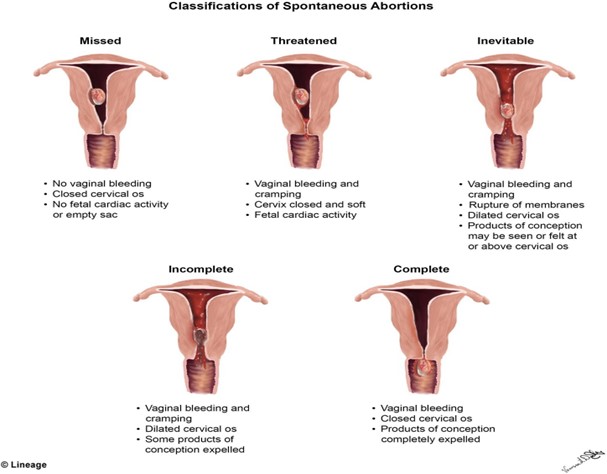
A woman presents to the emergency department complaining of bleeding and cramping. The initial history is significant for a last menstrual period 6 weeks ago. On sterile speculum examination, the care provider finds that the cervix is closed. The anticipated plan of care for this woman would be based on a probable diagnosis of which type of spontaneous abortion?
Threatened
Inevitable
Missed
Incomplete
The Correct Answer is A
Based on the provided information, the probable diagnosis for the spontaneous abortion in this woman would be a threatened abortion, since the cervix is closed and there is no evidence of expulsion of fetal or placental tissue. A threatened abortion is defined as vaginal bleeding occurring before the 20th week of gestation, with a closed cervical os, and no expulsion of fetal or placental tissue.
The other types of spontaneous abortion are defined as follows:
B. Inevitable abortion: vaginal bleeding and cramping with an open cervical os, with or without expulsion of fetal or placental tissue
C. Missed abortion: fetal demise without expulsion of fetal tissue, and may be associated with a closed cervical os and absence of uterine contractions
D. Incomplete abortion: partial expulsion of fetal or placental tissue, with or without vaginal bleeding, and may be associated with an open cervical os and uterine contractions
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Perineal hematoma is a complication that can occur after vaginal births, typically due to trauma or injury to the perineum during delivery. Wound dehiscence, UTIs, and DVTs are all possible complications associated with cesarean births. Wound dehiscence is a separation of the layers of the surgical incision, UTIs can occur due to catheterization during the surgery, and DVTs can occur due to immobility during the recovery period.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Smoking has been linked to a variety of health issues, including decreased fertility in both men and women. It can cause damage to sperm DNA and reduce sperm motility, which can make it more difficult for sperm to reach and fertilize an egg. Therefore, smoking can contribute to infertility issues. It's important for the man to quit smoking or at least reduce his cigarette consumption to increase his chances of conception with his wife.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
