A nurse is caring for an infant who has gastroenteritis.
Which of the following assessment findings should the nurse report to the provider?
Sunken fontanels and dry mucous membranes.
Temperature 38° C (100.4° F) and pulse rate 124/min.
Decreased appetite and irritability.
Pale and a 24-hr fluid deficit of 30 mL.
The Correct Answer is A
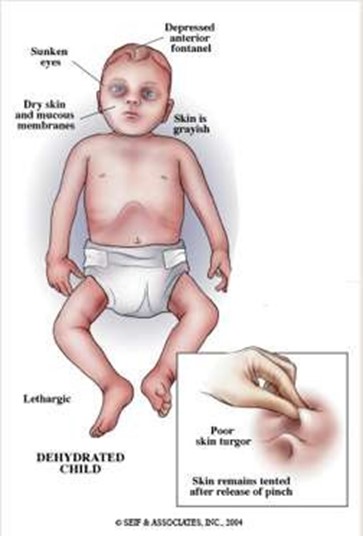
These are signs of severe dehydration in an infant, which can be life-threatening and should be reported to the provider immediately. The infant may need intravenous fluids and electrolytes to restore hydration and prevent complications.
Choice B is wrong because a temperature of 38° C (100.4° F) and a pulse rate of 124/min are not abnormal for an infant and do not indicate severe dehydration. These are common findings in an infant who has gastroenteritis, which is an inflammation of the stomach and intestines caused by a virus, bacteria, or parasite.
Choice C is wrong because decreased appetite and irritability are also common findings in an infant who has gastroenteritis, but they do not indicate severe dehydration. The nurse should encourage oral rehydration with fluids such as breast milk, formula, or oral electrolyte solution.
Choice D is wrong because pale skin and a 24-hr fluid deficit of 30 mL are not signs of severe dehydration in an infant.
A fluid deficit of 30 mL is less than 1 oz and is not significant for an infant who weighs about 10 kg (22 lbs). A fluid deficit of more than 10% of body weight would indicate severe dehydration.
Normal ranges for vital signs in infants are as follows:
• Temperature: 36.5° C to 37.5° C (97.7° F to 99.5° F)
• Pulse rate: 100 to 160/min
• Respiratory rate: 30 to 60/min
• Blood pressure: 65/41 to 100/50 mm Hg
Normal ranges for fluid intake and output in infants are as follows:
• Fluid intake: 100 to 150 mL/kg/day
• Fluid output: 1 to 2 mL/kg/hr
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
A thoracentesis is a procedure that involves inserting a needle into the pleural space to remove excess fluid or air. Coughing can increase the risk of pneumothorax (collapsed lung) or bleeding during the procedure.
Choice B is wrong because the client does not need to be NPO (nothing by mouth) for 6 hr prior to the procedure. There is no risk of aspiration during a thoracentesis.
Choice C is wrong because the client should be positioned on the unaffected side for 4 hr following the procedure. This allows the affected lung to re-expand and prevents fluid from accumulating in the pleural space again.
Choice D is wrong because the client should not be placed in the prone position during the procedure. The prone position makes it difficult to access the pleural space and can compromise breathing.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
The correct answer is Choice D, "We can provide a copy of your records, but the therapist's notes are not included."
Rationale for Choice A:
- Puts the client on the defensive:Asking "Why are you interested in seeing your therapist's notes?" can make the client feel like they need to justify their request,potentially leading to defensiveness or withdrawal.
- May not uncover true motivation:The client may not feel comfortable revealing their true reasons for wanting to see the notes,and this approach could hinder open communication.
- Undermines client autonomy:It's important to respect the client's right to access their own information,even if it's not always beneficial.Questioning their motives could make them feel less empowered in their treatment.
Rationale for Choice B:
- Paternalistic and dismissive:Saying "I don't think you will benefit from reviewing your therapist's notes right now" assumes that the nurse knows what's best for the client without exploring their perspective.
- Discourages open communication:It shuts down conversation and may prevent the client from expressing their concerns or needs.
- Could damage therapeutic relationship:By dismissing the client's request,the nurse risks eroding trust and rapport,which are essential for effective therapy.
Rationale for Choice C:
- Assumes dissatisfaction with treatment:Asking "Are you not happy with your treatment?" immediately focuses on potential problems rather than understanding the client's motivations.
- May not be accurate:The client's request may not stem from dissatisfaction with treatment but rather from curiosity,a desire for control,or other reasons.
- Could create unnecessary anxiety:Raising concerns about treatment satisfaction without proper exploration could create anxiety or doubts in the client's mind.
Rationale for Choice D:
- Clear and informative:It directly addresses the client's request while providing accurate information about the availability of records.
- Protects therapist's notes:It upholds the therapist's right to maintain confidentiality of their thought processes and clinical impressions.
- Offers alternative solutions:It suggests that the client can access other parts of their record,potentially addressing their underlying need for information.
- Professional and respectful:It maintains professional boundaries and respects the client's right to information without disclosing protected notes.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
