A patient is scheduled for catheter ablation therapy.
When describing this procedure to the patient’s family, what aspect of the treatment should the nurse address?
Clearance of partially occluded coronary arteries.
Resetting of the heart’s contractility.
Destruction of specific cardiac cells.
Correction of structural cardiac abnormalities.
The Correct Answer is D
Choice A rationale:
Clearance of partially occluded coronary arteries is not a primary goal of catheter ablation therapy. This procedure is not designed to remove blockages in the coronary arteries. Instead, it focuses on targeting and disrupting abnormal electrical signals within the heart.
While coronary artery disease (CAD) can coexist with heart rhythm problems, and both may share risk factors like high blood pressure and cholesterol, catheter ablation specifically addresses electrical disturbances, not structural blockages in blood vessels.
Procedures like angioplasty or coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) are used to address coronary artery blockages.
Choice B rationale:
Resetting of the heart’s contractility is not the primary mechanism of catheter ablation. While the procedure can sometimes improve heart function by reducing abnormal heart rhythms, its primary aim is to eliminate the abnormal electrical signals that cause arrhythmias, not directly enhance the heart's pumping ability.
Medications like beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers are often used to address contractility issues.
Choice C rationale:
Destruction of specific cardiac cells is the correct answer. Catheter ablation works by using energy (usually radiofrequency or cryoablation) to destroy small areas of heart tissue that are responsible for generating or conducting abnormal electrical signals.
By targeting these specific cells, the procedure can interrupt the pathways that cause arrhythmias, effectively eliminating or significantly reducing their occurrence.
This targeted approach is what distinguishes catheter ablation from medications, which often act on the entire heart rather than specific areas.
Choice D rationale:
Correction of structural cardiac abnormalities is not a goal of catheter ablation. This procedure is designed to address electrical problems within the heart, not structural defects like valve problems or holes in the heart walls.
Surgical procedures are typically used to correct structural abnormalities.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Antipyretic action refers to the ability to reduce fever. While aspirin does have antipyretic properties, this is not the primary reason it is administered during an MI. Fever is not a characteristic symptom of MI, and reducing fever would not directly address the underlying cause of the MI, which is the formation of a blood clot in a coronary artery.
Choice B rationale:
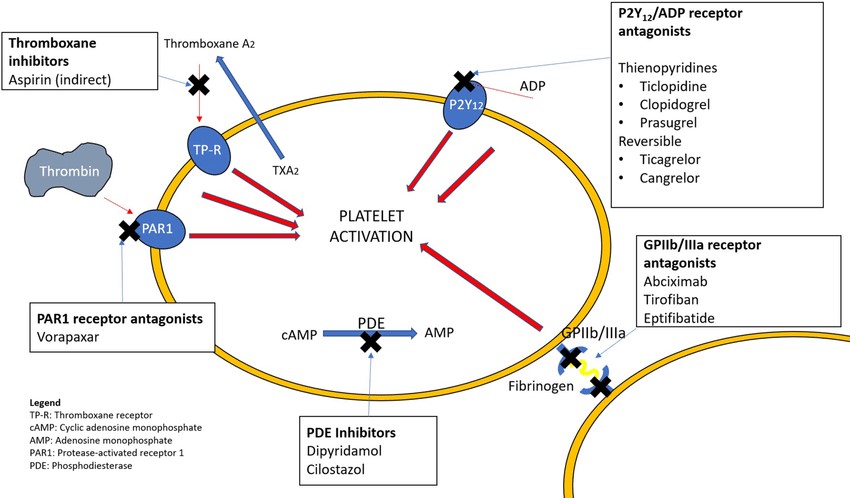
Antiplatelet action is the ability to prevent platelets from clumping together and forming blood clots. This is the crucial mechanism by which aspirin helps in the setting of an MI.
During an MI, a blood clot forms in a coronary artery, blocking blood flow to the heart muscle. This blockage can cause severe damage to the heart muscle, leading to chest pain, shortness of breath, and potentially life-threatening complications.
Aspirin irreversibly inhibits the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX), which is essential for platelet aggregation. By blocking COX, aspirin prevents platelets from sticking together and forming new clots. This can help to:
Limit the size of the existing clot in the coronary artery.
Prevent the formation of additional clots that could further block blood flow.
Allow for better blood flow to the heart muscle, reducing damage and improving outcomes.
Choice C rationale:
Analgesic action refers to the ability to relieve pain. While aspirin does have analgesic properties, this is not the primary reason it is administered during an MI. Pain relief is an important aspect of managing MI symptoms, but it does not directly address the underlying cause of the MI, which is the blood clot.
Choice D rationale:
Antithrombotic action is a broader term that encompasses any action that prevents or reduces blood clot formation. Aspirin's antiplatelet action is a specific type of antithrombotic action. However, it's important to note that aspirin does not directly dissolve existing clots; it primarily prevents new clots from forming.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
While it's important to assess for potential causative factors of premature ventricular contractions (PVCs), such as caffeine intake, it's not the immediate priority in this scenario.
The nurse's primary focus should be on assessing the patient's hemodynamic stability and oxygenation status, as frequent PVCs can compromise cardiac function and lead to serious complications.
Assessment of causative factors can be done subsequently, once the patient's immediate physiological needs have been addressed.
Choice B rationale:
The patient's subjective experience of palpitations or fluttering is valuable information, but it doesn't provide objective data about their cardiovascular status.
The nurse needs to prioritize objective assessment of vital signs, such as blood pressure and oxygen saturation, to evaluate the patient's hemodynamic stability and oxygenation.
Subjective symptoms can be further explored after obtaining objective data.
Choice D rationale:
Precipitating factors, such as infection, can contribute to PVCs, but they are not the immediate priority in this case.
The nurse's focus should be on assessing the patient's current cardiovascular status and ensuring their stability.
Investigation of potential precipitating factors can be done later, as part of a comprehensive assessment and management plan.
Choice C rationale:
Blood pressure and oxygen saturation are the most crucial parameters to assess in a patient with frequent PVCs.
Here's why:
Blood pressure: PVCs can disrupt the normal rhythm of the heart, potentially leading to a decrease in cardiac output and hypotension.
Hypotension can compromise perfusion to vital organs, such as the brain and kidneys, and can be a sign of hemodynamic instability.
Therefore, it's essential to monitor the patient's blood pressure closely.
Oxygen saturation: PVCs can also impair the heart's ability to pump blood effectively, which can lead to decreased oxygen delivery to the tissues.
This can result in hypoxemia, which can further worsen cardiac function and cause other complications.
Monitoring oxygen saturation using pulse oximetry is crucial to ensure adequate oxygenation.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
