Please identify the following rhythm: 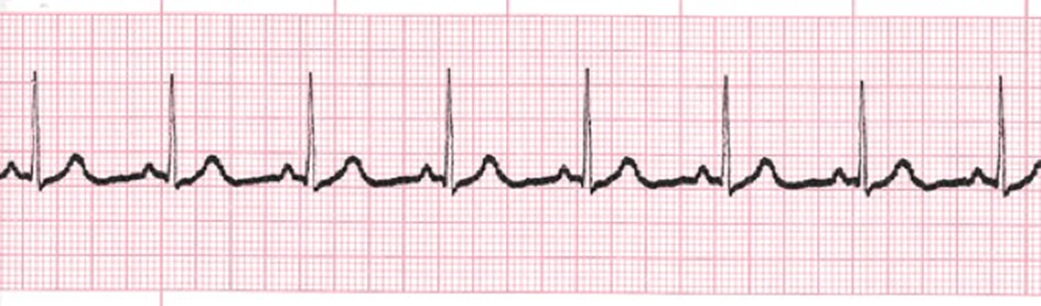
Asystole
Atrial Flutter
Normal Sinus Rhythm
Sinus Bradycardia
The Correct Answer is C
Answer and explanation
The correct answer is C. Normal Sinus Rhythm.
Choice A rationale:
Asystole is the absence of all electrical activity in the heart, as evidenced by a flat line on the electrocardiogram (ECG). It is a medical emergency that requires immediate cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and defibrillation.
Key features of asystole on ECG:
No discernible P waves, QRS complexes, or T waves.
A completely flat or nearly flat line on the ECG tracing.
Choice B rationale:
Atrial flutter is a rapid heart rhythm that arises from abnormal electrical activity in the atria. It is characterized by a sawtooth pattern on the ECG, with atrial rates typically between 250 and 350 beats per minute.
Key features of atrial flutter on ECG:
Absence of distinct P waves, instead replaced by flutter waves (sawtooth pattern).
Regular, rapid atrial rate (typically 250-350 bpm).
QRS complexes may be normal or slightly irregular in appearance.
Choice C rationale:
Normal sinus rhythm is the natural, healthy rhythm of the heart. It originates in the sinoatrial (SA) node, the heart's natural pacemaker, and is characterized by a regular rate of 60-100 beats per minute, with consistent P waves, QRS complexes, and T waves on the ECG.
Key features of normal sinus rhythm on ECG:
Presence of distinct P waves, QRS complexes, and T waves.
Regular rhythm with a rate of 60-100 beats per minute.
PR interval (the time between the P wave and QRS complex) is 0.12-0.20 seconds.
QRS duration (the time it takes for the ventricles to depolarize) is less than 0.12 seconds.
Choice D rationale:
Sinus bradycardia is a slow heart rhythm, with a rate below 60 beats per minute. It is often a normal finding in healthy individuals, especially athletes or during sleep. However, it can also be a sign of underlying medical conditions.
Key features of sinus bradycardia on ECG:
Presence of distinct P waves, QRS complexes, and T waves.
Regular rhythm with a rate less than 60 beats per minute.
PR interval and QRS duration are typically normal.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is E
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
While aspirin can help improve heart function in certain cases, such as by reducing inflammation, it's not accurate to say it directly restores normal heart function. This statement oversimplifies aspirin's mechanism of action and could mislead the client.
It's essential to emphasize aspirin's role in preventing clots, which is the primary reason for its use in coronary artery disease.
Choice B rationale:
Aspirin does not affect the oxygen-carrying capacity of blood. This function is primarily carried out by hemoglobin in red blood cells.
Stating that aspirin increases oxygen-carrying capacity could create misunderstandings about its role in coronary artery disease.
Choice C rationale:
Aspirin does not directly make blood penetrate the heart more freely. Its action primarily involves preventing blood clots from forming within blood vessels.
This statement could lead to a misconception about aspirin's mechanism of action, potentially affecting adherence to treatment.
Choice D rationale:
This is the most accurate and comprehensive response. It directly addresses the client's question and highlights the primary reason for daily aspirin use in coronary artery disease.
Aspirin inhibits platelet aggregation, reducing the risk of blood clots that can obstruct coronary arteries and trigger heart attacks or chest pain.
By preventing these blockages, aspirin can help prevent future cardiovascular events and improve the client's overall health outcomes.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Sinus tachycardia is a heart rhythm characterized by a rate greater than 100 beats per minute, with normal P waves preceding each QRS complex.
It can be caused by various factors, including exercise, stress, fever, dehydration, medications, and medical conditions such as anemia, hyperthyroidism, and heart failure.
In the given rhythm, the rate is within the normal range (60-100 beats per minute), and the P waves are not clearly visible, making sinus tachycardia unlikely.
Choice B rationale:
Atrial flutter is a type of supraventricular tachycardia characterized by a rapid, regular atrial rate of around 250-350 beats per minute, with a characteristic "sawtooth" pattern on the ECG.
It is typically caused by a re-entry circuit within the atria, often involving the cavo-tricuspid isthmus.
The ventricular rate is usually slower than the atrial rate due to the atrioventricular (AV) node's inability to conduct all atrial impulses.
Atrial flutter can cause symptoms such as palpitations, shortness of breath, lightheadedness, and fatigue.
It can also lead to complications such as stroke and heart failure.
The given rhythm shows a regular atrial rate with a sawtooth pattern, consistent with atrial flutter.
Choice C rationale:
Atrial fibrillation is another type of supraventricular tachycardia characterized by rapid, irregular atrial activity with no discernible P waves on the ECG.
It is also caused by disorganized electrical activity in the atria.
The ventricular rate in atrial fibrillation is also irregular, and the rhythm is often described as "irregularly irregular." The given rhythm shows a regular atrial rate, making atrial fibrillation unlikely.
Choice D rationale:
Normal sinus rhythm is the heart's natural rhythm, characterized by a rate of 60-100 beats per minute, with normal P waves preceding each QRS complex.
The given rhythm does not have normal P waves, making normal sinus rhythm unlikely.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
