What is the most important nursing action in caring for a patient who has just recovered from rheumatic fever?
Educate the patient on the necessity of continuous antibiotic prophylaxis.
Inform the patient about the importance of ongoing anticoagulation.
Instruct the patient on the need to adhere to standard infection control procedures.
Guide the patient on how to manage their physical activity.
The Correct Answer is A
Choice A rationale
Education on the necessity of continuous antibiotic prophylaxis is crucial for patients who have just recovered from rheumatic fever. Rheumatic fever is an inflammatory disease that can develop as a complication of untreated or inadequately treated strep throat or scarlet fever.
Patients who have had rheumatic fever are at risk of getting it again if they have another strep infection. Continuous antibiotic prophylaxis can prevent recurrent infections and the development of rheumatic heart disease.
Choice B rationale
While anticoagulation therapy may be necessary for some patients with heart conditions, it is not typically the most important nursing action for a patient who has just recovered from rheumatic fever. Rheumatic fever can cause inflammation and damage to the heart valves, but it does not typically cause blood clots, which are the primary reason for anticoagulation therapy.
Choice C rationale
Adherence to standard infection control procedures is important for all patients, but it is not the most important nursing action for a patient who has just recovered from rheumatic fever. The primary concern for these patients is preventing recurrent strep infections, which can be achieved through continuous antibiotic prophylaxis.
Choice D rationale
While physical activity management may be part of the overall care plan for a patient who has just recovered from rheumatic fever, it is not typically the most important nursing action. The primary concern for these patients is preventing recurrent strep infections, which can be achieved through continuous antibiotic prophylaxis.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A rationale: Adenosine Adenosine is a naturally occurring substance that relaxes and dilates blood vessels. It also affects the electrical activity of the heart. Adenosine is used to help restore normal heartbeats in people with certain heart rhythm disorders. However, it is not typically used for atrial fibrillation.
Choice B rationale: Diltiazem Diltiazem belongs to a class of medications called calcium-channel blockers. It works by relaxing the blood vessels so the heart does not have to pump as hard. Diltiazem also increases the supply of blood and oxygen to the heart. It is used in adults alone or in combination with other medications to treat hypertension (high blood pressure) or symptoms of angina (chest pain). Diltiazem injection is used in adults to treat certain heart rhythm disorders such as atrial fibrillation.
Choice C rationale: Atropine Atropine is a tropane alkaloid and anticholinergic medication used to treat certain types of nerve agent and pesticide poisonings as well as some types of slow heart rate, and to decrease saliva production during surgery. However, it is not typically used for atrial fibrillation.
Choice D rationale: Captopril Captopril is used in adults alone or in combination with other medications to treat high blood pressure (hypertension) and congestive heart failure.
Captopril is also used to improve survival and reduce the risk of heart failure after a heart attack in patients with a heart condition called left ventricular hypertrophy (enlargement of the walls of the left side of the heart)4. However, it is not typically used for atrial fibrillation.
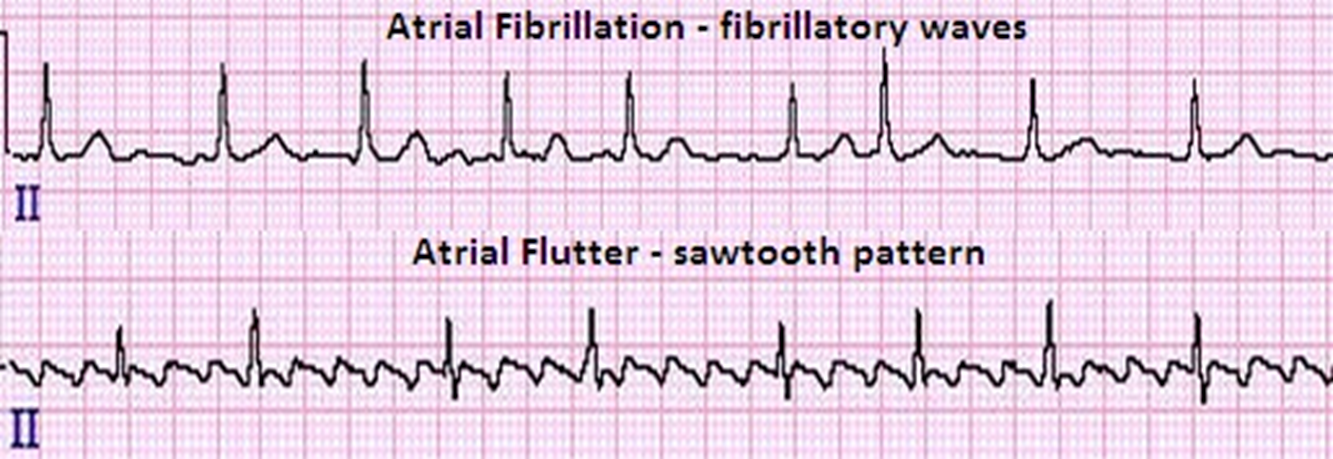
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A rationale
Atrial Flutter is a type of arrhythmia where the atria beat regularly, but much faster than usual. The treatment for Atrial Flutter is typically medication, not cardioversion.
Choice B rationale
Ventricular Tachycardia is a fast, abnormal heart rate. It starts in your heart’s lower chambers, or ventricles. Ventricular Tachycardia is a serious condition and can be life-threatening. While cardioversion can be used in some cases, it is not the primary treatment.
Choice C rationale
Atrial Fibrillation is when the upper chambers of the heart (atria) beat irregularly. This causes the atria to twitch, leading to an abnormal heart rhythm. The treatment for Atrial Fibrillation is typically medication, not cardioversion.
Choice D rationale
Ventricular Fibrillation is a life-threatening heart rhythm that results in a rapid, erratic heartbeat. During Ventricular Fibrillation, the heart quivers and can’t pump any blood, causing cardiac arrest. The treatment for Ventricular Fibrillation is Defibrillation.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
