct- This is a sign of tension pneumothorax, which is a life-threatening complication of thoracentesis. Tension pneumothorax occurs when air accumulates in the pleural space and creates positive pressure that pushes the mediastinum (the heart, great vessels, and trachea) to the opposite side of the chest. This can impair venous return, cardiac output, and respiratory function. The nurse should report this finding to the healthcare provider immediately and prepare to assist with needle decompression or chest tube insertion.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
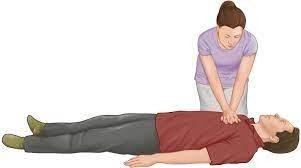
A) Incorrect- Observing for swelling at the fracture site is important for assessing the client's musculoskeletal condition, but it is not the priority intervention in this situation. The absence of spontaneous respirations and palpable carotid pulse indicates cardiac arrest, and immediate intervention is needed.
B) Incorrect- Analyzing the cardiac rhythm in another lead is not the first priority when the client is in cardiac arrest. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) should be initiated immediately to restore circulation.
C) Incorrect- Obtaining a 12-lead electrocardiogram is not the initial intervention in a client in cardiac arrest. CPR and defibrillation (if indicated) are the immediate actions to provide circulation and oxygenation to the vital organs.
D) Correct- The absence of spontaneous respirations and palpable carotid pulse indicates cardiac arrest. In this situation, immediate initiation of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is critical to provide circulation and oxygenation to the vital organs. Chest compressions are the initial step to address cardiac arrest and ensure blood flow to the body.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A) Incorrect - While discussing the potential for asymptomatic partners is important, addressing the client's concerns and providing accurate information is more immediate.
B) Correct- Syphilis and other STIs are important public health concerns. The nurse should provide accurate information, answer questions, and correct any misconceptions the client might have. This approach supports the client's knowledge and understanding of their health condition and prevents the spread of misinformation.
C) Incorrect - While discussing contraceptives is relevant to sexual health education, it may not directly address the client's concerns about their prior infections.
D) Incorrect - Notifying local health departments is important for reporting communicable diseases, but it doesn't directly address the client's current situation and concerns.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
