A nurse is reviewing a client's laboratory results before administering furosemide 40 mg IV bolus. For which of the following values should the nurse withhold the medication and contact the provider?
Sodium 141 mEq/L
Potassium 2.5 mEq/L
WBC count 8,000/mm3
INR 1.0
The Correct Answer is B
Choice A Reason:
Sodium 141 mEq/L is incorrect. This value is within the normal range (usually around 135-145 mEq/L).
Choice B Reason:
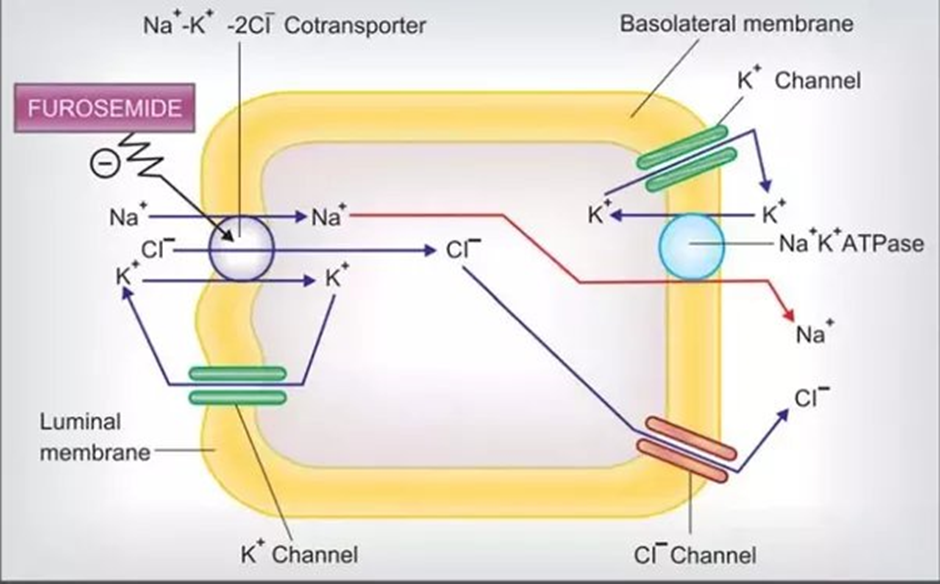
Potassium 2.5 mEq/ is correct. Furosemide, a loop diuretic, can lead to potassium loss through increased urine output. If a client already has a low potassium level (hypokalemia), administering furosemide can further decrease potassium levels, potentially causing or worsening hypokalemia. Hypokalemia can lead to various complications, including cardiac arrhythmias.
Choice C Reason:
WBC count 8,000/mm3 is incorrect. This value falls within the normal range for white blood cell count.
Choice D Reason:
INR 1.0: An INR of 1.0 is within the normal range for a person not on anticoagulation therapy.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
There's no requirement to lie down for an hour after administering nasal cyanocobalamin.
Choice B Reason:
The duration of treatment might vary depending on the healthcare provider's instructions and the client's response, so stating a specific duration of 6 months may not be accurate.
Choice C Reason:
"Administer the medication into one nostril once per week. “Nasal cyanocobalamin is typically used weekly for the treatment of pernicious anemia. It's administered into one nostril as directed by a healthcare provider. This method allows for the absorption of vitamin B12 through the nasal mucosa.
Choice D Reason:
Using a nasal decongestant before administering the medication is not typically part of the recommended administration protocol for nasal cyanocobalamin.

Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Levothyroxine 100 mcg PO every morning is incorrect. Indicates the dosage (100 mcg) and the route (by mouth) to be taken every morning.
Choice B Reason:
Simvastatin 40 mg PO at bedtime: Specifies the dosage (40 mg) and the timing (at bedtime) for administration.
Choice C Reason:
Acetaminophen 500 mg every 4 hr RN for fever is correct. The term "RN" in this context might be interpreted as "right now" rather than the intended meaning, which could cause confusion regarding the frequency of acetaminophen administration. The nurse should seek clarification to ensure accurate and safe dosing instructions.
Choice D Reason:
Morphine 4 mg IV every 4 hr PRN for pain: Specifies the dosage (4 mg), the route (intravenous), and the frequency (every 4 hours as needed) for pain management.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
