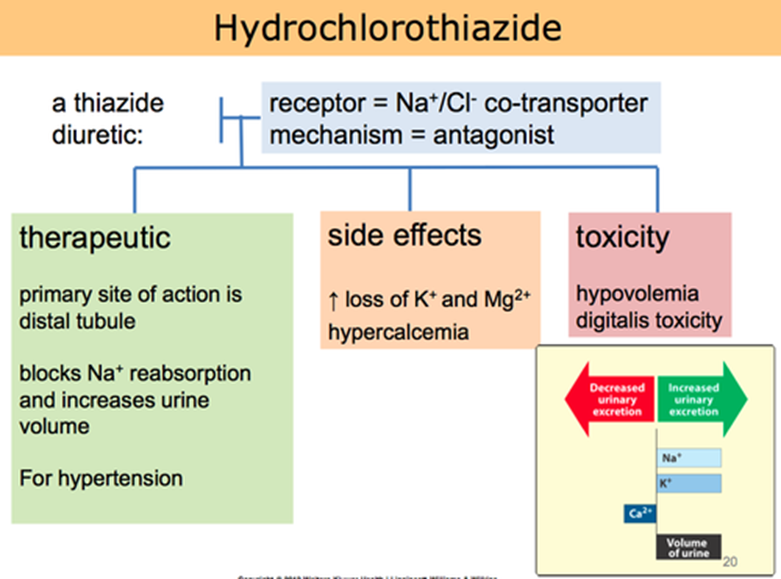
A nurse is caring for a client who has heart failure and is taking hydrochlorothiazide. The nurse should monitor the client for which of the following manifestations as an adverse effect of the medication?
Hypokalemia
Hypermagnesemia
Hypernatremia
Hypocalcemia
The Correct Answer is A
Choice A Reason:
Hypokalemia is correct. Hydrochlorothiazide is a thiazide diuretic that promotes the excretion of sodium and water in the kidneys, leading to increased urine production. However, it can also cause the loss of potassium (hypokalemia) as a side effect. Hypokalemia can manifest with symptoms such as muscle weakness, fatigue, irregular heart rhythms, and muscle cramps.
Choice B Reason:
Hypermagnesemia is incorrect. Hydrochlorothiazide typically promotes the loss of magnesium rather than causing elevated magnesium levels.
Choice C Reason:
Hypernatremia is incorrect. Hydrochlorothiazide is more likely to cause a decrease in sodium levels (hyponatremia) rather than an increase (hypernatremia).
Choice D Reason:
Hypocalcemia is incorrect. Hydrochlorothiazide can cause increased excretion of calcium but it's not a common adverse effect compared to the loss of potassium (hypokalemia).
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Using the applicator paper is appropriate for measuring the dosage accurately, but simply measuring the dosage is not the only step; the medication needs to be spread over the specified area of the skin.
Choice B Reason:
Spread the medication over a 12.7 cm (5 in) area of the client's skin. Nitroglycerin ointment is typically measured using a specific paper or measuring tape provided with the medication to ensure accurate dosing. The ointment is spread thinly and evenly over a specific measured area of the skin, usually about 12.7 cm (5 inches) in length, to maintain consistent dosing.
Choice C Reason:
Covering the medication with a sterile gauze pad is not typically done with nitroglycerin ointment. The ointment is meant to be absorbed through the skin, and covering it may interfere with its absorption.
Choice D Reason:
Nitroglycerin ointment is often applied to different sites to prevent skin irritation and tolerance from developing at one site. It's usually rotated to different clean areas of the skin to prevent skin irritation and tolerance buildup. Applying it to the same site for three consecutive days is not standard practice.
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
Choice A Reason:
Giving the prescribed dose of clindamycin is not appropriate due to the reported penicillin allergy, which increases the risk of an allergic reaction.
Choice B Reason:
Obtain a prescription for an alternative antibiotic is correct. Given the client's reported allergy to penicillin, which is in the same antibiotic class as clindamycin (both are antibiotics that belong to the beta-lactam group), there is a higher risk of cross-reactivity and potential allergic reaction. Therefore, it's important to avoid administering clindamycin in such cases and seek an alternative antibiotic that does not have a similar chemical structure to penicillin to prevent an allergic reaction.
Choice C Reason:
Premeditating the client with epinephrine before administering the antibiotic is not a standard practice in this context. Epinephrine is used to treat severe allergic reactions but is not used as a preventive measure before administering antibiotics.
Choice D Reason:
Administering the clindamycin using a desensitization schedule might be an option in certain situations under the guidance of an allergist or immunologist, but it's not typically performed by nurses and requires a specific protocol and expertise in managing drug allergies. Obtaining an alternative antibiotic is a more appropriate and immediate action to avoid the risk of an allergic reaction in this scenario.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
