A patient is admitted to the emergency room for evaluation of a possible myocardial infarction (MI). Which diagnostic procedure would be the priority?
Electrocardiogram
Papercut
Cardiac Angiogram
Echocardiogram
The Correct Answer is A
The correct answer is A. Electrocardiogram.
Choice A rationale:
Electrocardiogram (ECG) is the priority diagnostic procedure for a suspected myocardial infarction (MI) due to several compelling reasons:
Rapidity: An ECG can be performed quickly and easily at the bedside, providing immediate results within minutes. This swiftness is crucial in the context of MI, where time is of the essence to initiate appropriate treatment and salvage viable heart tissue.
Sensitivity: The ECG is highly sensitive in detecting the electrical changes that occur during an MI. It can identify characteristic ST-segment elevation or depression, T wave inversions, and other abnormalities that strongly suggest myocardial ischemia or infarction.
Specificity: While not perfectly specific for MI, the ECG can often distinguish it from other conditions that may cause chest pain, such as pericarditis or pulmonary embolism. This diagnostic differentiation is crucial for guiding appropriate management.
Non-invasiveness: The ECG is a non-invasive procedure that does not involve any needles, catheters, or exposure to radiation. This makes it a safe and readily accessible test, even for patients who may be hemodynamically unstable or have other medical conditions.
Cost-effectiveness: The ECG is a relatively inexpensive diagnostic tool compared to other imaging modalities like echocardiography or cardiac angiography. This cost-effectiveness makes it a valuable first-line test in evaluating potential MI, allowing for efficient resource allocation.
Rationales for other choices:
Choice B (Papercut): This is not a relevant diagnostic procedure for MI and is therefore incorrect.
Choice C (Cardiac Angiogram): While cardiac angiography can definitively visualize coronary artery blockages, it is an invasive procedure that carries risks and requires specialized facilities and personnel. It is typically reserved for cases where the diagnosis remains uncertain after non-invasive testing or when intervention is planned.
Choice D (Echocardiogram): Echocardiography can assess heart function and detect structural abnormalities, but it is less sensitive than ECG for the early electrical changes of MI. It may be used as an adjunct test to provide additional information, but it is not the priority procedure in the initial evaluation.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
While maintaining anticoagulation is important in atrial fibrillation to prevent blood clots, it is not the main goal of treatment in this specific scenario.
The client's blood pressure is elevated, suggesting that the rapid heart rate is the more immediate concern.
Additionally, the prompt indicates that heparin has already been administered, addressing the anticoagulation need.
Choice B rationale:
The client's respiratory rate and lung sounds are normal, indicating that oxygenation is not a primary concern at this time.
The fast heart rate is the more pressing issue, as it can lead to decreased cardiac output and potential complications.
Choice C rationale:
Controlling the ventricular heart rate is the main goal of treatment in this case.
Atrial fibrillation with a rapid ventricular response can lead to several detrimental consequences, including:
Decreased cardiac output due to shortened ventricular filling time
Increased myocardial oxygen demand, potentially causing angina or heart failure
Increased risk of stroke or other thromboembolic events
Diltiazem, a calcium channel blocker, is a medication commonly used to slow the heart rate in atrial fibrillation.
By slowing the conduction of electrical impulses through the atrioventricular (AV) node, it effectively reduces the number of impulses that reach the ventricles, thereby controlling the ventricular response.
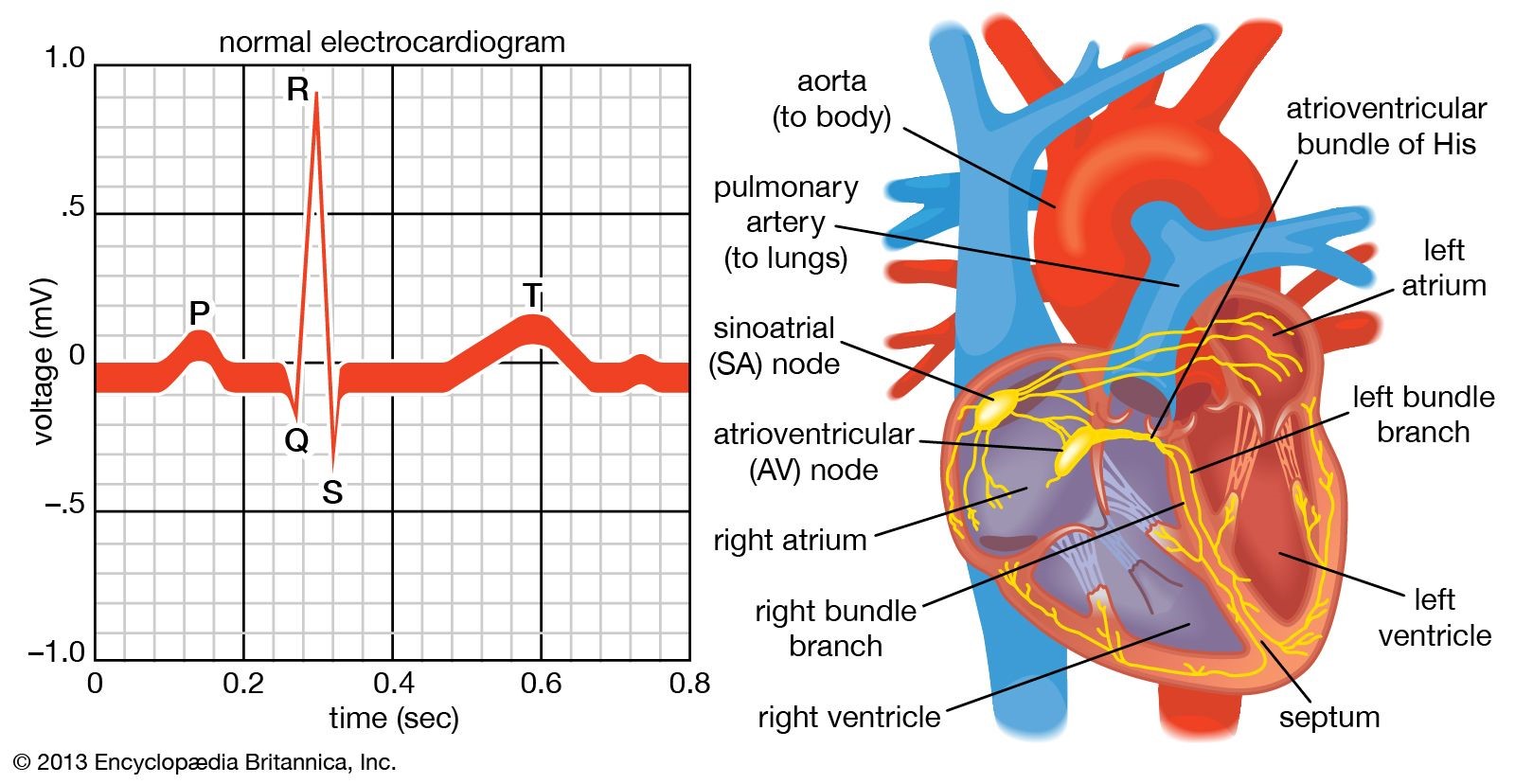
Choice D rationale:
Decreasing SA node conduction is not a primary goal in this situation.
The SA node is responsible for initiating the normal electrical impulses that trigger heart contractions.
In atrial fibrillation, the electrical activity is chaotic and originates from multiple foci within the atria, rather than the SA node.
Therefore, targeting the SA node would not effectively address the underlying rhythm disturbance.
Correct Answer is ["A","C","D"]
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
Duration of pain: Stable angina typically lasts for less than 5 minutes, while pain from a myocardial infarction (MI) typically lasts longer, often 20 minutes or more. This is because stable angina is caused by a temporary decrease in blood flow to the heart muscle, while an MI is caused by a complete blockage of blood flow, leading to more severe and prolonged pain.
Mechanism of pain: The pain in stable angina is due to ischemia, which is a lack of oxygen to the heart muscle. This occurs when the demand for oxygen by the heart muscle exceeds the supply of oxygenated blood.
Nitrates and ischemia: Nitrates, such as nitroglycerin, work by dilating the coronary arteries, which increases blood flow to the heart muscle and relieves ischemia. This is why nitroglycerin is often effective in relieving the pain of stable angina.
Choice B rationale:
Non-specific symptom: Shortness of breath can occur with both stable angina and MI, as well as other conditions such as lung disease or anxiety. Therefore, it is not a specific symptom that can be used to differentiate between the two conditions.
Choice C rationale:
Activity level: Stable angina is typically triggered by exertion or emotional stress, which increase the heart's demand for oxygen.
Rest and angina: The pain often subsides with rest or nitroglycerin.
MI and rest: In contrast, the pain of an MI can occur at rest and is not always relieved by nitroglycerin.
Choice D rationale:
Nitrates and stable angina: As mentioned earlier, nitrates are often effective in relieving the pain of stable angina.
Nitrates and MI: However, they may not be as effective in relieving the pain of an MI, as the blockage of blood flow is more severe.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
