A nurse is providing teaching for a client about testicular cancer. Which of the following manifestations should the nurse instruct the client to monitor for during self-examination?
A painless lump in the testicle.
Decreased size of the testicle.
Left testicle descending lower than right testicle.
Dilated veins above the testicle.
The Correct Answer is A
Choice A rationale:
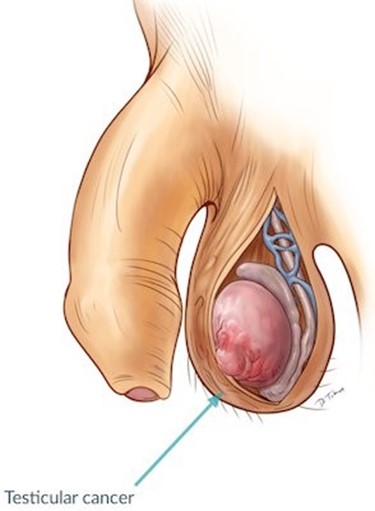
Testicular cancer may present as a painless lump or swelling in the testicle. It's important for the client to monitor for any new or unusual lumps, as they could be indicative of cancer.
Choice B rationale:
A decreased size of the testicle is not a typical manifestation of testicular cancer. It is more commonly associated with conditions like testicular atrophy due to other causes.
Choice C rationale:
Asymmetry in the position of the testicles, with one testicle descending lower than the other, is a normal variation and not a sign of testicular cancer.
Choice D rationale:
Dilated veins above the testicle can be a sign of a varicocele, which is a separate condition from testicular cancer. It is caused by abnormal enlargement of veins in the scrotum and is generally not associated with cancer.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
The nurse should not include the statement, "If your breath smells fruity, decrease your oral intake.”. in the discharge teaching for diabetic ketoacidosis. Fruity breath odor is a sign of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) due to ketone production. Decreasing oral intake would not address the underlying problem, and the client should be encouraged to seek medical attention promptly if experiencing this symptom.
Choice B rationale:
This is the correct choice. The nurse should instruct the client to check their urine for ketones if their blood sugar is greater than 300 milligrams per deciliter. High blood sugar levels can lead to ketone production, and monitoring ketones in the urine can help assess the severity of DKA and guide appropriate interventions.
Choice C rationale:
The statement, "Drink one liter of fluids daily.”. is not appropriate for a client with diabetic ketoacidosis. Clients with DKA often have fluid imbalances, and their fluid needs should be assessed and managed by healthcare professionals based on individual factors and laboratory values.
Choice D rationale:
The statement, "When nausea is present, drink chilled water.”. is not specific to diabetic ketoacidosis and may not be appropriate for all clients. Nausea can be caused by various factors, and addressing the underlying cause is important. Drinking chilled water may not necessarily alleviate nausea.
Correct Answer is ["A","C","E"]
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
An elevated white blood cell (WBC) count is an expected manifestation in a client with suspected appendicitis. Inflammation in the appendix leads to an immune response, causing an increase in WBC count.
Choice B rationale:
Elevated amylase level is not typically associated with appendicitis. Elevated amylase is more commonly seen in pancreatitis, not appendicitis.
Choice C rationale:
Rebound tenderness, which refers to increased pain when pressure is released rather than applied, is a classic symptom of appendicitis. The nurse should expect to find rebound tenderness during the abdominal assessment.
Choice D rationale:
Ascites are not a common manifestation of appendicitis. Ascites is the accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity and are more commonly seen in liver cirrhosis and certain other conditions, but not in appendicitis.
Choice E rationale:
Anorexia, or loss of appetite, can be seen in clients with appendicitis due to the inflammation and discomfort in the abdominal region.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
