A nurse is caring for a client that is immobile. The nurse recognizes that the appearance of non-blanchable erythema on the heels most likely indicates which of the following stages of pressure injuries?
Stage III pressure injury
Stage IV pressure injury
Stage II pressure injury
Stage I pressure injury
The Correct Answer is D
A. Stage III pressure injury
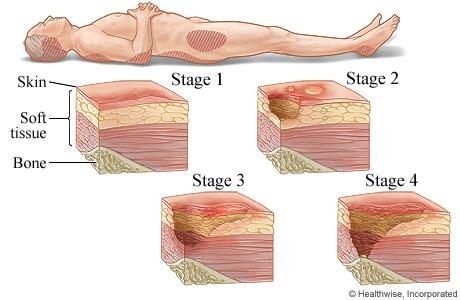
Stage III pressure injuries involve full-thickness skin loss, extending into the subcutaneous tissue but not through the fascia. These wounds typically present as deep craters and may involve undermining or tunneling. Non-blanchable erythema alone without visible skin loss is not characteristic of a Stage III pressure injury.
B. Stage IV pressure injury
Stage IV pressure injuries are the most severe and involve full-thickness tissue loss with exposed bone, tendon, or muscle. These wounds often have extensive tissue damage and can be difficult to manage. Again, non-blanchable erythema without visible skin loss is not indicative of a Stage IV pressure injury.
C. Stage II pressure injury
Stage II pressure injuries involve partial-thickness skin loss with damage to the epidermis and possibly the dermis. These wounds often present as shallow open ulcers or blisters and may have characteristics such as intact or ruptured blisters. While Stage II injuries can present with erythema, non-blanchable erythema specifically indicates a Stage I injury.
D. Stage I pressure injury
Stage I pressure injuries are the earliest stage and involve non-blanchable erythema of intact skin. The skin may be warmer or cooler than surrounding tissue and may have changes in sensation. There is no visible skin loss at this stage, but the area is at risk for further injury if pressure is not relieved. Therefore, non-blanchable erythema on the heels most likely indicates a Stage I pressure injury.
Nursing Test Bank
Naxlex Comprehensive Predictor Exams
Related Questions
Correct Answer is B
Explanation
A. Loose connective tissue:
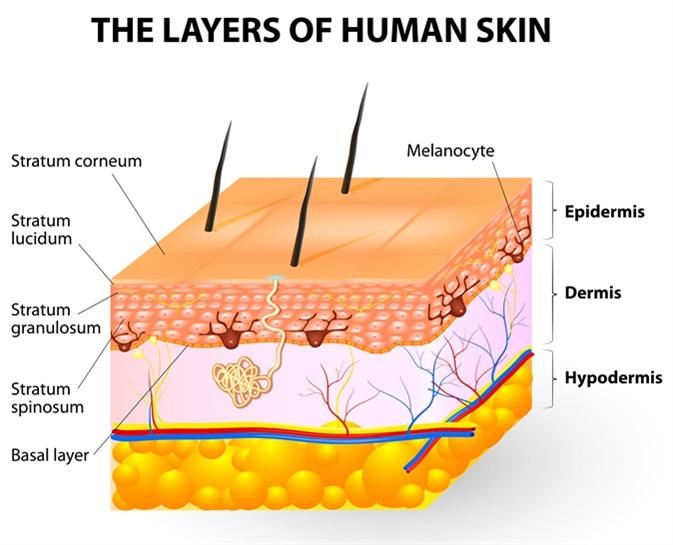
Melanocytes are not typically found in loose connective tissue. Their primary location is within the epidermis, specifically in the basal layer, where they interact with keratinocytes to produce melanin and contribute to skin color. Loose connective tissue contains collagen and elastin fibers, as well as fibroblasts, but it does not house melanocytes.
B. Epidermis:
This is the correct answer. Melanocytes are primarily located in the basal layer of the epidermis, which is the deepest layer of the epidermis. These cells produce melanin, a pigment that helps protect the skin from UV radiation and determines skin color. Melanocytes are interspersed among keratinocytes in the epidermis and transfer melanin to keratinocytes to provide skin pigmentation.
C. Dermis:
The dermis is the layer of skin beneath the epidermis and consists of connective tissue, blood vessels, nerves, hair follicles, and sweat glands. While the dermis plays a crucial role in supporting and nourishing the epidermis, melanocytes are not primarily located in the dermis. They are confined to the basal layer of the epidermis.
D. Superficial fascia:
The superficial fascia, also known as the subcutaneous tissue or hypodermis, lies beneath the dermis and consists of adipose (fat) tissue and connective tissue. It provides insulation, energy storage, and cushioning for underlying structures. However, melanocytes are not typically found in the superficial fascia. They are restricted to the epidermis, specifically the basal layer, where they carry out their function of melanin production.
Correct Answer is D
Explanation
A. Cardiac arrest related to septic shock:
Septic shock can occur in burn patients due to the breakdown of the skin barrier, which allows pathogens to enter the bloodstream and cause systemic infection. However, while septic shock is a serious complication of burn injuries, it is not the primary cause of death in the emergent phase. Septic shock can lead to multiple organ failure and contribute to mortality, but it is often a later complication rather than an immediate cause in the emergent phase.
B. Infection:
Infections are a significant concern in burn patients, especially as the burn wound provides an ideal environment for bacterial growth. However, infections typically contribute more significantly to mortality in the later phases of burn care rather than in the emergent phase. In the emergent phase, hypovolemic shock and other immediate complications have a greater impact on mortality.
C. Adrenal failure:
Adrenal failure, specifically acute adrenal insufficiency or Addisonian crisis, can occur in burn patients due to the stress response and corticosteroid depletion. While adrenal insufficiency is a concern in severe burn cases, it is not the primary cause of death in the emergent phase requiring referral to a burn center.
D. Hypovolemic shock and renal failure:
Hypovolemic shock is a critical concern in the emergent phase of burn trauma because burns can lead to significant fluid loss and electrolyte imbalances. Hypovolemic shock results from insufficient circulating blood volume, leading to inadequate perfusion of organs and tissues, which can be life-threatening. Additionally, renal failure can develop due to hypovolemia, decreased cardiac output, and the release of inflammatory mediators, leading to acute kidney injury (AKI). Hypovolemic shock and subsequent renal failure are major contributors to mortality in the emergent phase of burn trauma, necessitating prompt referral to a burn center for specialized care.
Whether you are a student looking to ace your exams or a practicing nurse seeking to enhance your expertise , our nursing education contents will empower you with the confidence and competence to make a difference in the lives of patients and become a respected leader in the healthcare field.
Visit Naxlex, invest in your future and unlock endless possibilities with our unparalleled nursing education contents today
Report Wrong Answer on the Current Question
Do you disagree with the answer? If yes, what is your expected answer? Explain.
Kindly be descriptive with the issue you are facing.
