A nurse is assessing a client diagnosed with peptic ulcer disease. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as the priority?
Dyspepsia
Epigastric discomfort
Hematemesis
Epigastric pain
The Correct Answer is C
A. Dyspepsia:
Dyspepsia refers to discomfort or pain in the upper abdomen, often described as indigestion. It is a common symptom of peptic ulcer disease but is not as urgent as the manifestation described in option C.
B. Epigastric discomfort:
Epigastric discomfort is a common symptom of peptic ulcer disease, but the priority is to identify more severe complications, such as bleeding.
C. Hematemesis:
This is the correct answer. Hematemesis refers to the vomiting of blood, which is a serious and potentially life-threatening complication of peptic ulcer disease. It indicates active bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract and requires prompt medical attention.
D. Epigastric pain:
Epigastric pain is similar to epigastric discomfort and is a common symptom of peptic ulcer disease. However, the priority in the given options is to identify the more severe complication of hematemesis.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
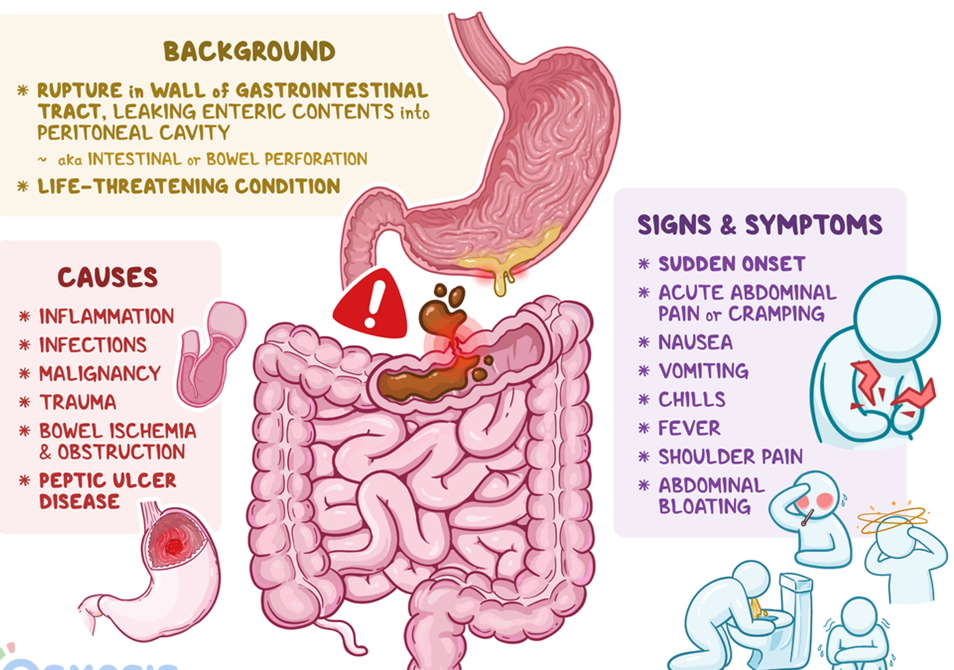
A. Bradycardia is not typically associated with gastrointestinal perforation. Instead, tachycardia may be observed due to the body's response to a potential emergency or shock.
B. Hyperactive bowel sounds are not typically associated with gastrointestinal perforation. In fact, bowel sounds may decrease or become absent in severe cases of peritonitis or abdominal emergencies.
C. Increased blood pressure is not typically associated with gastrointestinal perforation. Hypotension may be observed due to hypovolemia resulting from fluid leakage into the peritoneal cavity.
D. Sudden abdominal pain is a key clinical manifestation of gastrointestinal perforation. The perforation of the stomach or intestines allows the contents to leak into the abdominal cavity, leading to peritonitis. Sudden and severe abdominal pain is a hallmark symptom, often described as sharp, stabbing, and constant.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A. Atorvastatin: Atorvastatin is a statin medication used to lower cholesterol levels. It is not known to cause glucose intolerance.
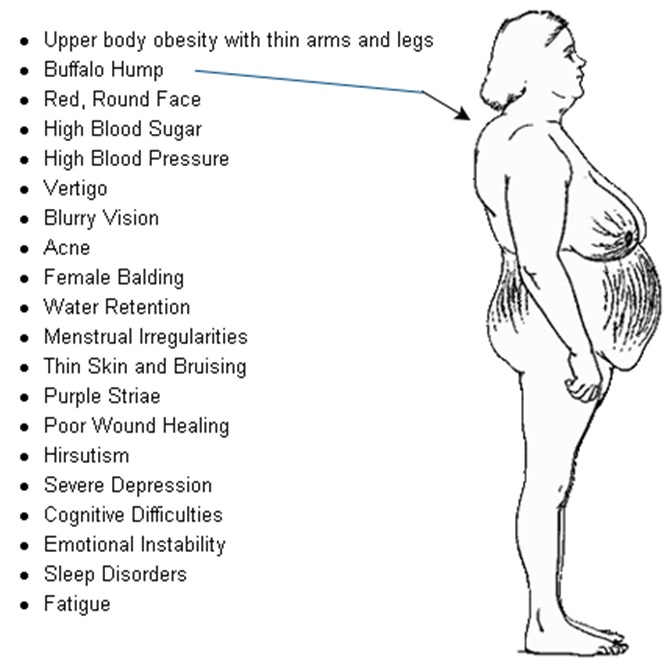
B. Prednisone: Prednisone is a corticosteroid and can cause glucose intolerance by increasing blood glucose levels. Corticosteroids can lead to insulin resistance, impaired glucose utilization, and increased gluconeogenesis.
C. Ranitidine: Ranitidine is an H2 receptor antagonist used to reduce stomach acid production. It is not known to cause glucose intolerance.
D. Guaifenesin: Guaifenesin is an expectorant used to help loosen mucus in the airways. It is not known to cause glucose intolerance.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
