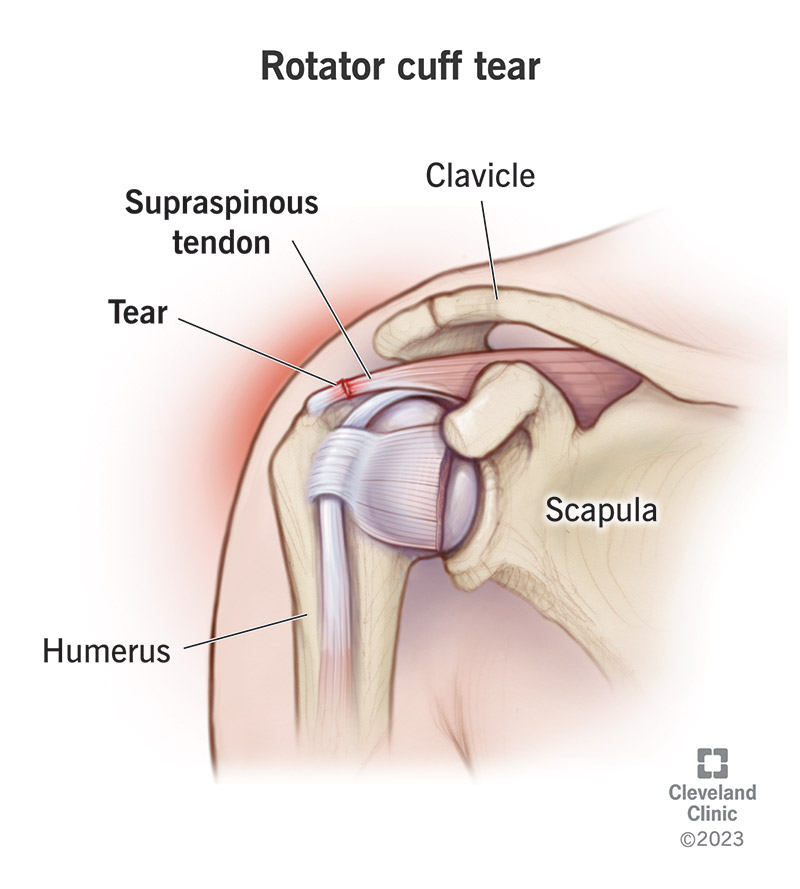
A nurse in a provider's office is assessing a client who reports shoulder pain. Which of the following findings by the nurse indicates a rotator cuff injury?
Inability to abduct the arm at the shoulder.
Negative drop arm test.
Alteration in the contour of the joint.
A positive Tinel's sign.
The Correct Answer is A
Choice A reason:
The inability to abduct the arm at the shoulder is a classic sign of a rotator cuff injury. The rotator cuff is responsible for stabilizing the shoulder joint and aiding in various movements, including abduction. When there is a tear or significant weakness in the rotator cuff muscles, especially the supraspinatus muscle, the patient may be unable to lift the arm away from the body or may experience pain while doing so.
Choice B reason:
A negative drop arm test would actually indicate that there is no rotator cuff injury. The drop arm test is performed by asking the patient to fully abduct the arm to 90 degrees and then slowly lower it. If the patient can control the motion and lower the arm smoothly, the test is negative. A positive drop arm test, where the patient cannot control the descent of the arm, would suggest a rotator cuff tear.
Choice C reason:
While an alteration in the contour of the joint may indicate some form of shoulder pathology, it is not specific to a rotator cuff injury. Changes in the contour could be due to various conditions, including dislocation, arthritis, or other musculoskeletal disorders.
Choice D reason:
A positive Tinel's sign is used to diagnose nerve compression or nerve damage, not rotator cuff injuries. It is performed by tapping over the course of a nerve to elicit a tingling sensation or pain in the distribution of the nerve. This sign is commonly associated with conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A reason:
Using an antibiotic ointment is not typically recommended as a preventive measure for skin integrity during radiation therapy. Antibiotic ointments are used to treat bacterial infections, and their use should be directed by a healthcare provider if an infection is present or there is skin breakdown.
Choice B reason:
It is important not to apply heat to the area of irradiation as heat can increase skin irritation and the risk of burns in the treated area. Patients undergoing radiation therapy are advised to avoid heat sources, including heating pads, hot water bottles, and direct sunlight, to prevent further damage to the skin.
Choice C reason:
Lubricating the skin with hypoallergenic lotion can help maintain skin integrity by keeping it moisturized. However, it is crucial to use lotions that are free of metals, alcohol, perfumes, and dyes, as these can react with radiation and cause skin irritation. Lotions should be applied after radiation therapy sessions and not immediately before treatment.
Choice D reason:
The instruction not to wash the area of irradiation is incorrect. It is essential to keep the skin clean to reduce the risk of infection. Patients should gently wash the irradiated area with lukewarm water and mild soap, and pat the area dry with a soft towel. They should avoid scrubbing or using harsh soaps that can irritate the skin.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A reason: Hypotension
Hypotension, or low blood pressure, can be a consequence of dehydration, which is a common complication of DI due to the excessive loss of water. However, hypotension is not a direct neurological effect of DI. It is more of a circulatory system response to the changes in fluid volume within the body.
Choice B reason: Poor skin turgor
Poor skin turgor is an indicator of dehydration, which can occur in DI due to the large volume of urine excreted. Skin turgor refers to the skin's ability to change shape and return to normal (elasticity), and it becomes less elastic when the body is dehydrated. While this is an important sign to monitor, it is not a neurological effect.
Choice C reason: Ataxia
Ataxia, which is a lack of muscle coordination affecting speech, eye movements, the ability to swallow, walking, picking up objects, and other voluntary movements, can be a neurological effect of DI if severe dehydration and electrolyte imbalance affect the brain. Symptoms such as confusion and muscle cramps can also be associated with ataxia, making it a relevant neurological effect to monitor in a client with DI.
Choice D reason: Dilute urine
Dilute urine is a primary symptom of DI, not a neurological effect. It is the result of the kidneys' inability to concentrate urine due to a deficiency in the anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) or the kidneys' response to ADH. Monitoring urine concentration is crucial in managing DI, but it does not represent a neurological effect.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
