A patient has arrived at the emergency department reporting intermittent fever and night sweats for the past three weeks and has developed a cough that is productive with small amounts of blood. What should be the nurse’s priority intervention?
Obtain a sputum sample.
Arrange transport for radiographic imaging.
Move the patient into airborne isolation.
Collect specimens for blood cultures.
The Correct Answer is C
Choice A rationale
Obtaining a sputum sample is important for diagnosing respiratory infections, but it is not the priority intervention in this case. The patient’s symptoms of intermittent fever, night sweats, and a productive cough with small amounts of blood are indicative of a possible airborne disease such as tuberculosis.
Choice B rationale
Arranging transport for radiographic imaging can be helpful in diagnosing the patient’s condition, but it is not the immediate priority. The primary concern should be to prevent the potential spread of an airborne disease.
Choice C rationale
Moving the patient into airborne isolation is the priority intervention. This action is taken to prevent the spread of potential airborne diseases to other patients and healthcare workers.
Choice D rationale
Collecting specimens for blood cultures can help identify the causative organism if the patient has a systemic infection. However, given the patient’s symptoms and the potential for an airborne disease, moving the patient into isolation is the priority.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A rationale
Keeping the head of the bed elevated until the treatment is completed is not typically recommended to reduce the risk of vesicant extravasation during intravenous chemotherapy.
Choice B rationale
Instructing the client to drink plenty of fluids during the treatment does not directly reduce the risk of vesicant extravasation. Hydration can help maintain good vein health, but it does not prevent extravasation.
Choice C rationale
Monitoring the client’s intravenous site hourly during the treatment is a key action to reduce the risk of vesicant extravasation. Regular monitoring allows for early detection of any signs of extravasation, such as swelling or redness at the IV site.
Choice D rationale
Administering an antiemetic before starting the chemotherapy can help manage side effects such as nausea and vomiting, but it does not reduce the risk of vesicant extravasation.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A rationale
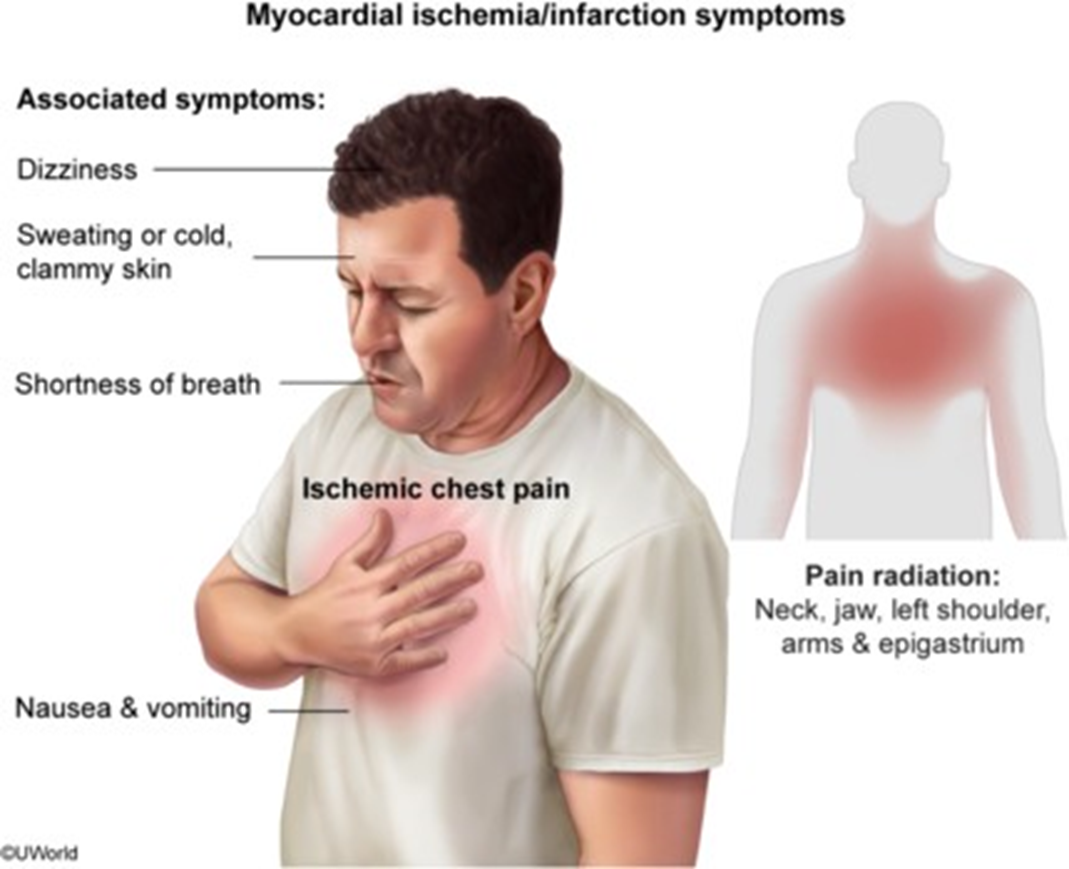
The client’s presentation of chest pain radiating to the left arm, shortness of breath, and diaphoresis are classic symptoms of a myocardial infarction (heart attack)56. Morphine is often administered in this situation to relieve pain and reduce the workload of the heart.
Choice B rationale
Oxycodone is a strong opioid medication used to treat severe pain. However, it is not typically the first choice for pain relief in the setting of a suspected heart attack.
Choice C rationale
Hydromorphone is another strong opioid medication used to treat severe pain. Like oxycodone, it is not typically the first choice for pain relief in the setting of a suspected heart attack.
Choice D rationale
Fentanyl is a potent opioid pain reliever. While it can be used in the management of severe pain, it is not typically the first choice for pain relief in the setting of a suspected heart attack.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
