A patient who complains of gastric distress from NSAIDS such as aspirin or indomethacin will most likely benefit from the administration of which medication?
Misoprostol (Cytotec)
Lansoprazole (Prevacid)
Magaldrate (Riopan)
Magnesium trisilicate (Gaviscon)
The Correct Answer is A
A. Misoprostol (Cytotec)
The patient complaining of gastric distress from NSAIDs (Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs) like aspirin or indomethacin may benefit from the administration of misoprostol (Cytotec). Misoprostol is a prostaglandin analog that helps protect the stomach lining and reduce the risk of NSAID-induced gastric ulcers.
B. Lansoprazole (Prevacid)
Lansoprazole is a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) that reduces stomach acid production. While PPIs can be used for certain acid-related conditions, they do not directly protect against NSAID-induced gastric distress.
C. Magaldrate (Riopan)
Magaldrate is an antacid that neutralizes stomach acid. It may provide relief from symptoms of indigestion but does not specifically address the gastric distress caused by NSAIDs.
D. Magnesium trisilicate (Gaviscon)
Magnesium trisilicate is an antacid that helps neutralize stomach acid. Like magaldrate, it may alleviate symptoms of indigestion but does not target the underlying issue of NSAID-induced gastric distress.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["125"]
Explanation
`To calculate the rate of infusion in mL/h, you need to divide the total volume of fluid by the total time of infusion.
In this case, you have 1,000 mL of normal saline (NS) to infuse in eight hours.
Therefore, the rate of infusion is 1,000 mL / 8 h = 125 mL/h.
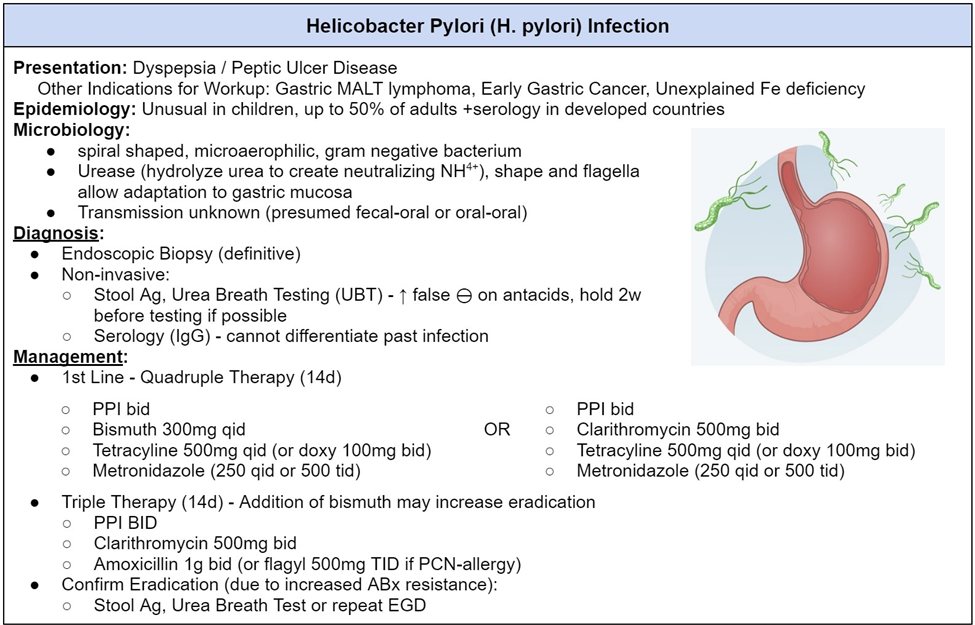
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
A. Blood cultures will need to be drawn.
Blood cultures are not typically used for diagnosing H. pylori infection. Instead, specific blood tests, such as serology or antibody tests, may be employed to detect antibodies against H. pylori.
B. A biopsy of the stomach will be done.
While a biopsy may be taken during an upper endoscopy to examine the stomach lining for ulcers and H. pylori infection, it is not the primary method for detecting the presence of H. pylori. The biopsy may be used for confirming the infection and assessing the severity of damage.
C. A breath test will be performed.
This is the correct choice. The breath test is a common and non-invasive method used to detect the presence of H. pylori. The patient drinks a solution containing a substance that H. pylori can break down, and the detection of carbon dioxide in the patient's breath indicates the presence of the bacteria.
D. Computerized scanning will identify if H. pylori is present.
Computerized scanning, such as computed tomography (CT) scans, is not a primary method for detecting H. pylori. Imaging studies are not typically used for H. pylori diagnosis, and the methods mentioned earlier, like breath tests and endoscopy, are more commonly employed.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
