A nurse is caring for a client in labor who has herpes simplex virus (HSV) with active lesions. Which of the following interventions should the nurse plan to implement to prevent the transmission of HSV to the newborn?
Apply cortisone ointment on the lesions prior to birth.
Administer erythromycin ointment in the newborn's eyes after birth.
Anticipate a scheduled cesarean birth.
Initiate IV penicillin G during the labor.
The Correct Answer is C
A. Apply cortisone ointment on the lesions prior to birth:
Cortisone ointment is not appropriate for the treatment of herpes simplex virus (HSV) lesions. Cortisone is a steroid medication that can suppress the immune response, potentially worsening the HSV infection. Additionally, cortisone ointment does not directly treat the virus or prevent its transmission. Therefore, applying cortisone ointment on the lesions would not be effective and could even be harmful to both the mother and the newborn.
B. Administer erythromycin ointment in the newborn's eyes after birth:
Erythromycin ointment is routinely used in newborns to prevent bacterial eye infections, such as those caused by Chlamydia trachomatis or Neisseria gonorrhoeae. However, it is not effective against viruses like HSV. Therefore, while erythromycin ointment is important for preventing bacterial infections in newborns, it does not address the risk of HSV transmission from the mother to the newborn during birth.
C. Anticipate a scheduled cesarean birth:
When a pregnant person has active genital herpes lesions near the time of delivery, a scheduled cesarean section (C-section) is often recommended to reduce the risk of neonatal herpes transmission. Delivering the baby via C-section can decrease the likelihood of the newborn coming into contact with the virus in the birth canal, thereby reducing the risk of neonatal herpes infection. This intervention is specifically targeted at preventing HSV transmission to the newborn and is considered the standard of care in such situations.
D. Initiate IV penicillin G during labor:
Penicillin G is an antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections, but it is not effective against viruses like HSV. Therefore, initiating IV penicillin G during labor would not prevent the transmission of HSV to the newborn. While antibiotics may be used in certain situations during labor to prevent bacterial infections, they do not address the risk of HSV transmission and are not indicated for this purpose.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A. "I should avoid breastfeeding for 2 weeks following the immunization."
This statement is incorrect. There is no need to avoid breastfeeding after receiving the rubella vaccine. Breastfeeding is safe and not contraindicated following immunization with the rubella vaccine. Breastfeeding can continue as usual without interruption.
B. "I should avoid becoming pregnant for at least 1 month following the immunization."
This statement is correct. Following administration of the rubella vaccine, it is recommended to avoid becoming pregnant for at least 1 month. This precaution is due to theoretical concerns about the vaccine potentially affecting the developing fetus if a woman were to become pregnant shortly after vaccination. Rubella infection during pregnancy can cause serious birth defects, so it's important to take precautions to avoid potential harm to the fetus.
C. "I will report joint pain that develops after the immunization to my provider immediately."
While joint pain can be a rare side effect of the rubella vaccine, it is not typically necessary to report it immediately unless it is severe or persistent. Mild joint pain is a common and expected side effect of some vaccines, including the rubella vaccine, and typically resolves on its own without intervention. However, if joint pain is severe or persistent, it may be appropriate to report it to a healthcare provider for further evaluation and management.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
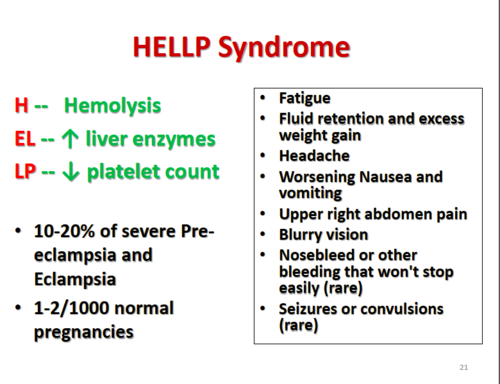
A. Bilirubin 1 mg/dL (0.1 to 1 mg/dL):
Bilirubin levels can be elevated in conditions involving liver dysfunction or hemolysis, such as HELLP syndrome. However, a bilirubin level of 1 mg/dL falls within the normal range (0.1 to 1 mg/dL). While bilirubin levels may be elevated in some cases of HELLP syndrome, this particular value is not indicative of HELLP syndrome.
B. Uric acid 6.8 mg/dL (2 to 6.6 mg/dL):
Elevated uric acid levels are commonly seen in preeclampsia, but they are not specific to HELLP syndrome. Uric acid levels can rise due to decreased renal function and increased cell breakdown. However, while a level of 6.8 mg/dL is slightly elevated compared to the normal range (2 to 6.6 mg/dL), it alone does not confirm the presence of HELLP syndrome.
C. Fibrinogen 500 mg/dL (200 to 400 mg/dL):
Fibrinogen levels are typically increased in pregnancy, but they can be decreased in conditions associated with consumption coagulopathy, such as disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). However, elevated fibrinogen levels are not typically associated with HELLP syndrome. A level of 500 mg/dL is above the normal range (200 to 400 mg/dL), but this finding alone does not indicate HELLP syndrome.
D. Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) 80 units/L (4 to 20 units/L):
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) is a liver enzyme that can be elevated in liver injury or dysfunction, which can occur in HELLP syndrome. An AST level of 80 units/L is significantly elevated compared to the normal range (4 to 20 units/L), suggesting liver dysfunction. Elevated liver enzymes are a characteristic feature of HELLP syndrome, making this finding the most indicative of HELLP syndrome among the options provided.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
