Types of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorders
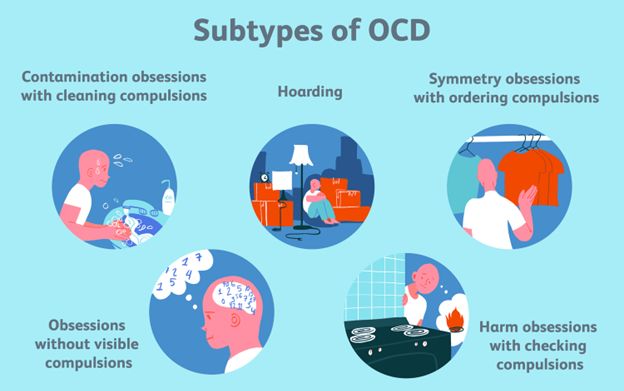
- Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD): This is the most common and well-known type of OCDs.
- It is characterized by the presence of obsessions and/or compulsions that cause significant distress or impairment in functioning.
- The obsessions and compulsions can be categorized into various themes, such as contamination/cleaning, symmetry/ordering, harm/aggression/avoidance, taboo thoughts/mental rituals, and hoarding.
- The diagnostic criteria for OCD are as follows:
- A. Presence of obsessions, compulsions, or both:
- Obsessions are defined by (1) and (2):
-
- Recurrent and persistent thoughts, urges, or images that are experienced, at some time during the disturbance, as intrusive and unwanted, and that in most individuals cause marked anxiety or distress.
- The individual attempts to ignore or suppress such thoughts, urges, or images, or to neutralize them with some other thought or action (i.e., by performing a compulsion).
-
- Compulsions are defined by (1) and (2):
-
- Repetitive behaviors (e.g., hand washing, ordering, checking) or mental acts (e.g., praying, counting, repeating words silently) that the individual feels driven to perform in response to an obsession or according to rules that must be applied rigidly.
- The behaviors or mental acts are aimed at preventing or reducing anxiety or distress, or preventing some dreaded event or situation; however, these behaviors or mental acts are not connected in a realistic way with what they are designed to neutralize or prevent, or are clearly excessive.
-
- Note: Young children may not be able to articulate the aims of these behaviors or mental acts.
- Obsessions are defined by (1) and (2):
- B. The obsessions or compulsions are time-consuming (e.g., take more than 1 hour per day) or cause clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning.
- C. The obsessive-compulsive symptoms are not attributable to the physiological effects of a substance (e.g., a drug of abuse, a medication) or another medical condition.
- D. The disturbance is not better explained by the symptoms of another mental disorder (e.g., excessive worries, as in generalized anxiety disorder; preoccupation with appearance, as in body dysmorphic disorder; difficulty discarding or parting with possessions, as in hoarding disorder; hair pulling, as in trichotillomania; skin picking, as in excoriation disorder; stereotypies, as in stereotypic movement disorder; ritualized eating behavior, as in eating disorders; preoccupation with substances or gambling, as in substance-related and addictive disorders; preoccupation with having an illness, as in illness anxiety disorder; sexual urges or fantasies, as in paraphilic disorders; impulses, as in disruptive, impulse-control, and conduct disorders; guilty ruminations, as in major depressive disorder; thought insertion or delusional beliefs, as in schizophrenia spectrum and other psychotic disorders; or repetitive patterns of behavior, as in autism spectrum disorder).
- Hoarding disorder: This is a type of OCDs that is characterized by persistent difficulty discarding or parting with possessions, regardless of their actual value
- .
- The difficulty is due to a perceived need to save the items and to distress associated with discarding them
- .
- The resulting accumulation of possessions congests and clutters the active living areas and substantially compromises their intended use
- .
- The hoarding causes clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning
- .
- The hoarding is not attributable to another medical condition (e.g., brain injury, cerebrovascular disease, Prader-Willi syndrome)
- , and is not better explained by the symptoms of another mental disorder (e.g., obsessions in OCD, decreased energy in major depressive disorder, delusions in schizophrenia spectrum and other psychotic disorders, cognitive deficits in major neurocognitive disorder, dementia, etc.).
- Body dysmorphic disorder (BDD): This is a type of OCDs that is characterized by a preoccupation with one or more perceived defects or flaws in physical appearance that are not observable or appear slight to others. The individual performs repetitive behaviors (e.g., mirror checking, excessive grooming, skin picking, reassurance seeking) or mental acts (e.g., comparing appearance with others) in response to appearance concerns. The preoccupation causes clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning. The appearance preoccupation is not better explained by concerns with body fat or weight in an individual whose symptoms meet diagnostic criteria for an eating disorder.
- Trichotillomania (hair-pulling disorder): This is a type of OCDs that is characterized by recurrent pulling out of one’s hair, resulting in hair loss. The individual has repeated attempts to decrease or stop hair pulling. The hair pulling causes clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning. The hair pulling is not attributable to another medical condition (e.g., a dermatological condition), and is not better explained by the symptoms of another mental disorder (e.g., attempts to improve a perceived defect or flaw in appearance in body dysmorphic disorder).
- Excoriation (skin-picking) disorder: This is a type of OCDs that is characterized by recurrent skin-picking resulting in skin lesions. The individual has repeated attempts to decrease or stop skin picking. The skin picking causes clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning. The skin picking is not attributable to another medical condition (e.g., scabies), and is not better explained by the symptoms of another mental disorder (e.g., delusions or tactile hallucinations in the schizophrenia spectrum and other psychotic disorders, stereotypies in the schizophrenia spectrum and other psychotic disorders, repetitive behaviors in autism spectrum disorder, etc.). The diagnostic criteria for excoriation disorder are as follows:
Nursing Test Bank
Quiz #1: RN Exams Pharmacology Exams
Quiz #2: RN Exams Medical-Surgical Exams
Quiz #3: RN Exams Fundamentals Exams
Quiz #4: RN Exams Maternal-Newborn Exams
Quiz #5: RN Exams Anatomy and Physiology Exams
Quiz #6: RN Exams Obstetrics and Pediatrics Exams
Quiz #7: RN Exams Fluid and Electrolytes Exams
Quiz #8: RN Exams Community Health Exams
Quiz #9: RN Exams Promoting Health across the lifespan Exams
Quiz #10: RN Exams Multidimensional care Exams
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Quiz #1: Naxlex RN Comprehensive online practice 2019 B with NGN
Quiz #2: Naxlex RN Comprehensive Predictor 2023
Quiz #3: Naxlex RN Comprehensive Predictor 2023 Exit Exam A
Quiz #4: Naxlex HESI Exit LPN Exam
Quiz #5: Naxlex PN Comprehensive Predictor PN 2020
Quiz #6: Naxlex VATI PN Comprehensive Predictor 2020
Quiz #8: Naxlex PN Comprehensive Predictor 2023 - Exam 1
Quiz #10: Naxlex HESI PN Exit exam
Quiz #11: Naxlex HESI PN EXIT Exam 2
Questions on Types of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorders
Correct Answer is ["B","E","C"]
Explanation
Participating in team meetings. This is a correct answer. Participating in team meetings is vital for effective collaboration in the care of clients with eating disorders. These meetings provide an opportunity to discuss the client's progress, adjust treatment plans, and share insights from different perspectives. Regular communication among team members promotes a well-rounded approach to care.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Obsessive-compulsive disorder. This choice describes the client's condition rather than a nursing diagnosis. Nursing diagnoses are used to identify specific client problems that nurses can address through care and interventions.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Praise the client for decreasing the frequency of handwashing. While positive reinforcement can be useful, it may not be the priority intervention for someone with OCD. The focus should be on structured interventions that challenge and reduce the compulsive behaviors over time.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Offering to "help you wash your hands" reinforces the client's compulsion rather than addressing the root cause of their anxiety. Enabling their compulsive behavior can contribute to the maintenance of their OCD symptoms.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Providing relaxation techniques can be helpful for managing anxiety, but for someone with OCD who is avoiding situations due to contamination fears, the primary intervention should focus on exposure therapy to address the specific OCD-related fears.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Taking a warm bath before bed can promote relaxation and potentially aid in sleep, but it might not be as effective in resolving the client's specific sleep problems related to SSRI use.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
The statement "I'm not sure if I'm really sick or if I'm just imagining it" suggests uncertainty and doubt, which are common features of OCD. However, this choice does not emphasize the typical compulsions that accompany OCD. It focuses more on self-doubt rather than specific ritualistic behaviors.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
<p>Brain tumor is an organic condition that can cause neurological and psychological symptoms. However, brain tumors are not a common or primary cause of OCD. The focus in the etiology of OCD is on neurotransmitter imbalances, genetic factors, and brain circuitry, rather than structural brain abnormalities like tumors.</p>
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Thought stopping involves interrupting obsessive thoughts by using cues or distractions. This technique is not as effective in treating OCD as exposure and response prevention, which directly addresses the connection between obsessions and compulsions. Thought stopping may not provide the individual with a comprehensive strategy for managing their OCD symptoms.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
The ventral tegmental circuit involving the substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area is primarily associated with the brain's reward system and the regulation of mood and motivation. It is not a key player in OCD's pathophysiology.
Correct Answer is ["B","C","D"]
Explanation
The strong desire to organize items by color, shape, and size is more indicative of perfectionism or certain personality traits rather than a typical theme in OCD. OCD usually involves distressing and unwanted thoughts (obsessions) and the corresponding rituals or repetitive behaviors (compulsions) aimed at reducing the distress.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
The statement "I keep having thoughts that my family will get hurt if I don't touch the doorknob three times" reflects an obsession. The distressing thought of family harm is the unwanted obsession, and the ritual of touching the doorknob three times is the compulsion aimed at reducing the anxiety caused by the obsession.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
This is the correct choice. Collaboratively developing strategies to gradually reduce compulsive behaviors is a standard approach in treating OCD. This method is aligned with exposure and response prevention therapy, a well-established treatment for OCD. By gradually facing the situations that trigger obsessive thoughts and then refraining from performing compulsions, clients can learn to manage their anxiety and reduce their reliance on compulsive behaviors.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
This option is incorrect. The symptoms of OCD should not be better explained by the symptoms of another mental disorder. While comorbidities can exist, OCD has its own unique set of obsessions and compulsions that differentiate it from other mental disorders.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Organizing possessions meticulously to maintain a clutter-free environment is not consistent with hoarding disorder. People with hoarding disorder struggle with organization and often have difficulty maintaining clutter-free spaces due to the accumulation of possessions.
Correct Answer is ["B","D"]
Explanation
<p>This choice indicates a symptom of BDD. Avoiding social situations due to the fear of being negatively evaluated or judged based on one's perceived flaws is a classic sign of BDD. Individuals with BDD often believe that others are fixated on their perceived defects.</p>
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
<p>Avoiding mirrors might be counterproductive. For some individuals with trichotillomania, avoiding mirrors might increase anxiety and preoccupation, as they may feel disconnected from their appearance. It's important to address the underlying behavior rather than avoiding triggers.</p>
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
This choice is the correct answer. Individuals with OCD recognize that their obsessions and compulsions are irrational and excessive, but they struggle to control them. This recognition is a hallmark of OCD and helps differentiate it from other conditions where the person might not be aware of the irrationality of their behavior.
<p>Obsessions and compulsions cause impairment in daily functioning. This statement accurately describes another characteristic of OCD. The obsessions and compulsions associated with OCD can be time-consuming and interfere significantly with a person's daily activities, relationships, and overal
"In exposure and response prevention, we eliminate all exposure to the situations that cause distress and anxiety." This statement is incorrect. ERP involves controlled exposure to distressing situations or triggers, not complete avoidance. The goal is to help individuals build tolerance to the anxi
"SSRIs are reserved for individuals who have ego-syntonic obsessions and compulsions." This statement is incorrect. Ego-syntonic obsessions and compulsions are those that are consistent with a person's self-image and beliefs, and individuals may not feel a strong need to resist or change them. SSRIs
The correct answer. In OCD, individuals are aware that their obsessions and compulsions are irrational and excessive. This self-awareness differentiates OCD from other disorders where the beliefs and behaviors might be seen as reasonable by the individual.
No explanation
The statement that medication will eliminate the need for any psychotherapeutic interventions is overly optimistic. A comprehensive treatment approach for OCD often includes a combination of medication and psychotherapy for optimal results.
The type and severity of OCD, along with the client's preferences and tolerance, are key factors that influence the choice of medication for treating OCD. OCD symptoms can vary widely between individuals, and different medications may be more effective for specific symptom profiles. Additionally, th
Respiratory function optimization is unrelated to the outcomes of patients with OCD. This outcome is more relevant to conditions affecting the respiratory system, such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and not to OCD.
Educating about nutrition is not a priority intervention for OCD patients. While maintaining overall health is important, nutritional education is not a central component of managing obsessive-compulsive disorder.
The statement "I'll stop taking my medication if I experience any discomfort" indicates a need for further education. Discomfort is a broad term that could encompass various mild side effects or adjustments that might be necessary when starting a new medication. It's important not to discontinue med
Focusing only on situations that are easy to tolerate would not be effective in exposure therapy. The essence of exposure therapy is to confront situations that provoke anxiety gradually, starting with less anxiety-provoking situations and progressing to more challenging ones. This process helps the
Initiating exposure therapy sessions might exacerbate the client's distress at this point. Exposure therapy involves deliberately confronting feared situations, and it's important to prepare the client for this type of intervention before initiating it. Starting with relaxation techniques is a more
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is actually recommended as one of the most effective treatments for OCD. CBT, including exposure and response prevention, helps individuals learn to manage their symptoms by changing maladaptive thought patterns and behaviors associated with OCD. Therefore, stating
Dismissing the client's worries by saying there's no need to worry about the thoughts undermines their feelings and doesn't address the distress caused by the thoughts.
Coordinating medication adjustments is a collaborative action as medications are often managed by healthcare professionals such as doctors or nurse practitioners. Adjustments should be made collectively to ensure the best outcome for the patient.
<p>Cognitive therapy within CBT aims to challenge and modify cognitive distortions and unrealistic beliefs that underlie OCD. Individuals with OCD often have distorted thought patterns, such as catastrophic thinking or black-and-white reasoning. Cognitive therapy helps individuals recognize and refr
<p>Dopamine agonists are not commonly used for OCD treatment. In fact, they can potentially exacerbate symptoms, as imbalances in dopamine transmission are implicated in the pathophysiology of OCD. Using dopamine agonists without a clear rationale could worsen the condition.</p>
<p>Acknowledging the client's efforts in therapy fosters a positive therapeutic relationship and boosts their self-esteem. Recognizing progress and hard work encourages continued engagement in treatment.</p>
Search Here
Related Topics
- Types of Eating Disorders DSM 5 - Eating and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorders
- Obsessive-compulsive disorders - Eating and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorders
- Clinical Picture of Abuse and Violence - Eating and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorders
- Child and Elder Abuse - Eating and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorders
- Child Abuse - Eating and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorders
- Elder Abuse - Eating and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorders
More on Nursing
Free Nursing Study Materials
Access to all study guides and practice questions for nursing for free.
- Free Nursing Study Trials
- Free Nursing Video tutorials
- Free Nursing Practice Tests
- Free Exam and Study Modes
- Free Nursing Revision Quizlets
