A nurse is preparing a child who has suspected bacterial meningitis for a lumbar puncture. Which of the following cerebrospinal fluid findings supports the diagnosis?
Decreased WBCs.
Elevated glucose.
Elevated total protein.
Decreased pressure.
The Correct Answer is C
Choice A rationale:
Decreased white blood cells (WBCs) in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) would not support the diagnosis of bacterial meningitis. In bacterial meningitis, the presence of bacteria triggers an inflammatory response, leading to an increase in WBCs in the CSF (pleocytosis).
Choice B rationale:
Elevated glucose levels in CSF would actually be more consistent with viral rather than bacterial meningitis. In bacterial meningitis, glucose levels are typically decreased due to the high metabolic demands of bacteria on the glucose present in the CSF.
Choice C rationale:
Elevated total protein in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is indicative of inflammation and disruption of the blood-brain barrier. Bacterial meningitis causes an intense inflammatory response, leading to an increase in total protein in the CSF.
Choice D rationale:
Decreased pressure in the CSF would not be a characteristic finding in bacterial meningitis. In fact, bacterial meningitis often leads to an increase in CSF pressure due to the inflammation and accumulation of inflammatory cells and proteins.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Extremities warm to the touch. This manifestation is not indicative of decreased cardiac output. Warm extremities suggest adequate peripheral perfusion and circulation. In a child with decreased cardiac output, the body might attempt to shunt blood away from the extremities to prioritize vital organs, leading to cooler extremities.
Choice B rationale:
Capillary refill 2 seconds. A capillary refill time of 2 seconds is within the normal range for a preschool-aged child. This quick capillary refill suggests adequate circulation and is not a sign of decreased cardiac output. Prolonged capillary refill time might be indicative of poor peripheral perfusion.
Choice C rationale:
Blood pressure 112/66 mm Hg. While a blood pressure of 112/66 mm Hg might be within the normal range for a preschooler, it is not the most reliable indicator of decreased cardiac output. Blood pressure can be influenced by various factors, and a seemingly normal blood pressure does not rule out decreased cardiac output if other manifestations are present.
Choice D rationale:
Diminished pulses. This is the correct choice. Diminished or weak pulses are indicative of decreased cardiac output. Inadequate blood volume being pumped by the heart can lead to reduced peripheral perfusion, resulting in diminished pulses. This sign is important in assessing the child's cardiovascular status postoperatively, especially after a corrective procedure for tetralogy of Fallot.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Encouraging active range of motion of the extremity is not recommended during the first 12 to 24 hours after a sprained wrist. Early movement can potentially worsen the swelling and delay the healing process.
Choice B rationale:
Applying warm compresses to the extremity is not the best choice to minimize swelling in the initial 12 to 24 hours after a sprained wrist. Heat can actually increase blood flow and promote more swelling in the injured area.
Choice C rationale:
Elevating the extremity above the level of the heart is the correct choice for minimizing swelling in the first 12 to 24 hours after a sprained wrist. Elevating the injured area helps to reduce blood flow to the area, which in turn decreases swelling and promotes healing.
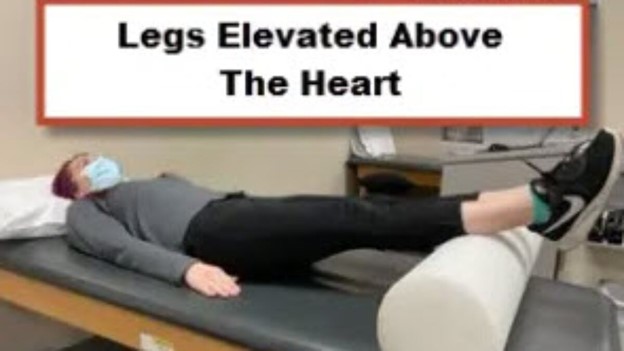
Choice D rationale:
Wrapping the extremity loosely with an elastic bandage might be beneficial for providing support, but it's not the primary intervention for minimizing swelling in the first 12 to 24 hours after a sprained wrist. Elevation is more effective for reducing swelling during this initial period.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
