The nurse is caring for a client who has developed dumping syndrome while recovering from a bariatric surgery. What recommendation should the nurse make to the client?
Drink a minimum of 12 ounces of fluid with each meal.
Choose foods that are high in simple carbohydrates.
Stay upright when eating and for 30 minutes afterward.
Eat several small meals daily spaced at equal intervals.
The Correct Answer is D
Choice A reason: Drinking a minimum of 12 ounces of fluid with each meal is not recommended for a client who has dumping syndrome. Fluids can increase the gastric volume and accelerate the gastric emptying, leading to more severe symptoms. The nurse should advise the client to drink fluids between meals, not with meals.
Choice B reason: Choosing foods that are high in simple carbohydrates is not recommended for a client who has dumping syndrome. Simple carbohydrates can cause a rapid rise and fall of blood glucose levels, resulting in hypoglycemia and weakness. The nurse should advise the client to choose foods that are high in protein and fat, and low in sugar.
Choice C reason: Staying upright when eating and for 30 minutes afterward is not recommended for a client who has dumping syndrome. This position can facilitate the gastric emptying and worsen the symptoms. The nurse should advise the client to lie down after eating to slow down the gastric emptying.
Choice D reason: Eating several small meals daily spaced at equal intervals is recommended for a client who has dumping syndrome. This can help reduce the gastric volume and pressure, and prevent the rapid delivery of food into the small intestine. The nurse should advise the client to eat four to six small meals per day, and avoid skipping meals.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A reason: This is not a correct answer because 0.9% Sodium Chloride is an isotonic solution, which means it has the same osmolarity as the blood plasma. It does not cause any fluid shifts between the intracellular and extracellular compartments.
Choice B reason: This is not a correct answer because Lactated Ringer's is an isotonic solution, which means it has the same osmolarity as the blood plasma. It does not cause any fluid shifts between the intracellular and extracellular compartments.
Choice C reason: This is not a correct answer because D5W (5% Dextrose in Water) is an isotonic solution when it is in the IV bag, but it becomes hypotonic once it enters the body, as the dextrose is rapidly metabolized and only water remains. However, it is not a preferred solution for a patient with critically high sodium, as it can cause cerebral edema and worsen the neurological status.
Choice D reason: This is a correct answer because 0.45% Sodium Chloride is a hypotonic solution, which means it has a lower osmolarity than the blood plasma. It causes fluid to shift from the extracellular to the intracellular compartment, which can help lower the sodium level and correct the fluid imbalance.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A reason: Active transport is not the process that allows fluid to pass through a membrane from a dilute to a more concentrated area. Active transport is the process that moves solutes across a membrane against their concentration gradient, using energy from ATP. Active transport can create or maintain a concentration difference between two sides of a membrane.
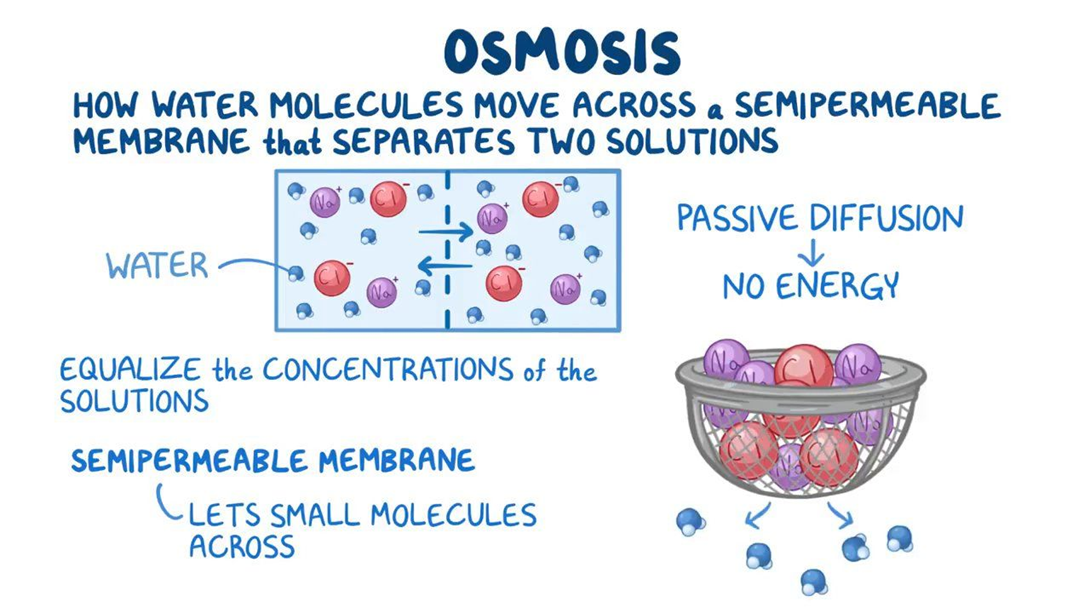
Choice B reason: Osmosis is the process that allows fluid to pass through a membrane from a dilute to a more concentrated area. Osmosis is the movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration. Osmosis can equalize the concentration of solutes on both sides of a membrane.
Choice C reason: Filtration is not the process that allows fluid to pass through a membrane from a dilute to a more concentrated area. Filtration is the movement of fluid and solutes across a membrane due to a pressure difference between two sides of a membrane. Filtration can separate solutes from fluid based on their size and charge.
Choice D reason: Diffusion is not the process that allows fluid to pass through a membrane from a dilute to a more concentrated area. Diffusion is the movement of solutes across a membrane from an area of high solute concentration to an area of low solute concentration. Diffusion can also equalize the concentration of solutes on both sides of a membrane.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
