A nurse is caring for a client who is experiencing anxiety as well as numbness and tingling of the lips and fingers. The client's ABGs are pH 7.48, PCO2 30 mm Hg, HCO3 24 mEq/L, PaO2 85 mm Hg. Which of the following acid-base imbalances should the nurse identify that the client is experiencing?
Respiratory alkalosis.
Respiratory acidosis.
Metabolic alkalosis.
Metabolic acidosis.
The Correct Answer is A
Choice A rationale:
The client's ABG values show a pH of 7.48, PCO2 of 30 mm Hg, HCO3 of 24 mEq/L, and PaO2 of 85 mm Hg. The elevated pH and decreased PCO2 (respiratory component) suggest respiratory alkalosis. Respiratory alkalosis occurs when there is excessive ventilation, leading to a decrease in carbon dioxide levels (hypocapnia) and subsequent alkalosis.
Choice B rationale:
Respiratory acidosis is characterized by an elevated PCO2 and decreased pH. In this case, the client's PCO2 is decreased, indicating respiratory alkalosis rather than respiratory acidosis.
Choice C rationale:
Metabolic alkalosis is characterized by an elevated HCO3 (bicarbonate) level and an increased pH. The client's HCO3 level is within the normal range, making metabolic alkalosis an incorrect identification.
Choice D rationale:
Metabolic acidosis is characterized by a decreased HCO3 level and a decreased pH. The client's HCO3 level is within the normal range, ruling out metabolic acidosis as the acid-base imbalance in this case.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is ["A","B","D"]
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
The nurse should administer oxygen to the client experiencing a sickle cell crisis. Sickle cell crisis can cause vaso-occlusion, leading to tissue hypoxia and pain. Administering oxygen helps to improve tissue oxygenation and relieve symptoms.
Choice B rationale:
Administering opioids is appropriate for managing the severe pain associated with a sickle cell crisis. Opioids are effective analgesics that can help alleviate the acute pain experienced by the client.
Choice C rationale:
Administering whole blood is not typically indicated for a sickle cell crisis. Whole blood transfusion is reserved for specific indications, such as severe anemia or acute blood loss, but it is not a standard treatment for sickle cell crisis pain.
Choice D rationale:
Elevating the head of the bed to 30° can improve oxygenation and reduce the workload on the respiratory system, which is beneficial for clients experiencing a sickle cell crisis. It helps to optimize lung expansion and alleviate hypoxia.
Choice E rationale:
Keeping the client NPO (nothing by mouth) is not necessary in a sickle cell crisis. There is no indication that the client cannot tolerate oral intake, so allowing them to eat and drink as usual is appropriate.
Correct Answer is A
Explanation
Choice A rationale:
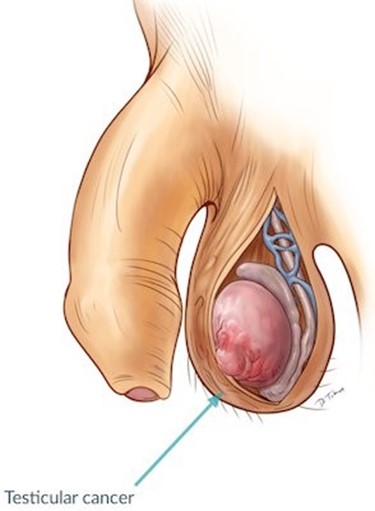
Testicular cancer may present as a painless lump or swelling in the testicle. It's important for the client to monitor for any new or unusual lumps, as they could be indicative of cancer.
Choice B rationale:
A decreased size of the testicle is not a typical manifestation of testicular cancer. It is more commonly associated with conditions like testicular atrophy due to other causes.
Choice C rationale:
Asymmetry in the position of the testicles, with one testicle descending lower than the other, is a normal variation and not a sign of testicular cancer.
Choice D rationale:
Dilated veins above the testicle can be a sign of a varicocele, which is a separate condition from testicular cancer. It is caused by abnormal enlargement of veins in the scrotum and is generally not associated with cancer.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
