14:20: 87-year-old client admitted to the ED from the independent living apartment with a new report of episodic acute confusion. urinary frequency and incontinence, and severe fatigue. The child states that the client is independent in ADCs and has no history of dementia.
15:30: Normal BMP and CBC results, except for WBCs of 16,000/mm3 (16 x 109 /L) with bands greater than 10%.
Based on the assessment findings presented which condition would the nurse suspect?
Diabetic ketoacidosis
Dehydration
Urinary tract infection
Hepatitis
The Correct Answer is C
Based on the assessment findings presented, the nurse would suspect a urinary tract infection (UTI). The client's symptoms of acute confusion, urinary frequency and incontinence, and elevated WBC count with bands suggest a possible infection. Dehydration or diabetic ketoacidosis could also cause confusion and fatigue, but these conditions are less likely given the normal BMP and CBC results.
Hepatitis would not typically present with these specific symptoms.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Based on the assessment findings presented, the nurse would suspect a urinary tract infection (UTI). The client's symptoms of acute confusion, urinary frequency and incontinence, and elevated WBC count with bands suggest a possible infection. Dehydration or diabetic ketoacidosis could also cause confusion and fatigue, but these conditions are less likely given the normal BMP and CBC results.
Hepatitis would not typically present with these specific symptoms.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
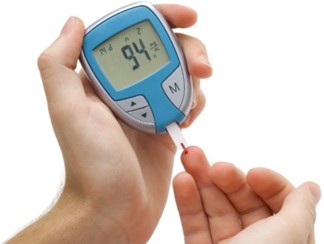
When performing a self-monitoring blood glucose test, it is essential to choose the puncture site on the side of the fingertip, slightly off-center, and to rotate the puncture sites to prevent lipoatrophy and injury to the nerves and blood vessels in the finger. Puncturing the center of the fingertip can lead to pain, injury to the nerves, and tissue damage.
Options a, b, and c are correct and indicate appropriate actions during self-monitoring of blood glucose. Washing the puncture site using warm water and soap helps to reduce the risk of infection. Waiting for a minute with the arm down before puncturing the site helps to increase blood flow and make it easier to obtain a blood sample. A blood glucose result of 120 mg/dL indicates good blood sugar control within the target range for many patients with diabetes.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
