A nurse is teaching a client who has major depressive disorder about electroconvulsive therapy. Which of the following information should the nurse include?
"This therapy works as a cure for major depressive disorders."
"You will be awake and alert during the procedure."
"You might experience confusion for a few hours after treatment."
"This therapy will stimulate the vagus nerve to improve your mood."
The Correct Answer is C
Choice A reason:
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is not considered a cure for major depressive disorders. While ECT can be highly effective in alleviating symptoms of severe depression, it does not prevent future episodes. Patients often require ongoing treatment with medications or psychotherapy to maintain the benefits of ECT.
Choice B reason:
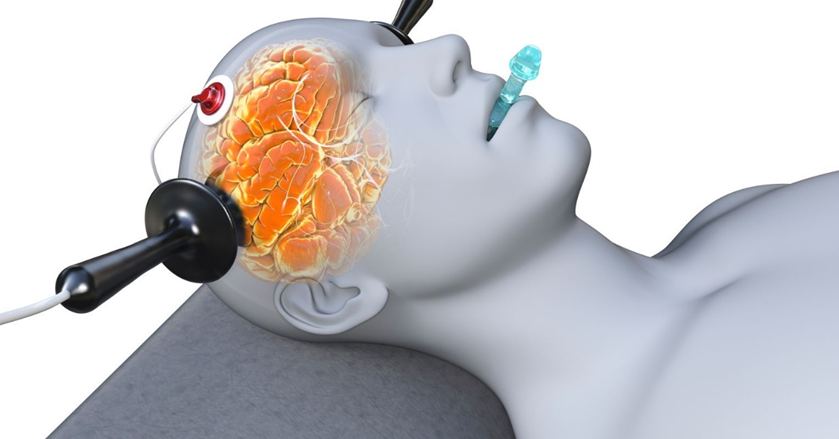
During ECT, the patient is not awake and alert. The procedure is performed under general anesthesia, meaning the patient is unconscious and does not feel the electrical stimulation or the induced seizure. This ensures the procedure is painless and the patient is unaware during the treatment.
Choice C reason:
It is common for patients to experience confusion for a few hours after ECT. This confusion is partly due to the anesthesia and partly due to the treatment itself. In most cases, the confusion resolves within a few hours, but it can sometimes last longer, especially in older adults.
Choice D reason:
ECT does not stimulate the vagus nerve. Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) is a different treatment that involves using a device to send electrical impulses to the vagus nerve. ECT works by inducing a controlled seizure in the brain, which can help alleviate symptoms of severe depression.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A reason:
Writing a detailed daily activity schedule is not typically associated with acute mania. In fact, individuals experiencing mania often have difficulty maintaining structured routines due to their heightened energy levels and racing thoughts.
Choice B reason:
Refusing to engage in conversation is more indicative of depressive episodes rather than manic episodes. During mania, individuals are usually more talkative and may have pressured speech.
Choice C reason:
Isolating oneself from others is another behavior more commonly associated with depression. In contrast, those experiencing mania often seek out social interactions and may be overly sociable.
Choice D reason:
Reporting a lack of sleep is a hallmark symptom of acute mania. Individuals in a manic state often feel little need for sleep and may go for days with minimal rest without feeling tired. This lack of sleep can exacerbate other manic symptoms, such as irritability, impulsivity, and grandiosity.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
Choice A reason:
Asking "Why do you think this has happened?" may not be the most supportive approach. This question can lead to feelings of guilt or frustration, as the client might not have an answer and could feel blamed for their condition. It is more beneficial to focus on the client's current feelings and coping mechanisms.
Choice B reason:
Asking "Are you okay with not being able to do some things you used to do?" can be perceived as insensitive. It highlights the client's limitations rather than focusing on their strengths and coping strategies. This question might make the client feel more helpless and discouraged.
Choice C reason:
Asking "Is anyone available to assist you with your hygiene?" is important for assessing the client's support system and daily needs, but it does not directly address their emotional coping. While practical support is crucial, understanding the client's emotional and psychological state is equally important.
Choice D reason:
Asking "How has this impacted your life?" is an open-ended question that allows the client to express their feelings and experiences. It helps the nurse understand the client's perspective and coping mechanisms. This question encourages the client to share their emotional journey and can provide valuable insights into their mental and emotional well-being.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
