A patient with a head injury opens his eyes to verbal stimulation, shouts out when stimulated, and does not respond to a verbal command to move but attempts to push away a painful stimulus. How would the nurse record the patient's Glasgow Coma Scale score?
9
11
15
13
The Correct Answer is A
Choice A Reason: This is correct because the patient's Glasgow Coma Scale score is 9. The Glasgow Coma Scale is a tool that assesses the level of consciousness of a patient with a head injury by measuring three parameters: eye opening, verbal response, and motor response. The patient's eye opening score is 3 (opens eyes to verbal command), verbal response score is 4 (confused speech), and motor response score is 2 (withdraws from pain). The total score is the sum of these three scores, which is 9.
Choice B Reason: This is incorrect because the patient's Glasgow Coma Scale score is not 11. To get a score of 11, the patient would need to have a higher motor response score, such as 4 (withdraws to touch) or 5 (localizes to pain).
Choice C Reason: This is incorrect because the patient's Glasgow Coma Scale score is not 15. To get a score of 15, the patient would need to have the highest scores for all three parameters, such as 4 (opens eyes spontaneously), 5 (oriented speech), and 6 (obeys commands).
Choice D Reason: This is incorrect because the patient's Glasgow Coma Scale score is not 13. To get a score of 13, the patient would need to have a higher verbal response score, such as 5 (oriented speech).
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
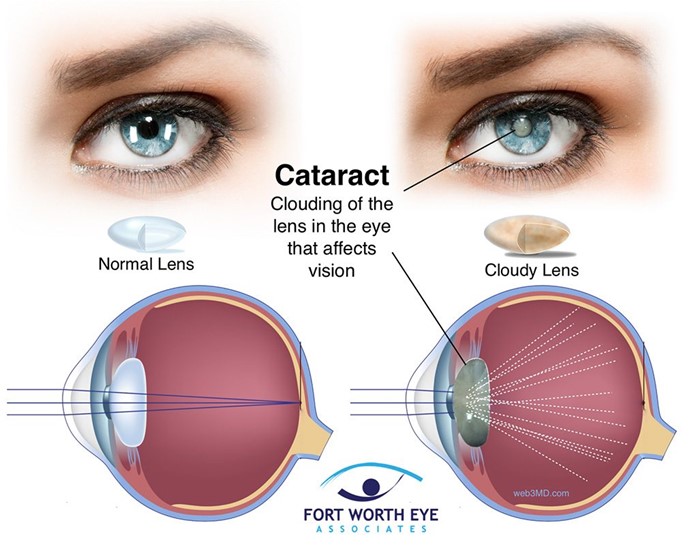
Choice A reason: Resting in bed for at least 2 days is not necessary after cataract surgery. The client should resume normal activities as soon as possible, but avoid strenuous activities that increase intraocular pressure.
Choice B reason: Deep breathing and coughing four times a day are not related to cataract surgery. This is a technique to prevent respiratory complications after abdominal or thoracic surgery.
Choice C reason: After two days, a creamy discharge is not normal. This could indicate an infection or inflammation of the eye. The client should report any changes in vision, pain, redness, swelling, or discharge to the provider.
Choice D reason: Keeping the head up and straight is the correct instruction. This helps to prevent increased intraocular pressure and bleeding in the eye. The client should also avoid rubbing or touching the eye, wearing sunglasses to protect from bright light, and using prescribed eye drops as directed.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A Reason: A virus is not detected by the KOH test, which is used to diagnose fungal infections of the skin, hair, or nails. A virus can be detected by other tests, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) or viral culture.
Choice B Reason: A fungal infection is detected by the KOH test, which dissolves the skin cells and leaves behind the fungal elements that can be seen under a microscope. A fungal infection can cause symptoms such as itching, scaling, redness, or blisters.
Choice C Reason: A bacterial infection is not detected by the KOH test, which is specific for fungi. A bacterial infection can be detected by other tests, such as gram stain or culture.
Choice D Reason: Cancer is not detected by the KOH test, which is not a screening tool for malignancy. Cancer can be detected by other tests, such as biopsy or imaging.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
