A nurse is caring for a client who is 2 hours postoperative following a transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) gland. Which of the following assessments should the nurse view as an indication of a postoperative complication?
Oral temperature of 38.2°C (100.76°F)
Output of burgundy-colored urine
Pulse rate of 88/min
An urge to void despite having an indwelling urinary catheter
The Correct Answer is A
Choice A reason: An elevated oral temperature of 38.2°C (100.76°F) postoperatively can indicate an infection, which is a common complication after surgical procedures. In the context of TURP, a fever could suggest a urinary tract infection or sepsis, especially if accompanied by other symptoms such as chills or an elevated white blood cell count.
Choice B reason: The output of burgundy-colored urine can be expected in the immediate postoperative period following a TURP due to bleeding. However, it should gradually lighten in color. Persistent or worsening hematuria could indicate a complication, but it is not uncommon to see some blood in the urine shortly after the procedure
Choice C reason: A pulse rate of 88/min is within the normal range (60-100 beats per minute) and is not typically indicative of a postoperative complication. It is important to consider the patient's baseline heart rate and any other symptoms they may be experiencing.
Choice D reason: Feeling an urge to void despite having an indwelling urinary catheter can occur due to bladder spasms or irritation from the catheter itself. While uncomfortable, this sensation is not uncommon after TURP and does not necessarily indicate a complication.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A reason:
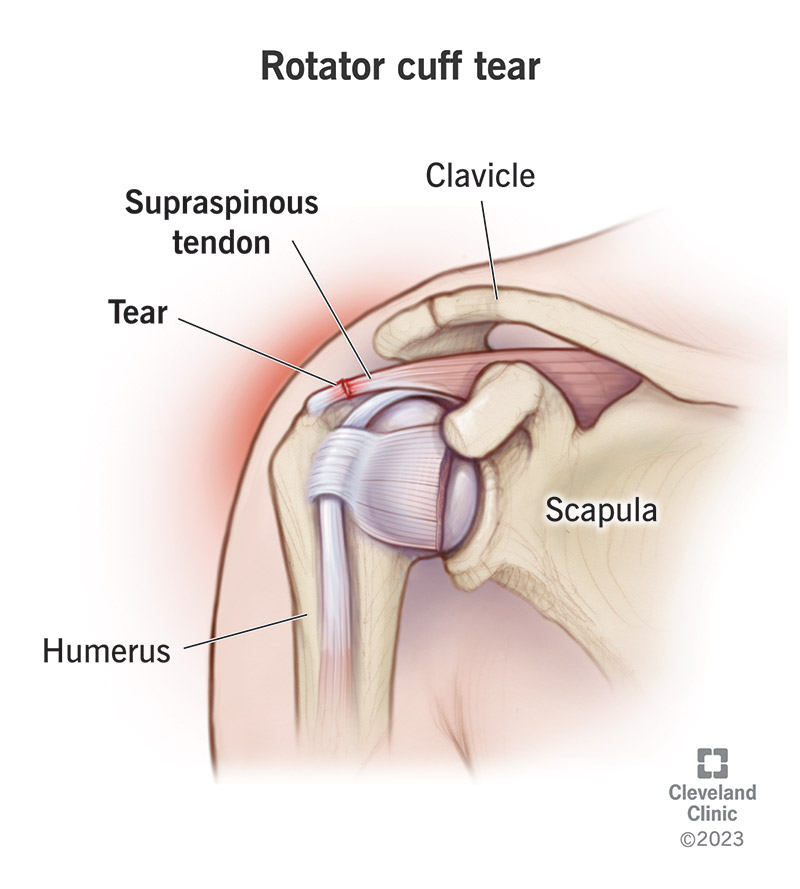
The inability to abduct the arm at the shoulder is a classic sign of a rotator cuff injury. The rotator cuff is responsible for stabilizing the shoulder joint and aiding in various movements, including abduction. When there is a tear or significant weakness in the rotator cuff muscles, especially the supraspinatus muscle, the patient may be unable to lift the arm away from the body or may experience pain while doing so.
Choice B reason:
A negative drop arm test would actually indicate that there is no rotator cuff injury. The drop arm test is performed by asking the patient to fully abduct the arm to 90 degrees and then slowly lower it. If the patient can control the motion and lower the arm smoothly, the test is negative. A positive drop arm test, where the patient cannot control the descent of the arm, would suggest a rotator cuff tear.
Choice C reason:
While an alteration in the contour of the joint may indicate some form of shoulder pathology, it is not specific to a rotator cuff injury. Changes in the contour could be due to various conditions, including dislocation, arthritis, or other musculoskeletal disorders.
Choice D reason:
A positive Tinel's sign is used to diagnose nerve compression or nerve damage, not rotator cuff injuries. It is performed by tapping over the course of a nerve to elicit a tingling sensation or pain in the distribution of the nerve. This sign is commonly associated with conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A reason:
Ecchymosis, or bruising, of the surrounding skin is a common finding associated with fractures due to the trauma to blood vessels in the area. While it can indicate bleeding or injury, ecchymosis itself does not specifically indicate impaired venous return.
Choice B reason:
Acute pain is a typical symptom following a fracture and results from the injury to the bone and surrounding tissues. Pain is an expected finding and does not directly suggest an issue with venous return.
Choice C reason:
A bounding distal pulse may actually suggest increased arterial flow or could be a sign of other conditions such as high blood pressure or fever. It does not indicate impaired venous return, which is typically characterized by a lack of pulse or a very weak pulse.
Choice D reason:
Increasing edema, or swelling, in the affected arm is a sign of impaired venous return. When veins are unable to effectively return blood to the heart, fluid can accumulate in the tissues, leading to edema. In the context of a fracture, this could be due to compression or damage to the veins, which can impede blood flow and result in swelling.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
