A nurse is assessing a client who has disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). Which of the following findings should the nurse expect?
Excessive thrombosis and bleeding
Increased clotting factors
Progressive increase in platelet production
Immediate sodium and fluid retention
The Correct Answer is A
A. Excessive thrombosis and bleeding
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC) is a complex and serious condition characterized by widespread activation of the coagulation cascade, leading to both excessive clot formation (thrombosis) and simultaneous consumption of clotting factors and platelets, resulting in bleeding. DIC can occur as a secondary complication to various conditions such as sepsis, trauma, or obstetric complications.
B. Increased clotting factors: In DIC, there is consumption and depletion of clotting factors, not an increase.
C. Progressive increase in platelet production: Platelet production does not increase in DIC; instead, there is consumption and decreased platelet count.
D. Immediate sodium and fluid retention: DIC is not associated with immediate sodium and fluid retention; instead, it is characterized by fluid loss due to bleeding.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A. "This test will help my provider adjust my warfarin dosages": aPTT is not typically used to monitor warfarin therapy. Instead, it is more commonly associated with monitoring heparin therapy.
B. "If my levels are too low, I am at an increased risk for bleeding": This statement is inaccurate. Low levels of clotting factors could lead to a prolonged aPTT, which might increase the risk of bleeding.
C. "It measures deficiencies in clotting factors."
Activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) is a laboratory test that evaluates the intrinsic pathway of the coagulation cascade. The aPTT measures the time it takes for a clot to form and reflects the activity of various clotting factors, including factors VIII, IX, XI, and XII. An elevated aPTT may indicate a deficiency or dysfunction of one or more clotting factors.
D. "I will need to skip breakfast until after the test is complete": There is no need for the client to skip breakfast before an aPTT test. The test is not affected by food intake.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
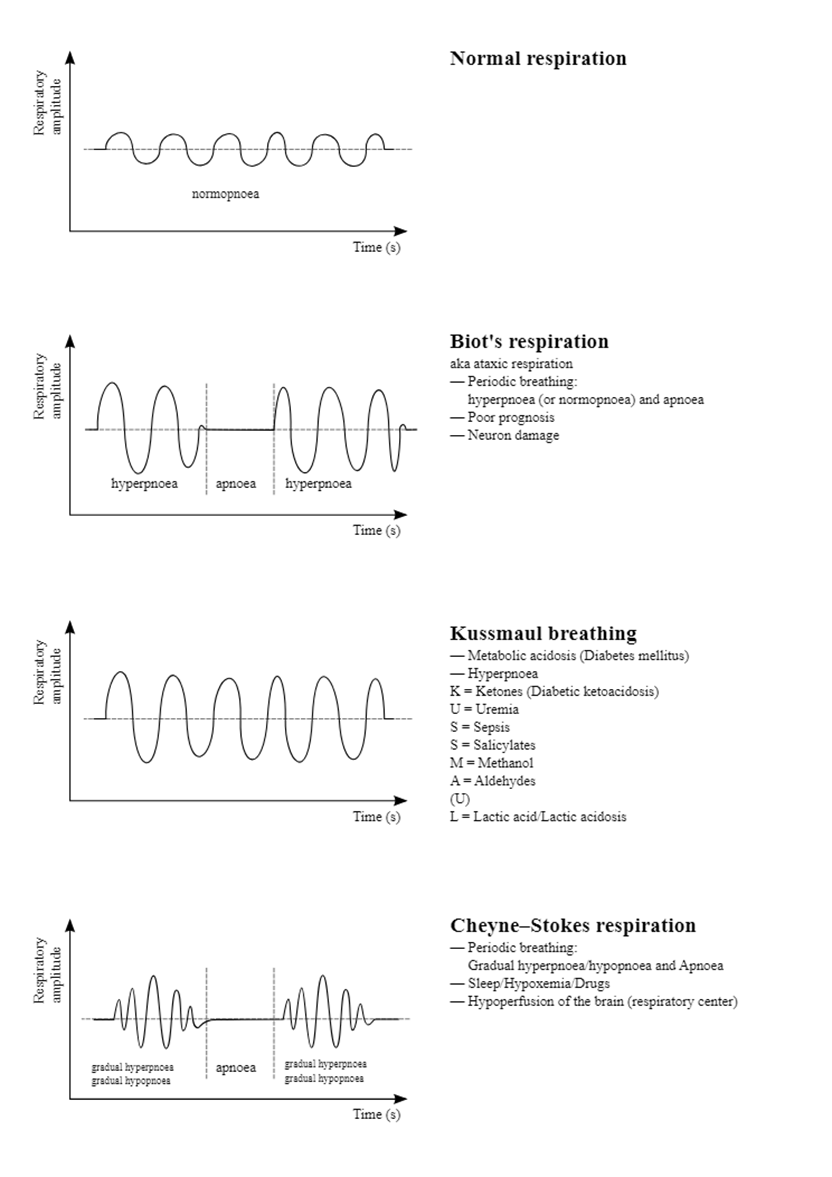
A. Cheyne-Stokes respirations: Cheyne-Stokes respirations are characterized by alternating periods of hyperventilation followed by apnea. This respiratory pattern is often observed in clients with conditions affecting the central nervous system, such as brain injury or stroke.
B. Apneustic respirations: Apneustic respirations are characterized by prolonged, gasping inhalations followed by extremely short, ineffective exhalations. This pattern is associated with damage to the pons, a part of the brainstem.
C. Stridor: Stridor is a high-pitched, noisy breathing sound caused by turbulent airflow through a partially obstructed airway. It is not related to the described alternating pattern of hyperventilation and apnea.
D. Kussmaul respirations: Kussmaul respirations are deep, rapid respirations often seen in metabolic acidosis. They are not characterized by the alternating pattern described in the scenario.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
