A nurse is caring for a client who is obese and is prescribed a calorie reduction of 500 fewer calories per day. The nurse should expect the client to have which of the following rates of weight loss?
0.45 kg (1 lb)/day
0.23 kg (0.5 lb)/day
0.23 kg (0.5 lb)/week
0.45 kg (1 lb)/week
The Correct Answer is D
Choice D reason: A calorie reduction of 500 fewer calories per day can result in a weight loss of about 0.45 kg (1 lb) per week, which is a safe and realistic goal for most clients. A pound of fat contains about 3,500 calories, so reducing the daily intake by 500 calories can create a deficit of 3,500 calories per week.
Choice A reason: A weight loss of 0.45 kg (1 lb) per day is too rapid and unhealthy, as it can cause dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, muscle loss, and metabolic slowdown. It can also be unsustainable and lead to weight regain. A calorie reduction of 500 fewer calories per day cannot achieve such a drastic weight loss.
Choice B reason: A weight loss of 0.23 kg (0.5 lb) per day is also too rapid and unhealthy, for the same reasons as choice A. A calorie reduction of 500 fewer calories per day cannot achieve such a drastic weight loss.
Choice C reason: A weight loss of 0.23 kg (0.5 lb) per week is too slow and unlikely, as it would require a calorie reduction of only 250 fewer calories per day. This is not enough to create a significant deficit and stimulate weight loss. A calorie reduction of 500 fewer calories per day can result in a faster weight loss.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A reason: The standard DASH diet limits sodium intake to 2,300 milligrams per day, which is about the amount of sodium in 1 teaspoon of table salt¹. A lower sodium version of DASH restricts sodium to 1,500 milligrams per day, which may lower blood pressure even further¹. Therefore, limiting sodium intake to 3,200 milligrams per day is not consistent with the DASH diet.
Choice B reason: The DASH diet recommends eating fewer refined carbohydrates and less sugar, as they can increase blood pressure and cholesterol levels². Instead, the DASH diet emphasizes eating more whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, which are rich in fiber, potassium, calcium, and magnesium².
Choice C reason: The DASH diet encourages consuming foods that are high in calcium, such as fat-free or low-fat dairy products, fish, beans, and nuts¹. Calcium is a mineral that helps regulate blood pressure and supports bone health³. Studies have shown that increasing calcium intake can lower blood pressure in people with hypertension³.
Choice D reason: The DASH diet advises limiting foods that are high in saturated fat, such as fatty meats, full-fat dairy products, and tropical oils such as coconut, palm kernel, and palm oils¹. Saturated fat can raise blood pressure and cholesterol levels, which can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke. The DASH diet recommends consuming no more than six percent of total calories from saturated fat¹.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A reason: Abdominal distention is a possible complication of enteral nutrition, as it may indicate gas accumulation, constipation, or intolerance to the formula. However, it is not the greatest risk to the client, as it can be prevented or managed by adjusting the formula, rate, or volume of the feeding, or by administering medications or enemas.
Choice B reason: Fluid overload is a possible complication of enteral nutrition, as it may indicate excessive fluid intake, renal impairment, or heart failure. However, it is not the greatest risk to the client, as it can be prevented or managed by monitoring the fluid balance, electrolytes, and vital signs, or by administering diuretics or fluid restriction.
Choice C reason: Glycosuria is a possible complication of enteral nutrition, as it may indicate hyperglycemia, diabetes, or infection. However, it is not the greatest risk to the client, as it can be prevented or managed by monitoring the blood glucose, urine output, and signs of infection, or by administering insulin or antibiotics.
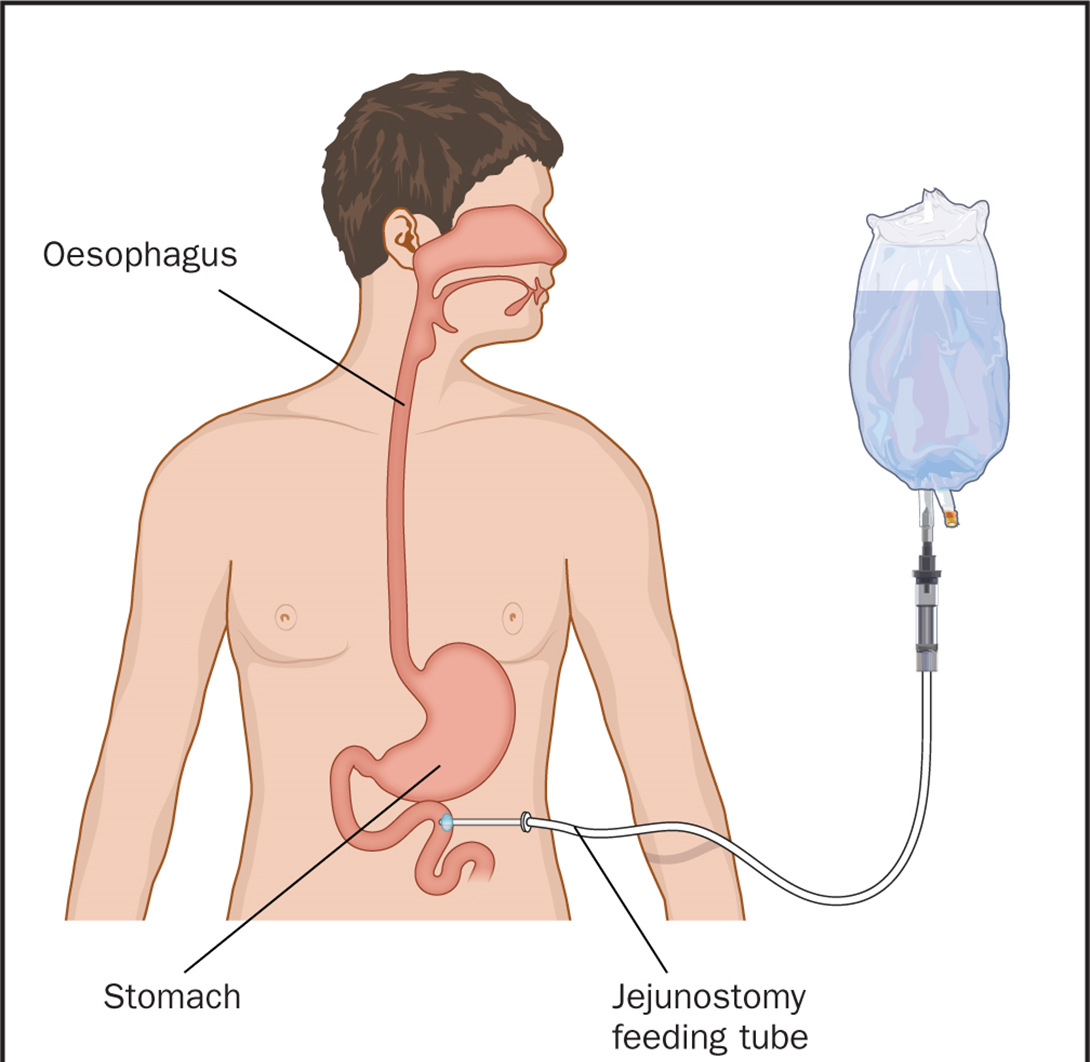
Choice D reason: Tube obstruction is the greatest risk to the client, as it may indicate clogging, kinking, or twisting of the tube, which can impair the delivery of the nutrition and medication, and cause aspiration, infection, or perforation. Tube obstruction can be prevented by flushing the tube with water before and after each feeding or medication, and by using a syringe or a pump to administer the formula. Tube obstruction can be managed by using warm water, carbonated beverages, or pancreatic enzymes to unclog the tube, or by replacing the tube if necessary.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
