What information should the nurse include in a teaching plan for a patient who is being discharged home after knee surgery with a prescription for hydrocodone? Select All That Apply
Dietary restriction while taking hydrocodone
Instructions not to exceed recommended dosage
Instructions not to use alcohol or CNS depressants while taking hydrocodone
Instructions on how to prevent constipation
Side effects to report
Correct Answer : B,C,D,E
A. Dietary restriction while taking hydrocodone
There are no specific dietary restrictions associated with hydrocodone use. This option is not relevant to hydrocodone therapy.
B. Instructions not to exceed recommended dosage
It is crucial to emphasize to the patient not to exceed the recommended dosage of hydrocodone. Exceeding the prescribed dose can lead to adverse effects, including respiratory depression.
C. Instructions not to use alcohol or CNS depressants while taking hydrocodone
Hydrocodone is a central nervous system (CNS) depressant. Combining it with alcohol or other CNS depressants can increase the risk of respiratory depression and sedation. Patients should be advised to avoid alcohol and other drugs that depress the CNS.
D. Instructions on how to prevent constipation
Opioid medications, including hydrocodone, can cause constipation. Patients should receive instructions on how to prevent constipation, such as increasing fluid and fiber intake and incorporating regular physical activity.
E. Side effects to report
Patients should be educated about potential side effects of hydrocodone and instructed to report any unusual or severe side effects to their healthcare provider promptly. This may include symptoms such as respiratory distress, severe drowsiness, or allergic reactions.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
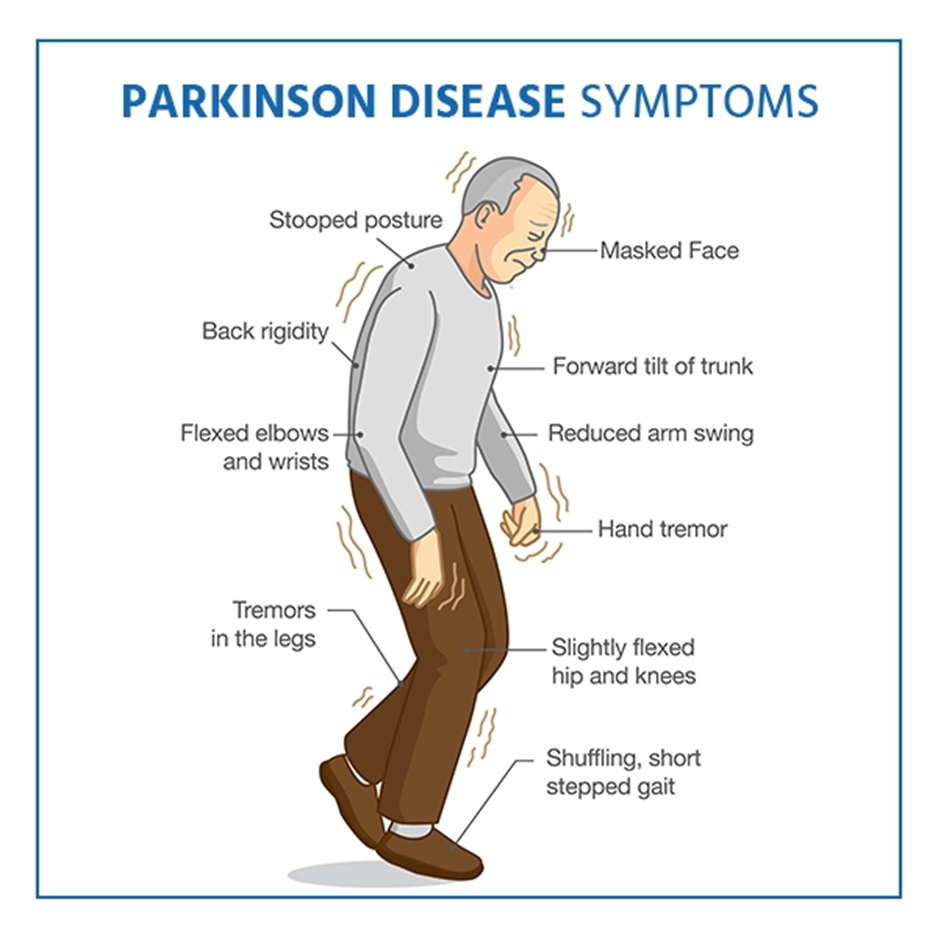
A. Carbidopa-levodopa
The symptoms described, including a shuffling gait, lack of facial expression, and tremors at rest, are characteristic of Parkinson's disease. Carbidopa-levodopa is a common medication used in the management of Parkinson's disease.
B. Donepezil
Donepezil is used in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, a condition characterized by cognitive decline and memory impairment. It is not indicated for Parkinson's disease.
C. Rivastigmine
Rivastigmine is another medication used in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, and it is also used in Parkinson's disease dementia. However, it is not the primary medication for the motor symptoms of Parkinson's disease.
D. Tacrine
Tacrine was once used in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, but it is no longer commonly prescribed due to safety concerns and the availability of newer, safer medications. It is not indicated for Parkinson's disease.
Correct Answer is ["A","D"]
Explanation
A. Acetaminophen
Acetaminophen is a non-opioid analgesic that can be used for mild to moderate pain relief. It is suitable for managing pain associated with abrasions.
B. Aspirin
Aspirin is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) with analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties. While it can be used for pain relief, it may increase the risk of bleeding, and its use is generally avoided in acute injuries with bleeding.
C. Hydrocodone
Hydrocodone is an opioid analgesic and is typically reserved for moderate to severe pain. It may not be the first choice for managing pain associated with abrasions unless the pain is more intense.
D. Ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a NSAID that provides analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects. It is suitable for managing pain and inflammation associated with abrasions.
E. Morphine
Morphine is a strong opioid analgesic and is generally reserved for severe pain, such as post-surgical pain or pain associated with more significant injuries. It may be excessive for managing pain from abrasions.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
