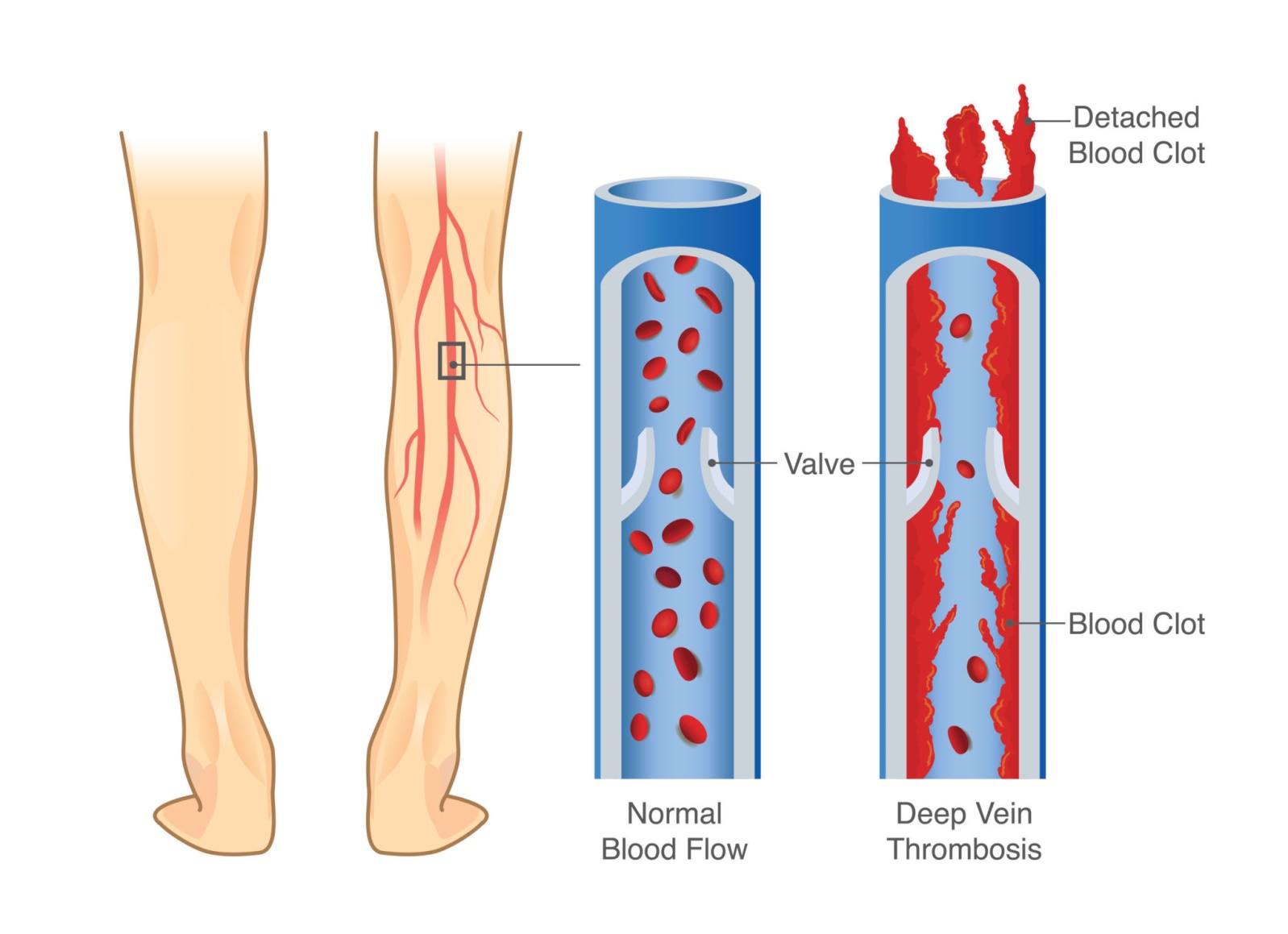
A nurse is caring for a client who is receiving warfarin therapy to prevent deep vein thrombosis. Which of the following medications should the nurse have available in the event of an overdose?
Epinephrine
Vitamin K
Atropine
Protamine
The Correct Answer is B
Choice A reason : Epinephrine is an adrenergic agonist primarily used in the management of cardiac arrest, anaphylaxis, and severe asthma attacks. It is not used to reverse the effects of warfarin overdose. Warfarin acts as an anticoagulant by inhibiting vitamin K-dependent clotting factors, and epinephrine has no role in this mechanism.
Choice B reason : Vitamin K is the antidote for warfarin toxicity. Warfarin works by inhibiting the vitamin K-dependent clotting factors II, VII, IX, and X. In the event of an overdose, vitamin K is administered to reverse the anticoagulant effects of warfarin and restore the clotting factor levels to normal. The administration can be oral or intravenous, depending on the severity of the overdose and the urgency of the situation.
Choice C reason : Atropine is an anticholinergic drug used to treat bradycardia (slow heart rate) and as an antidote for organophosphate poisoning. It does not have a role in reversing warfarin overdose as it does not affect the clotting cascade or vitamin K metabolism.
Choice D reason : Protamine is used to reverse the effects of heparin, another anticoagulant, but not warfarin. Protamine sulfate binds to heparin, forming a stable complex and neutralizing its anticoagulant effects. Since warfarin's mechanism of action is different from heparin's, protamine is not effective in reversing warfarin toxicity.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
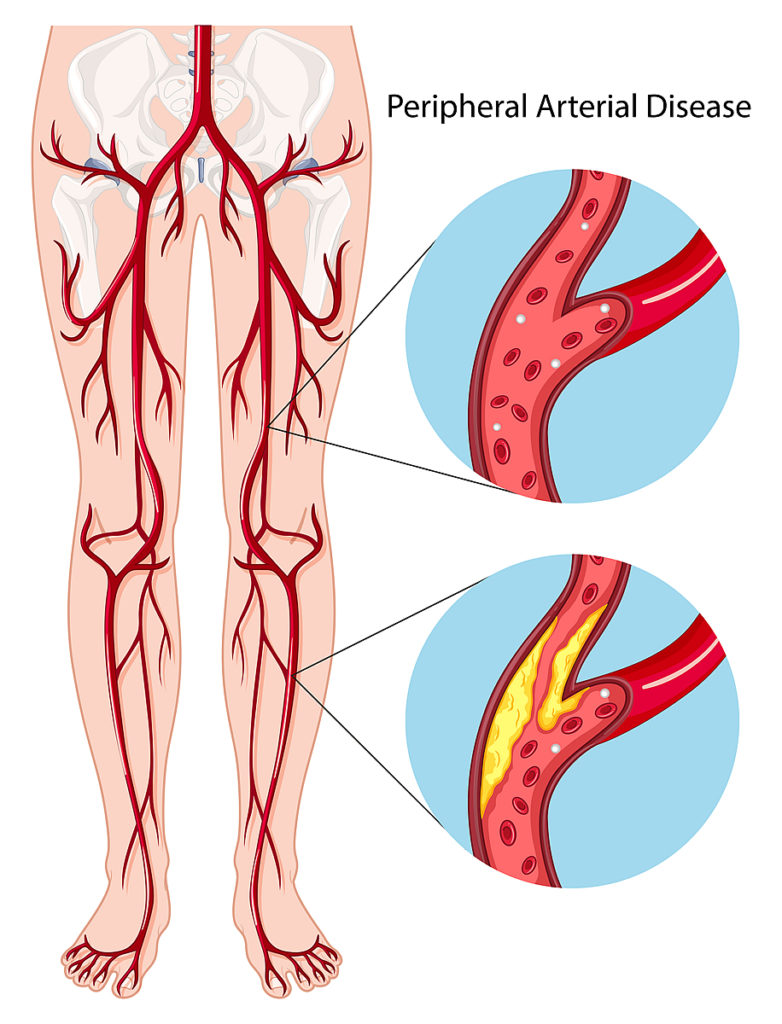
Choice A reason: Walking is a highly beneficial activity for individuals with peripheral vascular disease (PVD). It helps improve circulation, which can be compromised in PVD due to narrowed or blocked blood vessels. Regular walking can lead to the development of collateral circulation, which is the formation of new blood vessels that bypass the blockages and improve blood flow to the affected areas. This can help alleviate symptoms such as pain and cramping during walking, known as claudication. Walking should be done at a pace that is comfortable and should be stopped if pain occurs. Over time, walking can increase the distance a person with PVD can walk without pain.
Choice B reason: Compression stockings are often recommended for individuals with PVD to help improve blood flow. Knee-length stockings exert pressure on the lower legs, helping to reduce edema and discomfort associated with PVD. They can also help prevent deep vein thrombosis, a potential complication of PVD.
Choice C reason: Elevating the legs can help reduce swelling and improve venous return in clients with PVD. It is recommended to elevate the legs above the level of the heart to maximize the effect. This can be done by placing pillows under the legs while lying down.
Choice D reason: Shopping for shoes in the morning is advised because feet can swell throughout the day, especially in clients with PVD. Fitting shoes in the morning can help ensure a more accurate fit, reducing the risk of pressure points that could lead to skin breakdown and ulcers.
Correct Answer is C
Explanation
Choice A reason : Setting a goal body weight within 25% of the ideal body weight can be misleading. The ideal body weight should be determined based on body mass index (BMI), considering the individual's height and weight. A BMI of 18.5 to 24.9 is considered normal.
Choice B reason : This is a general guideline for alcohol consumption, but for individuals with hypertension, it is often recommended to limit alcohol intake even further to help manage blood pressure
Choice C reason : This is a key recommendation for managing hypertension. Reducing sodium intake helps lower blood pressure and is a widely accepted guideline
Choice D reason : Monitoring potassium levels is crucial when taking thiazide diuretics because these medications can decrease potassium levels in the blood, leading to hypokalemia.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
