A triage nurse finds a school-age child lying in the road following a school bus crash with multiple casualties. The child has a respiratory rate of 8/min, is unresponsive to verbal commands, and groans to painful stimuli. The nurse should assign the client which of the following triage tags?
Red
Yellow
Green
Black
The Correct Answer is A
Choice A Reason:
A red tag is used to label those who cannot survive without immediate treatment but who have a chance of survival. The child’s respiratory rate of 8/min, unresponsiveness to verbal commands, and groaning to painful stimuli indicate severe injuries that require urgent medical attention. Immediate intervention is necessary to address potential life-threatening conditions.
Choice B Reason:
A yellow tag is assigned to those who require observation and possible later re-triage. Their condition is stable for the moment, and they are not in immediate danger of death. Given the child’s critical condition, a yellow tag would not be appropriate as it suggests the child can wait for treatment, which is not the case here.
Choice C Reason:
A green tag is for the “walking wounded” who will need medical care at some point after more critical injuries have been treated. This tag is not suitable for the child in question, as their condition is far from minor and requires immediate attention.
Choice D Reason:
A black tag is used for the deceased or those whose injuries are so severe that they are not expected to survive despite receiving care. While the child’s condition is critical, they still have a chance of survival with immediate treatment, making a black tag inappropriate.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A Reason
“Avoid strenuous activities for 1 week following the procedure.” This statement is partially correct. While it is advisable to avoid strenuous activities, the exact duration can vary. Typically, patients are advised to avoid heavy lifting and vigorous activities for a few days to a week, depending on their recovery.
Choice B Reason
“You will lie on your back during the procedure.” This statement is incorrect. For a bone marrow biopsy from the iliac crest, the patient usually lies on their side or stomach to allow access to the hip bone. Lying on the back would not provide the necessary access for the procedure.
Choice C Reason
“You will receive general anesthesia for the procedure.” This statement is incorrect. Bone marrow biopsies are usually performed under local anesthesia to numb the area. General anesthesia is not typically required. The patient may also receive a mild sedative to help them relax.
Choice D Reason
“Take acetaminophen as prescribed for pain relief after the procedure.” This is the correct statement. Acetaminophen is commonly recommended for pain relief after a bone marrow biopsy because it is effective and has fewer side effects compared to other pain medications like NSAIDs, which can increase the risk of bleeding.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
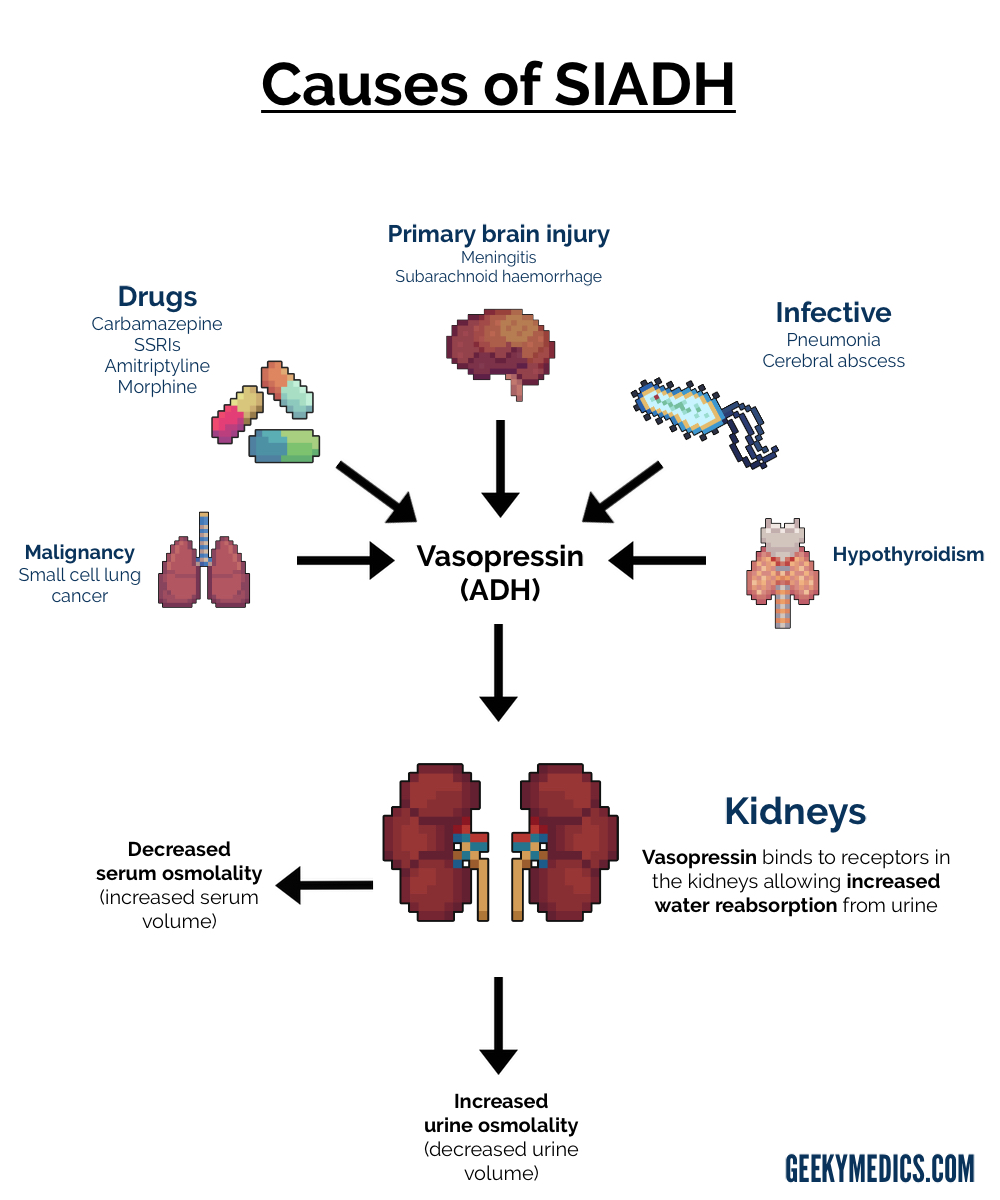
A urine specific gravity of 1.02 falls within the normal range (1.005 to 1.03) and indicates that the kidneys are excreting water appropriately. In SIADH, urine is typically concentrated due to excessive antidiuretic hormone (ADH) secretion. A normal urine specific gravity suggests that the ADH levels are normalizing and the condition is resolving.
Choice B Reason:
A sodium level of 119 mEq/L is significantly below the normal range (136 to 145 mEq/L) and indicates persistent hyponatremia. This finding suggests that the SIADH is not resolving, as effective treatment should lead to an increase in serum sodium levels.
Choice C Reason:
A BUN level of 8 mg/dL is slightly below the normal range (10 to 20 mg/dL) but is not a primary indicator of SIADH resolution. BUN levels can be influenced by various factors, including hydration status and renal function.
Choice D Reason:
A calcium level of 8.7 mg/dL is slightly below the normal range (9 to 10.5 mg/dL) but does not directly indicate the resolution of SIADH. Calcium levels are not typically used to monitor the effectiveness of SIADH treatment.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
