A nurse in a clinic is speaking with a parent of a 1-year-old toddler who received her scheduled immunizations 1 hour ago. Which of the following findings reported by the parent is the nurse's priority?
"My child has some swelling around her eyelids and mouth."
"My child has a temperature of 100.7 degrees Fahrenheit."
"My child only ate 2 ounces during her last feeding."
"My child cries when I touch the area where she received the shot.".
The Correct Answer is A
Choice A rationale:
Swelling around the eyelids and mouth could indicate an allergic reaction, which can be severe in some cases. Anaphylaxis is a life-threatening reaction that can occur after immunizations. The nurse's priority is to assess and address any signs of an allergic reaction promptly. Swelling of the face, particularly around the eyes and mouth, is a red flag for potential anaphylaxis, and immediate intervention is necessary to prevent further complications.
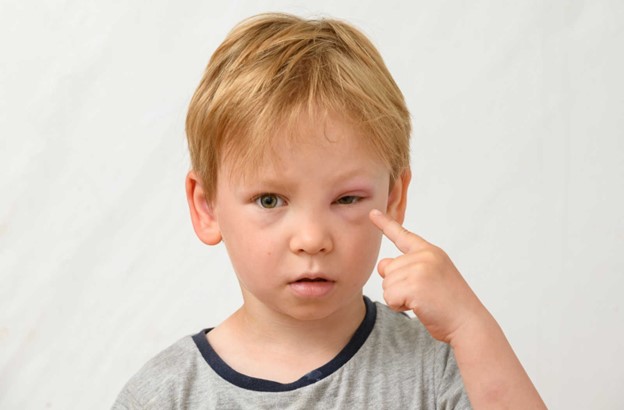
Choice B rationale:
A temperature of 100.7 degrees Fahrenheit is considered a mild fever. While it's important to monitor for fever after immunizations, a mild fever alone may not be the nurse's top priority, especially if the child is otherwise stable. Fever can be a common post-immunization response and is often self-limiting.
Choice C rationale:
While monitoring the child's intake is important, only eating 2 ounces during the last feeding is not a priority concern compared to potential allergic reactions or fever. A temporary decrease in appetite following immunizations can be expected and might resolve on its own.
Choice D rationale:
Crying when the injection site is touched is a common response to discomfort from the shot. While it's essential to provide comfort and support to the child, this finding is not indicative of a severe reaction. It's not the nurse's priority compared to potential signs of an allergic reaction or a more significant fever.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Extremities warm to the touch. This manifestation is not indicative of decreased cardiac output. Warm extremities suggest adequate peripheral perfusion and circulation. In a child with decreased cardiac output, the body might attempt to shunt blood away from the extremities to prioritize vital organs, leading to cooler extremities.
Choice B rationale:
Capillary refill 2 seconds. A capillary refill time of 2 seconds is within the normal range for a preschool-aged child. This quick capillary refill suggests adequate circulation and is not a sign of decreased cardiac output. Prolonged capillary refill time might be indicative of poor peripheral perfusion.
Choice C rationale:
Blood pressure 112/66 mm Hg. While a blood pressure of 112/66 mm Hg might be within the normal range for a preschooler, it is not the most reliable indicator of decreased cardiac output. Blood pressure can be influenced by various factors, and a seemingly normal blood pressure does not rule out decreased cardiac output if other manifestations are present.
Choice D rationale:
Diminished pulses. This is the correct choice. Diminished or weak pulses are indicative of decreased cardiac output. Inadequate blood volume being pumped by the heart can lead to reduced peripheral perfusion, resulting in diminished pulses. This sign is important in assessing the child's cardiovascular status postoperatively, especially after a corrective procedure for tetralogy of Fallot.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
The answer is a. Hard-boiled egg.
Hard-boiled eggs are a safe snack for a toddler.They are soft, easy to chew, and rich in nutrients.
Now, let’s discuss why the other options are not recommended:
b. Grapes: Whole grapes are not recommended for toddlers due to the risk of choking.They are round and slippery, making them difficult for toddlers to chew properly.
c. Raw carrots: Similar to grapes, raw carrots pose a choking hazard for toddlers.They are hard and can break into large pieces that might block a toddler’s airway.
d. Popcorn: Popcorn is not safe for toddlers. The kernels can get stuck in a toddler’s throat and cause choking.Moreover, unpopped or partially popped kernels are hard and can also pose a choking risk.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
