A newborn frequently experiences cyanosis, typically during crying or after feeding. Which cardiac diagnosis is supported by this history?
Ventricular septal defect (VSD)
Atrioventricular canal (AVC) defect
Tetralogy of Fallot
Atrial septal defect (ASD) .
The Correct Answer is C
Choice A rationale
A Ventricular septal defect (VSD) is a hole in the wall separating the two lower chambers of the heart. While it can cause cyanosis, it would not typically cause cyanosis only during crying or after feeding.
Choice B rationale
An Atrioventricular canal (AVC) defect is a combination of heart problems resulting in a defect in the center of the heart. While it can cause cyanosis, it would not typically cause cyanosis only during crying or after feeding.
Choice C rationale
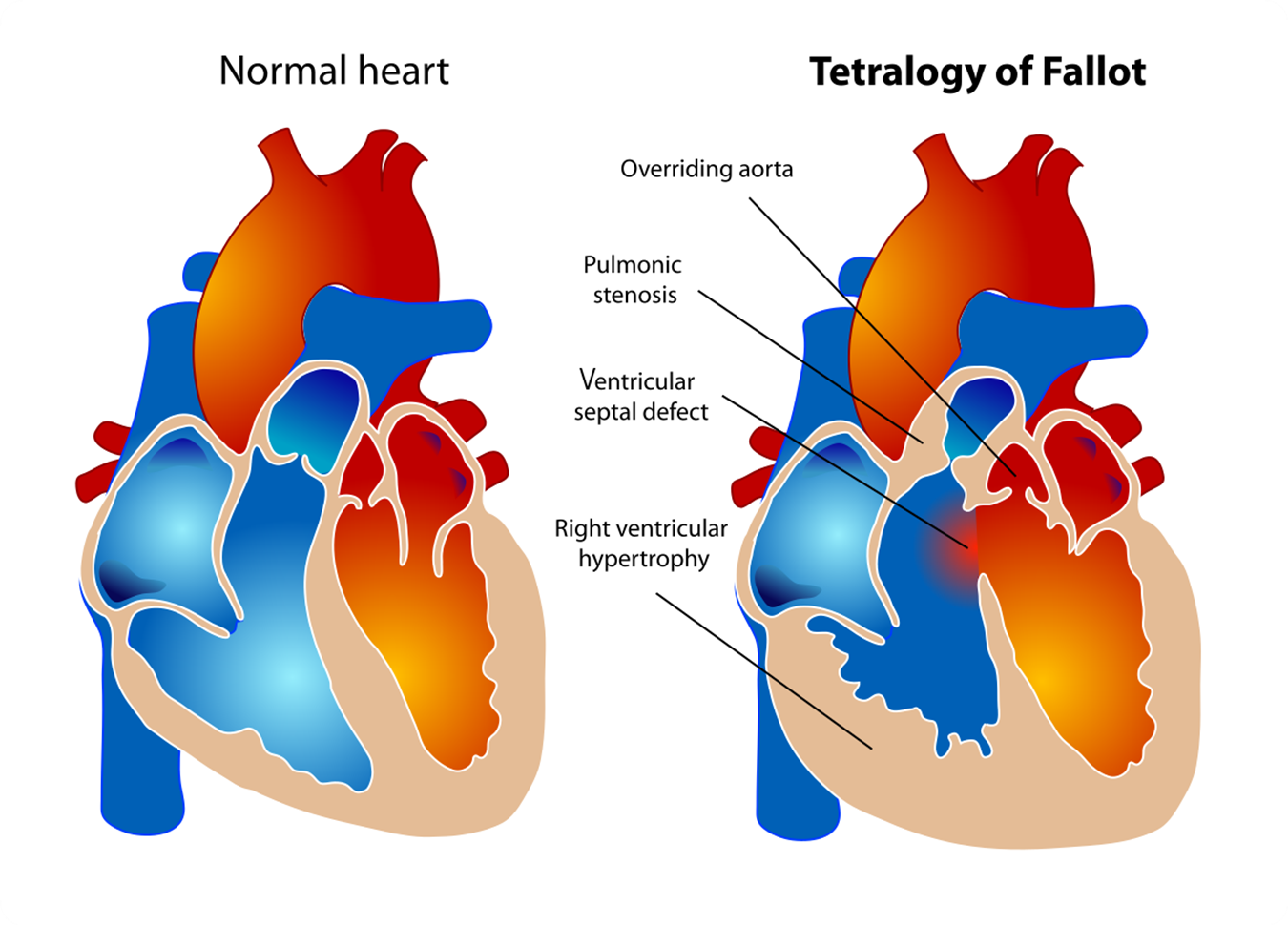
Tetralogy of Fallot is a rare condition caused by a combination of four heart defects that are present at birth. These defects, which affect the structure of the heart, cause oxygen-poor blood to flow out of the heart and into the rest of the body. Infants and children with Tetralogy of Fallot usually have blue-tinged skin because their blood doesn’t carry enough oxygen. This is often more noticeable during episodes of crying or feeding.
Choice D rationale
An Atrial septal defect (ASD) is a hole in the wall between the two upper chambers of your heart (atria). The condition is present at birth (congenital). Small defects might be found by chance and never cause a problem. Some small atrial septal defects close during infancy or early childhood. While it can cause cyanosis, it would not typically cause cyanosis only during crying or after feeding.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A rationale
Tetralogy of Fallot is a congenital heart condition that presents with a combination of four defects in the structure of the heart. The most common symptoms in a newborn with this condition include cyanosis (bluish color of the skin due to reduced oxygen in the blood) and hypoxia (low levels of oxygen in the body)34567.
Choice B rationale
While a high-pitched cry can be a sign of distress in a newborn, it is not specifically associated with tetralogy of Fallot. Dyspnea (difficulty breathing) can occur in severe cases, but it is not one of the primary symptoms of this condition.
Choice C rationale
Leg pain and twitching are not typical symptoms of tetralogy of Fallot. These symptoms could be indicative of other conditions, but they are not associated with this specific congenital heart defect.
Choice D rationale
Epistaxis (nosebleeds) and anemia are not typical symptoms of tetralogy of Fallot. While these conditions can occur in children for various reasons, they are not directly related to this specific congenital heart defect.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A rationale
While calf tenderness and swelling after a plane ride could potentially indicate a deep vein thrombosis, this condition is not immediately life-threatening in most cases. The patient would need evaluation and treatment, but other patients might have more urgent needs14.
Choice B rationale
A patient taking anticoagulants for atrial fibrillation who has black stools could potentially have gastrointestinal bleeding, which would need evaluation. However, this condition might not be immediately life-threatening, and other patients might have more urgent needs14.
Choice C rationale
A patient with a gangrenous foot ulcer and a weak pedal pulse would need evaluation and treatment. However, this condition might not be immediately life-threatening, and other patients might have more urgent needs14.
Choice D rationale
A patient reporting sudden sharp and severe upper back pain could potentially have an aortic dissection, which is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate evaluation and treatment. Therefore, this patient should be assessed first14.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
